Question: Figure 1: A directed unweighted graph for BFS and DFS. 2. Assume that DFS is performed on the graph in Fig. 1 using DFS(G) algorithm
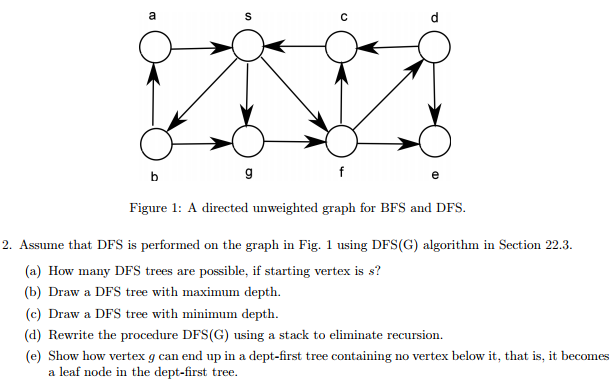
Figure 1: A directed unweighted graph for BFS and DFS. 2. Assume that DFS is performed on the graph in Fig. 1 using DFS(G) algorithm in Section 22.3. (a) How many DFS trees are possible, if starting vertex is s? (c) Draw a DFS tree with minimum depth. (d) Rewrite the procedure DFS(G) using a stack to eliminate recursion. (e) Show how vertex g can end up in a dept-first tree containing no vertex below it, that is, it becomes a leaf node in the dept-first tree Figure 1: A directed unweighted graph for BFS and DFS. 2. Assume that DFS is performed on the graph in Fig. 1 using DFS(G) algorithm in Section 22.3. (a) How many DFS trees are possible, if starting vertex is s? (c) Draw a DFS tree with minimum depth. (d) Rewrite the procedure DFS(G) using a stack to eliminate recursion. (e) Show how vertex g can end up in a dept-first tree containing no vertex below it, that is, it becomes a leaf node in the dept-first tree
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


