Question: Figure ( a ) shows a narrow charged solid cylinder that is coaxial with a larger charged cylindrical shell. Both are nonconducting and thin and
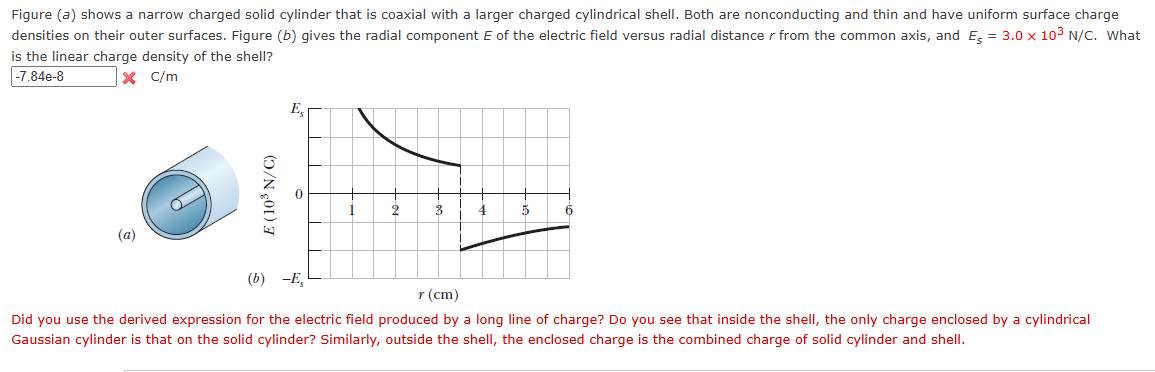
Figure a shows a narrow charged solid cylinder that is coaxial with a larger charged cylindrical shell. Both are nonconducting and thin and have uniform surface charge densities on their outer surfaces. Figure b gives the radial component E of the electric field versus radial distance r from the common axis, and Estimes mathrm~NmathrmC What is the linear charge density of the shell?
times mathrmCmathrmm
Did you use the derived expression for the electric field produced by a long line of charge? Do you see that inside the shell, the only charge enclosed by a cylindrical Gaussian cylinder is that on the solid cylinder? Similarly, outside the shell, the enclosed charge is the combined charge of solid cylinder and shell.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


