Question: fHow do fever: begin fa some this using R sfatfstkaf software? F. random sample of eight pairs of twins was randomly.r assigned to treatment A
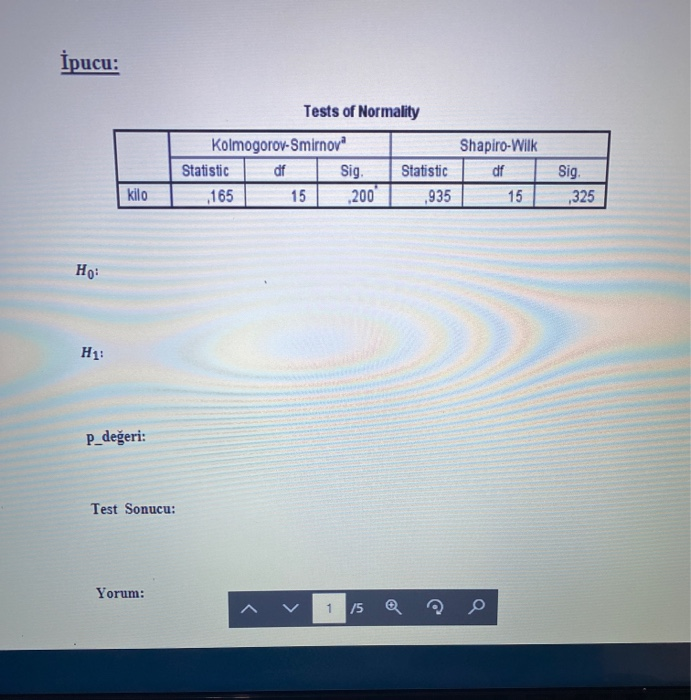
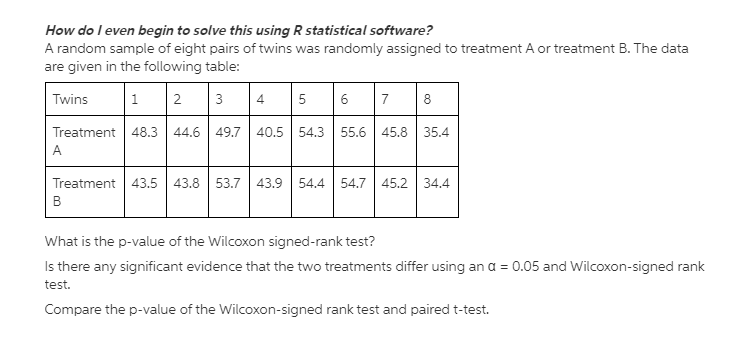

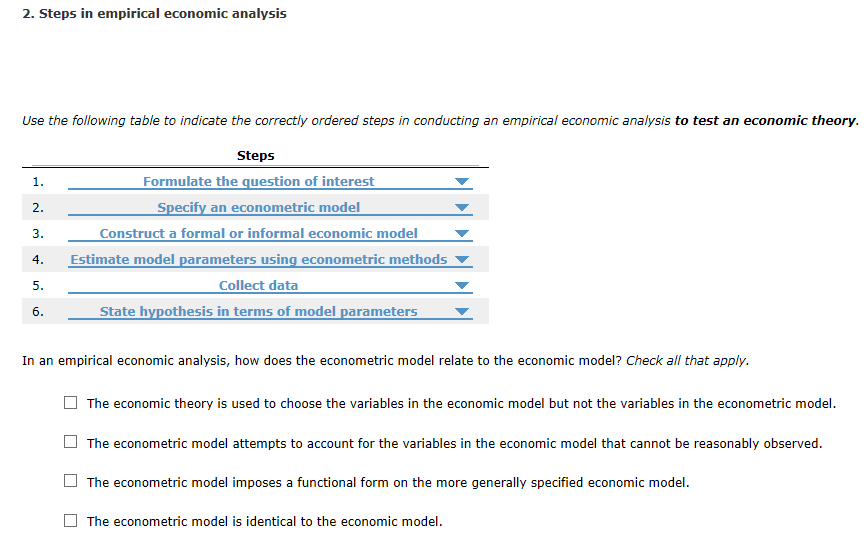
\fHow do fever: begin fa some this using R sfatfstkaf software? F. random sample of eight pairs of twins was randomly.r assigned to treatment A or treatment B. The data are given in the following table: "HIE .m. A B What is the pvalue of the 1|."v.l'il4:oxon signedrank test? Is there any significant evidence that the two treatments differ using an o = [105 and 1|."vr'ilazoxon-signed rank test. l'L'Zomrzrare the pvalue of the 1|."vr'ilcoxon-signed rank test and paired ttest. Explain the differences among the completely randomized design, randomized complete block designs, and factorial design. Choose the correct answer below. A. In a completely randomized design, the researcher examines a single factor and randomly distributes experimental units. In a randomized complete block design, the researcher partitions experimental units according to two fixed factors, factor A and factor B. In a factorial design, the researcher has a factor whose level cannot be fixed. O B. In a completely randomized design, the researcher examines many factors and randomly distributes experimental units. In a randomized complete block design, the researcher partitions experimental units according to two fixed factors, factor A and factor B. In a factorial design, the researcher has a factor whose level cannot be fixed. O C. In a completely randomized design, the researcher examines a single factor and randomly distributes experimental units. In a randomized complete block design, the researcher partitions experimental units according to a factor whose level cannot be fixed. In a factorial design, the researcher has two fixed factors, factor A and factor B. O D. In a completely randomized design, the researcher examines a random factor and randomly distributes experimental units. In a randomized complete block design, the researcher partitions experimental units according to a factor whose level is fixed. In a factorial design, the researcher has two fixed factors, factor A and factor B.2. Steps in empirical economic analysis Use the following table to indicate the correctly ordered steps in conducting an empirical economic analysis to test an economic theory. Steps 1. Formulate the question of interest 2. Specify an econometric model 3. Construct a formal or informal economic model 4. Estimate model parameters using econometric methods 5. Collect data 6. State hypothesis in terms of model parameters In an empirical economic analysis, how does the econometric model relate to the economic model? Check all that apply. The economic theory is used to choose the variables in the economic model but not the variables in the econometric model. The econometric model attempts to account for the variables in the economic model that cannot be reasonably observed. The econometric model imposes a functional form on the more generally specified economic model. The econometric model is identical to the economic model
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


