Question: Figure Q3 shows the implementation of interface (Shape) marked by an arrow leading from the subclasses (Rectangle and Triangle) to the interface. Shape (Interface)
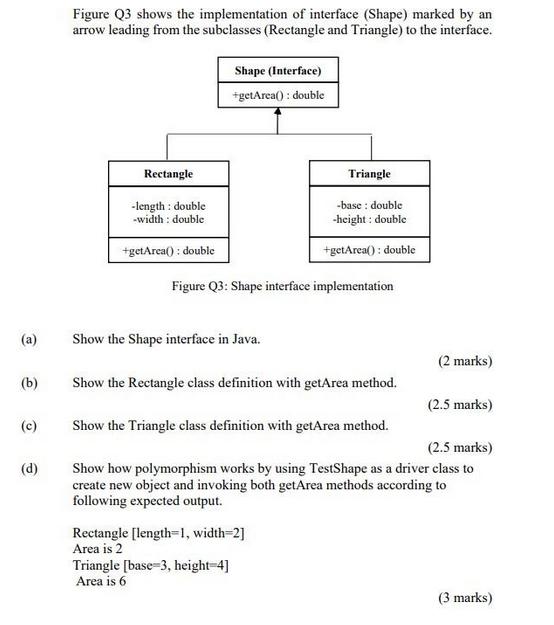
Figure Q3 shows the implementation of interface (Shape) marked by an arrow leading from the subclasses (Rectangle and Triangle) to the interface. Shape (Interface) +getArea(): double Rectangle Triangle -length double -width: double +getArea(): double -base double -height: double +getArea(): double Figure Q3: Shape interface implementation (a) Show the Shape interface in Java. (2 marks) (b) Show the Rectangle class definition with getArea method. (2.5 marks) (c) Show the Triangle class definition with getArea method. (2.5 marks) (d) Show how polymorphism works by using TestShape as a driver class to create new object and invoking both getArea methods according to following expected output. Rectangle [length-1, width=2] Area is 2 Triangle [base 3, height=4] Area is 6 (3 marks)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


