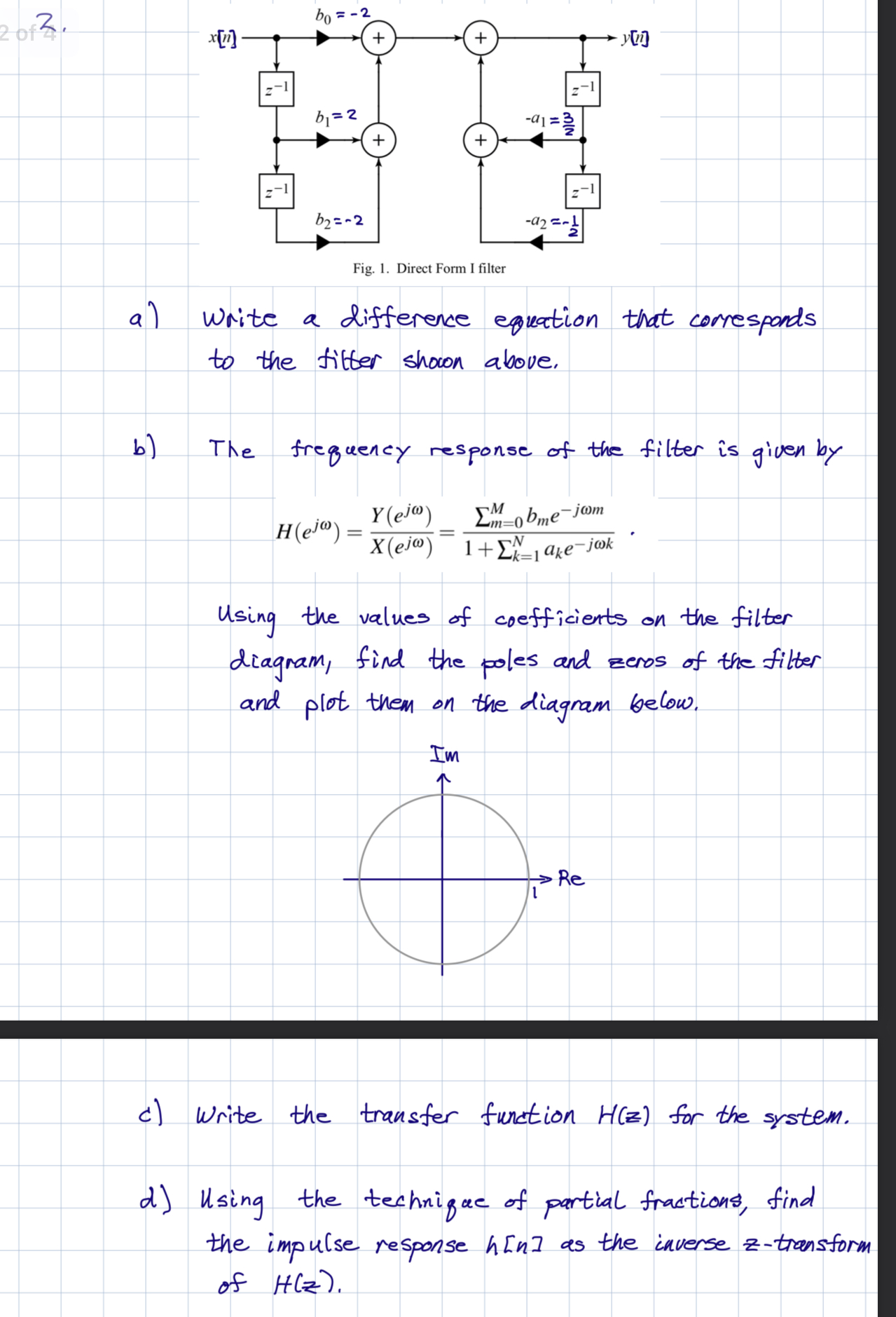
Question: Fig. 1 . Direct Form I filter aH ( e ^ ( j omega ) ) = ( Y ( e ^ ( j
Fig. Direct Form I filter
aHejomega Yejomega xejomega summM bmejomega msumkN akejomega k
Using the values of coefficients on the filter
diagram, find the poles and zeros of the filter
and plot them on the diagram below.
cHz for the system.
dhn as the inverse ztrensform
of Hz Fig. Direct Form I filter
aHejomega Yejomega xejomega summM bmejomega msumkN akejomega k
Using the values of coefficients on the filter
diagram, find the poles and zeros of the filter
and plot them on the diagram below.
cHz for the system.
dhn as the inverse ztrensform
of Hz e State whether the filter is stable or unstable and why.
f If just one of the coefficients of the filter hie one of a or b values is changed to the negative of its stated value, can the filter be made unstable? If so state why. If not, state why not.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


