Question: Figure Q 3 . b Figure Q 3 . d ( a ) Sketch the diagram of a 'forced vortex' and a 'free vortex' including
Figure Qb
Figure Qda Sketch the diagram of a 'forced vortex' and a 'free vortex' including the relation between tangential velocity and radial position In addition, give two examples of the occurrence of a 'free vortex' and two examples of a 'forced vortex'.
b Noting the diagram and the symbols used in Figure Qb derive an expression for the mass, in the small layer at the outer radius.
Figure Qb
c By applying the force balance on the small layer at the outer radius, show that the pressure gradient can be expressed as
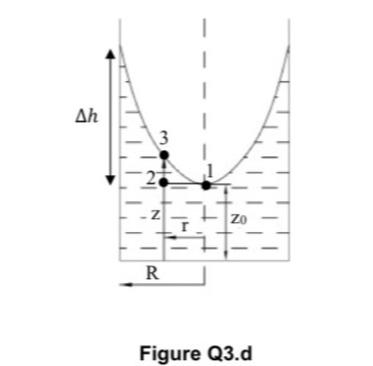
d Consider a cylindrical tank, partially filled with a liquid and rotating at angular speed around its axis. At steady state, the shape of the free surface of the liquid is given by the following expression
where is the free surface height, the gravitational constant and the radial coordinate see Figure Qd
Figure Qd
By using the following relation
i Obtain an expression for the pressure difference between points and
ii Obtain an expression for the pressure difference between points and
iii Use the expressions of and to derive the relation of the free surface shape.
e Consider the rotating tank described in part d If the tank diameter is and the angular velocity is calculate the distance see Figure Qd between the highest and lowest point reached by the free surface of the liquid.Answer hm
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


