Question: Feedback from the professor: First, while you present an informative discussion of resources and capabilities, your assessment can benefit from a more specific articulation regarding
Feedback from the professor: "First, while you present an informative discussion of resources and capabilities, your assessment can benefit from a more specific articulation regarding WHY a particular resource and/or capability is valuable, rare, difficult to imitate, and substitute. This discussion is key to your ability to identify core competencies that the firm can leverage for value growth.
Additionally, please note that while "Vertical Integration" can be considered a firm-specific strength, it is not a resource or capability, and therefore, should not be included in the VRIS exhibit and discussed accordingly. Since vertical integration reflects an internal structure, it should be integrated into your discussion of Tesla's internal value-chain activities.
Finally, while your discussion regarding the internal supply chain is informative, I suggest expanding the discussion regarding which internal activities utilize the company's key resources and capabilities and how that relates to Tesla's ability to execute its strategy."
Tesla
Resources & Capabilities
To compete in the automotive market a company needs to be differentiated as well as provide value and incentive to customers to be favored and gain an edge over the competition. As such Tesla's success will be driven by some key resources and capabilities that they have in hand to gain a competitive advantage. This matched with efficiency in operations and costs is a must, especially for an EV maker, like Tesla. Advanced Battery Technology: Tesla's advanced battery technology is a key part of its operations and allows it to lead sectors such as EV and renewable energies. This key resource gives Tesla a huge competitive advantage over its competitors, many of whom are still developing and trying to optimize their technology. Tesla's primary strength is its powertrain and battery pack technology which is regarded as a long-term competitive advantage, Composed of about 80% nickel, 15% cobalt, and 5% aluminum. Self-Driving Software & AI: Tesla's full self-driving (FSD) software technology provides a distinct advantage over competitors in the market. This advantage is specifically focused on how well the software performs and how it's implemented in vehicles. Across the competitive landscape tesla's FSD is the most researched and developed, not only this but through the ability to continually improve it makes Tesla a leader in this segment. Vertical Integration: While many large automakers outsource their manufacturing and then assemble finished products in their own facilities later, tesla does it differently. By vertically integrating operations, procurement, and research/development backward, then forwards in terms of manufacturing distribution and servicing. Tesla manufactures key components in-house (e.g., batteries, electric motors) and develops proprietary software. This allows Tesla to rapidly
innovate, adapt, and scale production without heavy reliance on or interruptions from third-party suppliers. Brand & Customer Loyalty: Tesla has built and maintained a strong brand image synonymous with innovation sustainability and performance. By aligning its brand with these values it has built up a fierce and highly advocate group of customers, which are so strong they are referred to as cult-like. This loyal customer base influenced by Tesla's strong product ecosystem, including vehicles and home charging integration, reinforced Tesla's brand image and strength. This allows Tesla to maintain its high-profit margins and charge a premium for its products over competitors while still outselling them.
SuperCharger Network: Charging an EV's battery is one of the drawbacks of owning an electric vehicle, since it takes time to charge it, you also need to locate a charging system, which is still a drawback in EV infrastructure. For this reason, tesla's key resource is its supercharger network which is increasingly important. Tesla has 60,000+ superchargers, spread across 1,870 supercharger stations worldwide. With this customers can get 200 miles of power within just 15 minutes. This makes this resource a major player in Tesla's operations. Value Creation Through Key Resources & Capabilities Self-Driving Software and AI: Tesla's FSD and software technology are among the most important capabilities that allow it to compete efficiently and effectively in the market. The value driven by this software is increased trust in vehicle capabilities and safety for consumers, lower costs to implement, and faster innovations and improvements, ultimately allowing Tesla to succeed in the EV market. Tesla's self-driving adds safety and convenience to its products, providing customers with a seamless and futuristic driving experience, which in return increases customer satisfaction and loyalty. Not only this but by implementing this software, it allows
Tesla to create additional streams of revenue, such as customers purchasing the software and even recurring subscriptions, which increases revenue beyond the initial vehicle's point of sale. Vertical Integration: Tesla's implementation and use of vertical integration allows it to achieve quality control, innovation, cost-efficiency, and scalability. With this, Tesla controls a majority of its supply chain, manufacturing, and distribution allowing it to have multiple strategic advantages and immense value added. By controlling a majority of operations in-house tesla can control the quality and innovation of its products while avoiding third-party markups and securing costs. Tesla's vertical integration capability includes its Gigafactories as well. With this tesla can produce on an immense scale while avoiding large costs and disruptions in quality. These values are then passed down to the customers in lower costs and increased product durability. An additional major point of value is Tesla's ability to adapt and speed of bringing products to market. With vertical integration, tesla can innovate and add new features and products while bypassing outsourcing delays to rapidly introduce products to the market. Advanced Battery Technology: Tesla's knowledge and ability to produce advanced battery technology is extremely important and one of the most critical aspects when it comes to competing in the EV market. This resource/capability allows Tesla to gain value in cost savings, sustainability, and performance, including quality. This technology allows Tesla to produce batteries quickly, more energy-dense, and of higher quality while having reduced costs. The value added is Tesla gains a better battery which can last for more miles than its competitors while being cheaper to make and being higher quality. This value is extremely important for Tesla and its consumers who will benefit highly and therefore support Tesla more fiercely. With this technology, tesla solves a major concern for customers which is the battery range in EVs. The value creation for Tesla from this technology is lower costs, which increases product
affordability, and superior product performance and innovation which allows Tesla to be differentiated in the market, attracting more customers. Corporate Structure
Tesla utilizes a functional organizational structure currently. As it has specialized functions divided such as manufacturing, sales/marketing, engineering/design, and administration/finance. This current structure is decent for Tesla as it allows Tesla to focus on innovation and design as well as have the ability to make decisions quickly with one boss which is Elon Musk at the top. Although this is the case, a more optimal structure would be divisional, as it would align better with Tesla's goals, key resources and capabilities, and external environment. As Tesla expands into the global market and diversifies its products a divisional structure supports scalability, enhanced adaption to regional needs, and ensures better achievement of goals. This divisional structure would be focused on division around key areas such as geography and products. The way this structure would look is different divisions among the geographic markets in which they operate, which can be seen as North America, Europe, and Asia. Then divided into products and services including, EVs, energy products such as solar panels and powerwalls, and also another design for software and self-driving development. This would allow Tesla to scale operations more effectively and more easily align with regulatory requirements, and market demand preferences in various regions as each region is different. This would also allow Tesla to have increased and enhanced flexibility in design and innovation for each product and region, allowing them to adapt quickly to threats in different regions, as well as better allocation of resources. Lastly, a major advantage of this structure is the increased accountability within in department, as each department will better be able to focus solely on their goals and be responsible for them.
Corporate Culture
Tesla utilizes a top-down approach to corporate culture development, where senior leaders, particularly CEO Elon Musk, play a pivotal role in shaping strategic vision and identifying the ideal behaviors required for its implementation. The firm's leadership sets a clear emphasis on innovation, speed, and disruption, expecting employees to embody these values in their daily work. This approach is reflected in Tesla's aggressive timelines for product development and expansion, demanding a culture that thrives on urgency, experimentation, and resilience. Senior managers not only define these desired behaviors but also exemplify them, creating a strong tone from the top that drives company-wide expectations and norms. Musk's hands-on involvement in Tesla's projects, including spending long hours alongside employees on the factory floor, fosters a sense of camaraderie and unity among team members. However, Musk's demanding leadership style and high expectations can also create a high-pressure work environment, leading to stress and burnout among employees.
Simultaneously, Tesla employs a bottom-up approach to reinforce its desired culture through hiring practices, training programs, and incentive structures. The company actively seeks out employees who exhibit traits such as risk-taking, a passion for innovation, and a tolerance for ambiguity which are key characteristics that align with its fast-paced, high-risk business strategy. New hires are integrated through intensive training and are rewarded based on performance metrics that emphasize innovation and rapid problem-solving. Compensation, promotions, and recognition programs are designed to reinforce the behaviors that support Tesla's strategic goals, effectively developing a culture where employees are driven to challenge the status quo and continuously seek improvements.
Tesla's corporate culture is well-aligned with the external pressures of the EV industry, which demands rapid technological advancement and adaptability. Internally, the culture leverages Tesla's strengths in innovation and vertical integration, enabling swift responses to market changes and maintaining a competitive edge. By combining top-down strategic direction with bottom-up cultural reinforcement, Tesla cultivates an environment where employees are empowered to contribute to the company's success, embodying "a safe, innovative, and inclusive culture, anyone with the talent, energy, and focus to solve hard problems has a seat at the table." (Tesla, 2024). This quote from Tesla's careers page underscores the company's commitment to fostering an open and dynamic corporate culture that aligns well with its strategic objectives and external environment
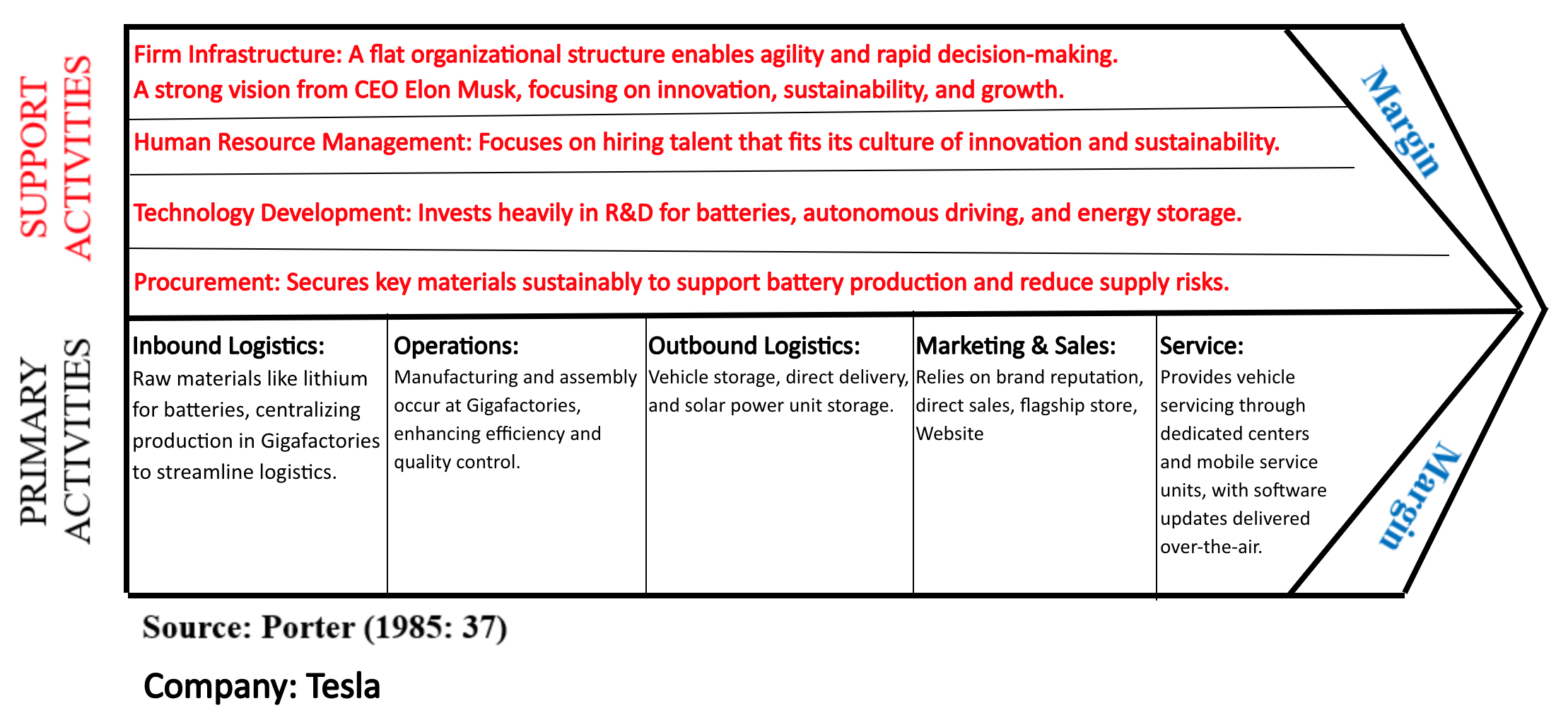
Internal Supply Chain (Please Reference Exhibit C) Tesla operates within the competitive electric vehicle (EV) industry, where companies
strive to differentiate themselves through technology innovation, sustainability, and efficient supply chains. Tesla's internal supply chain functions, including research and development, Production, Marketing, Finance, and Human Resources, are well-aligned with its strategic objectives. Research and development focuses on advanced battery technology and autonomous driving, aligning with Tesla's commitment to innovation and competitive differentiation. Production is streamlined in Gigafactories, enabling Tesla to scale efficiently while ensuring high quality. Marketing leverages Tesla's strong brand, promoting direct customer engagement. Finance supports Tesla's growth ambitions by securing capital for expansion, and Human Resources recruits talent who fit Tesla's culture of innovation and agility. This alignment across functions ensures that each part of the supply chain supports Tesla's goals of market leadership, efficiency, and sustainability.
Exhibit A. VRIS
| Resource/ Capability | Valuable | Rare | Costly to Imitate | Hard to Substitute | Competitive Consequence |
| Advanced Battery Technology | Y | Y | Y | Y | Sustainable Competitive Advantage with above average returns |
| Self-Driving Software/ AI | Y | Y | Y | Y | Sustainable Competitive Advantage with above average returns |
| Verticle Integration | Y | Y | Y | Y | Sustainable Competitive Advantage with above average returns |
| Brand and Customer Loyalty | Y | Y | N | N | Temporary Competitive Advantage with above-average returns. |
| Supercharg er Network | Y | Y | N | Y | Temporary Competitive Advantage with above-average returns. |
Exhibit B: IFAS
Tesla's IFAS score of 3.45 shows it does a decent job of using and advantageously managing key strengths but also shows the need to resolve key weaknesses. Tesla's key strengths are operated well but leadership and structure play an important role in the company's direction, and heavy reliance on a singular source of leadership making all the key decisions hinders individual product goals and regional development.
Exhibit C: Value Chain Diagram
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


