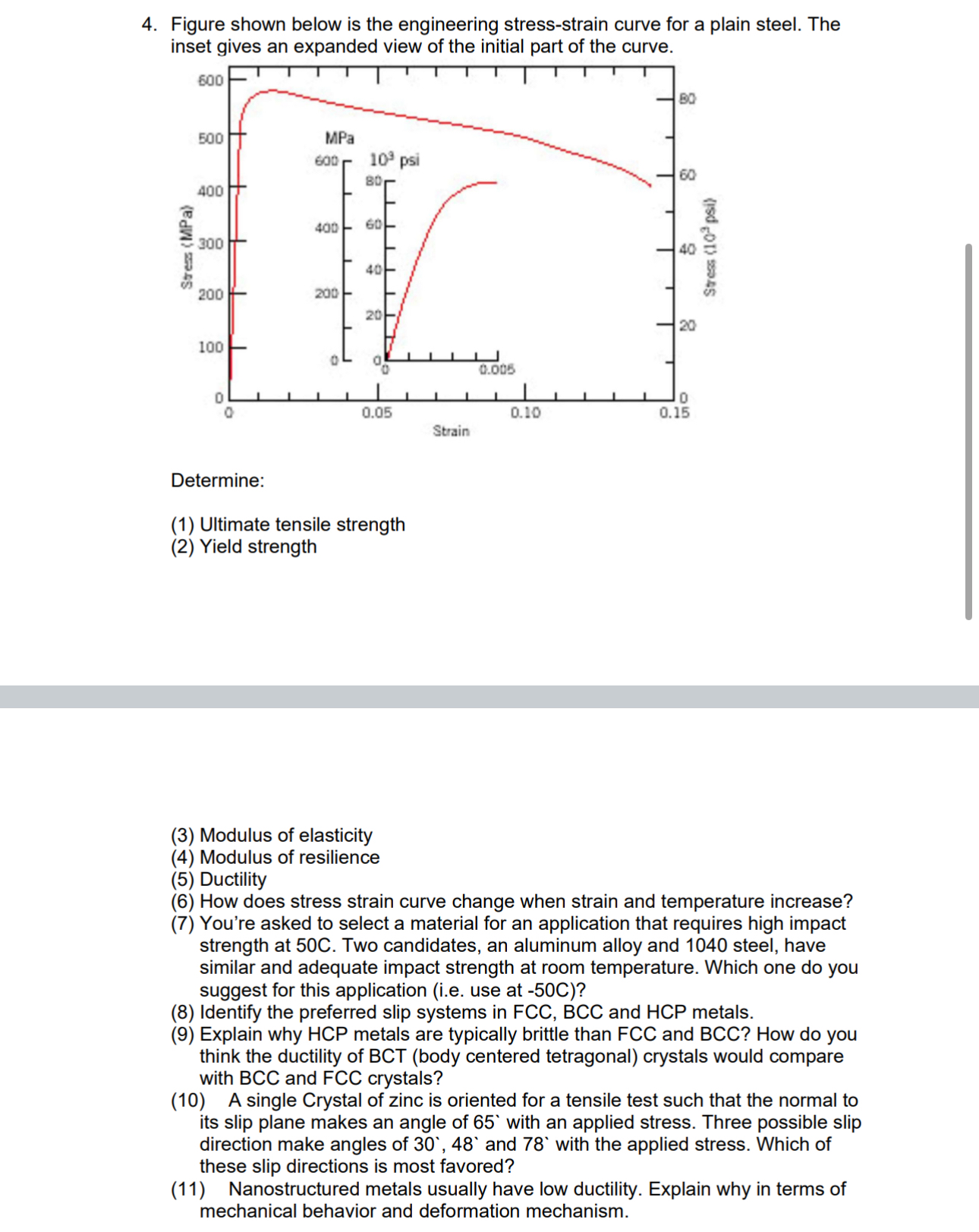
Question: Figure shown below is the engineering stress - strain curve for a plain steel. The Determine: ( 1 ) Ultimate tensile strength ( 2 )
Figure shown below is the engineering stressstrain curve for a plain steel. The
Determine:
Ultimate tensile strength
Yield strength
Modulus of elasticity
Modulus of resilience
Ductility
How does stress strain curve change when strain and temperature increase?
You're asked to select a material for an application that requires high impact strength at C Two candidates, an aluminum alloy and steel, have similar and adequate impact strength at room temperature. Which one do you suggest for this application ie use at C
Identify the preferred slip systems in FCC BCC and HCP metals.
Explain why HCP metals are typically brittle than FCC and BCC How do you think the ductility of BCT body centered tetragonal crystals would compare with BCC and FCC crystals?
A single Crystal of zinc is oriented for a tensile test such that the normal to its slip plane makes an angle of with an applied stress. Three possible slip direction make angles of and with the applied stress. Which of these slip directions is most favored?
Nanostructured metals usually have low ductility. Explain why in terms of mechanical behavior and deformation mechanism.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


