Question: File Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Rev 116 fx Changing Cells Dptimization Cells 35 Calculations 36 Riverne: 37 Trucks 38 Euvs 39 Sedans
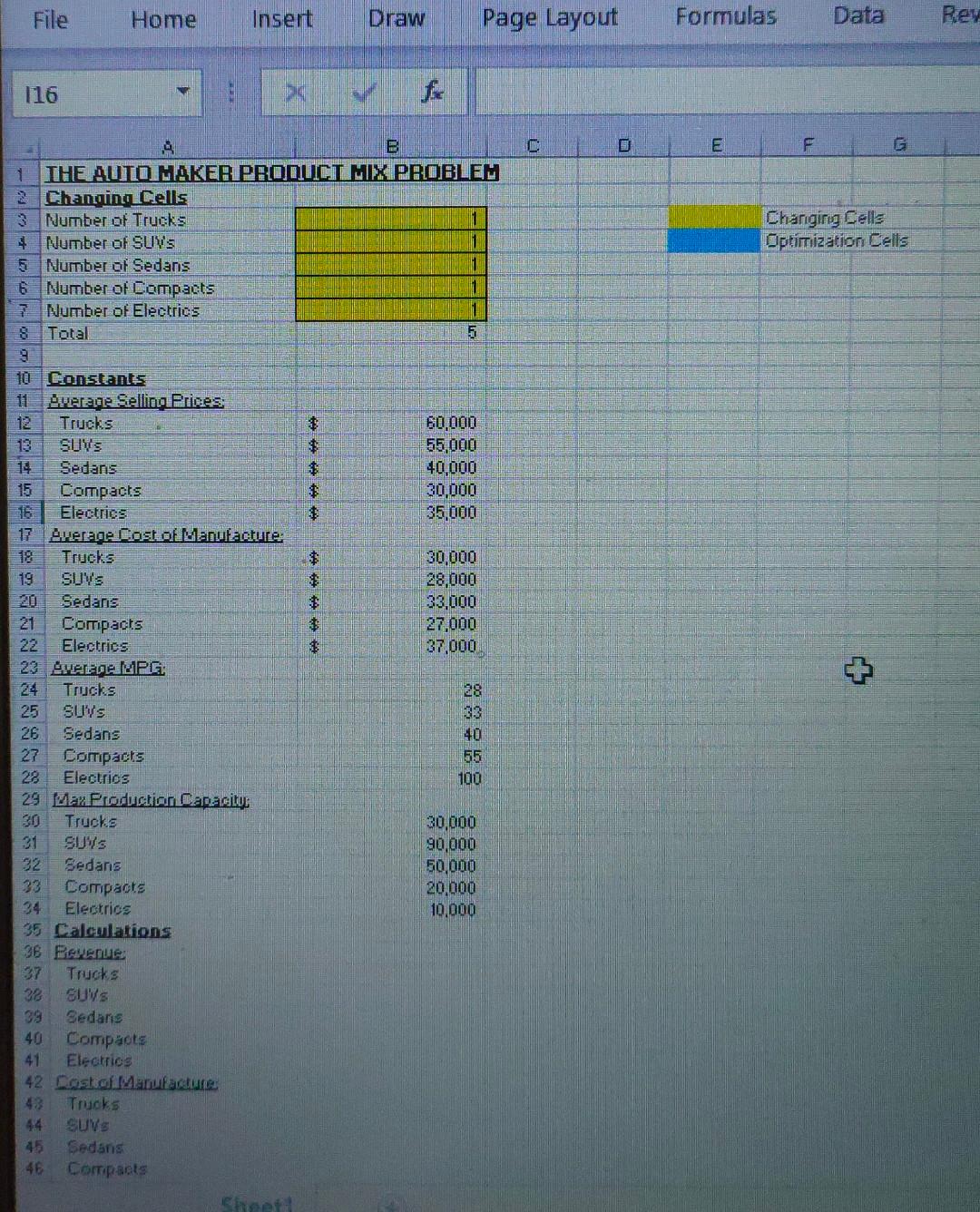
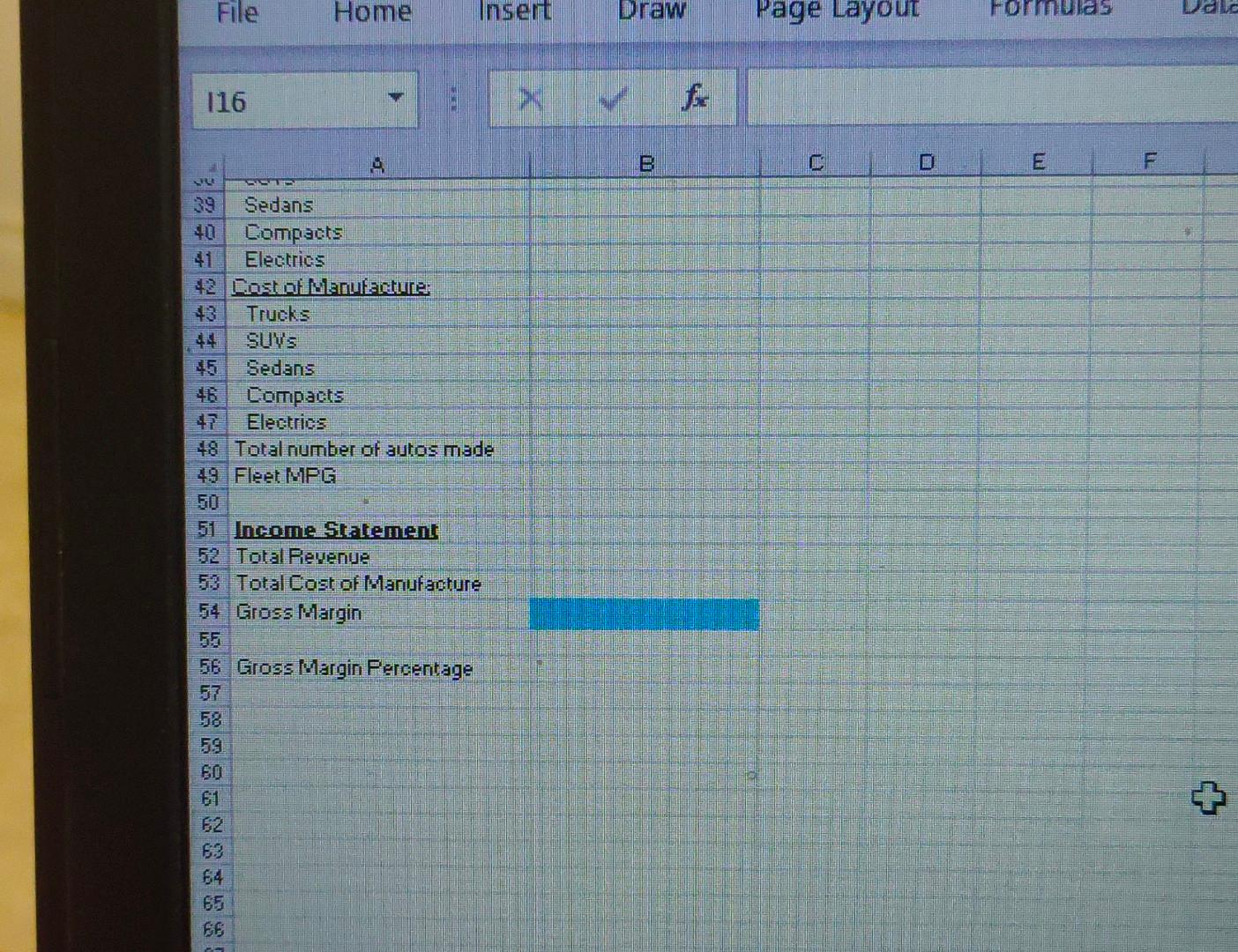
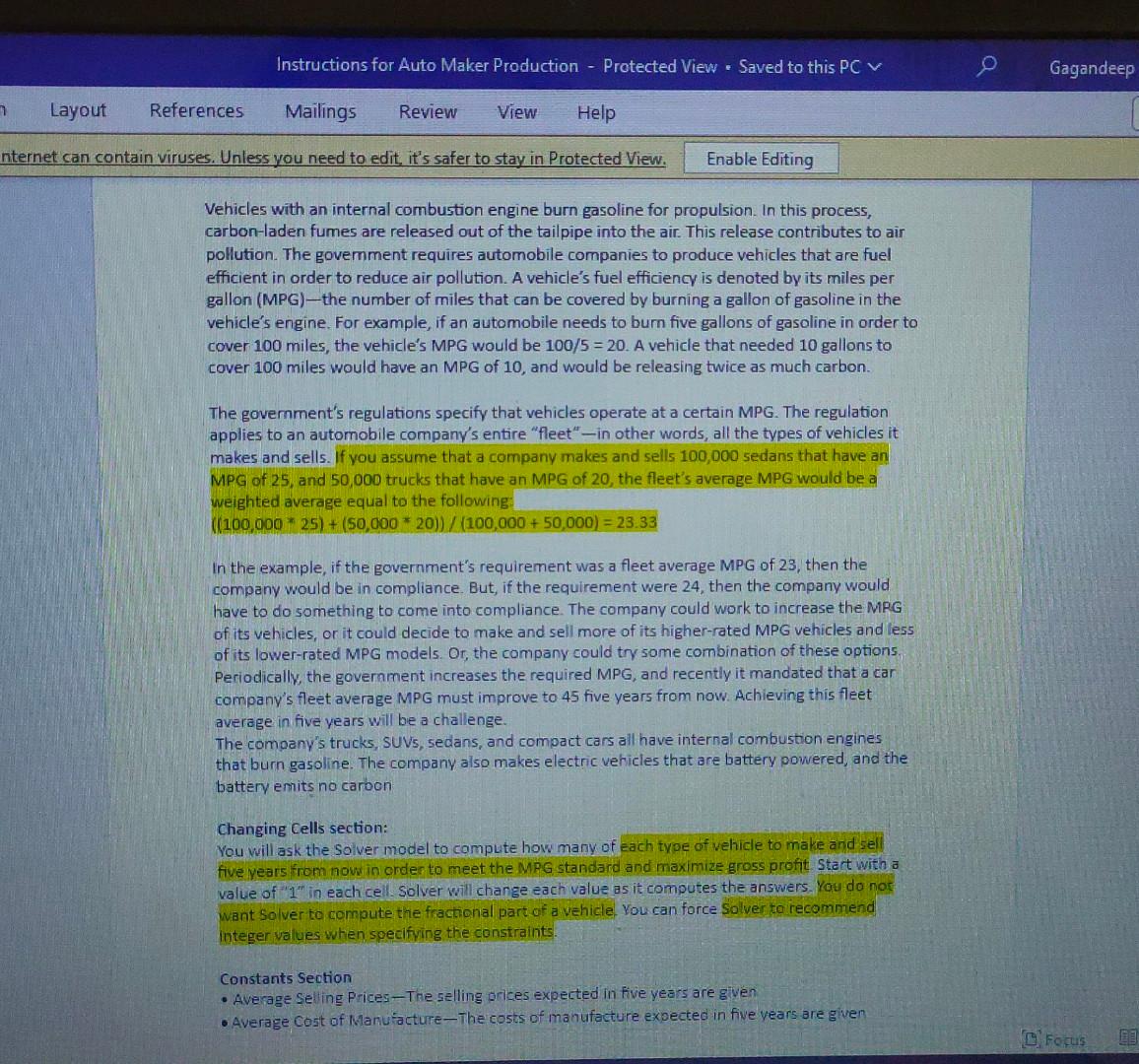
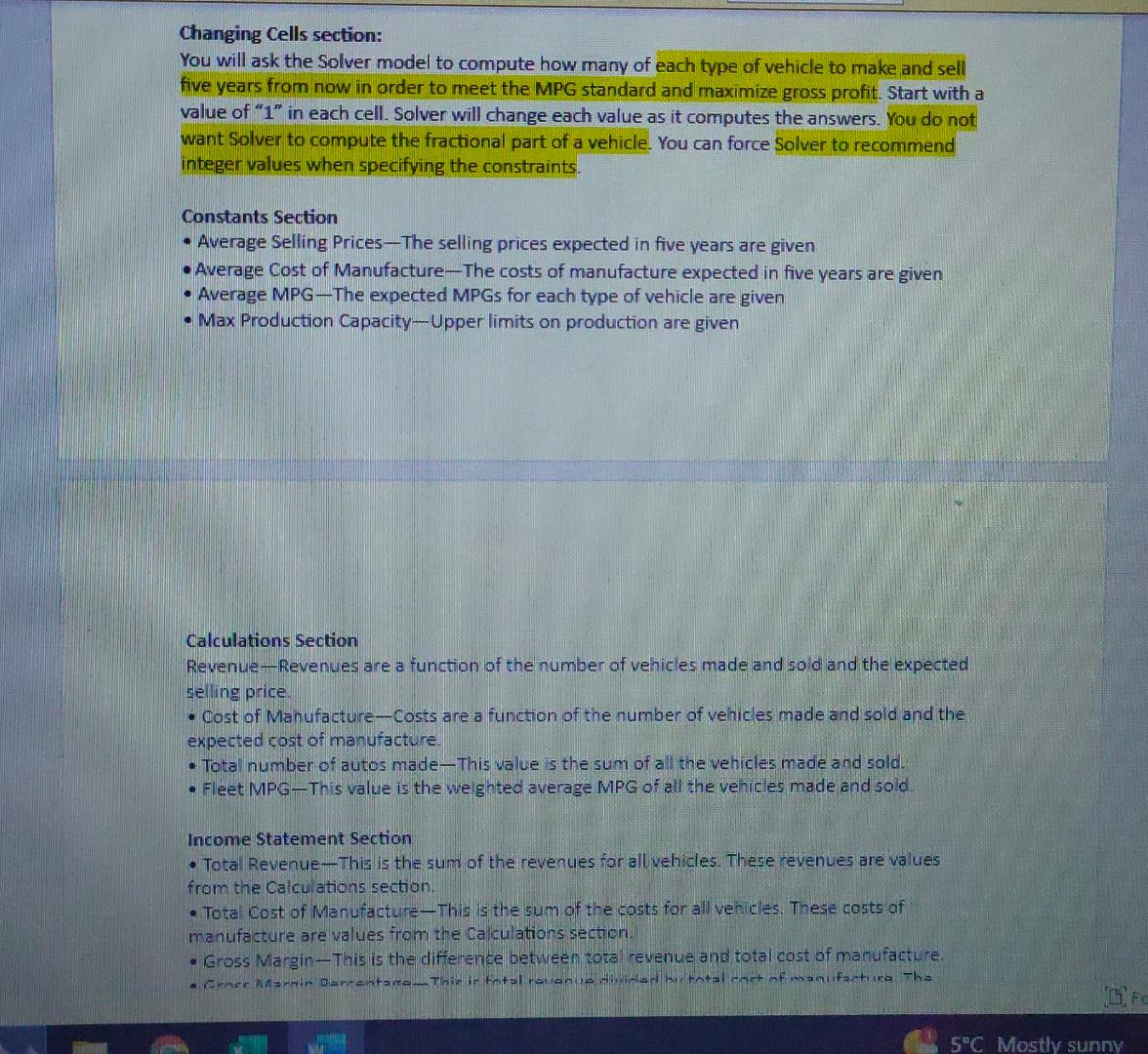
File Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Rev 116 fx Changing Cells Dptimization Cells 35 Calculations 36 Riverne: 37 Trucks 38 Euvs 39 Sedans 40 Compacts 41 Elearics 42. Costof Marnufacture: 4. Trucks 44 Suvs 45 Fedans 46 Compats Vehicles with an internal combustion engine burn gasoline for propulsion. In this process, carbon-laden fumes are released out of the tailpipe into the air. This release contributes to air pollution. The government requires automobile companies to produce vehicles that are fuel efficient in order to reduce air pollution. A vehicle's fuel efficiency is denoted by its miles per gallon (MPG) - the number of miles that can be covered by burning a gallon of gasoline in the vehicle's engine. For example, if an automobile needs to bum five gallons of gasoline in order to cover 100 miles, the vehicle's MPG would be 100/5=20. A vehicle that needed 10 gallons to cover 100 miles would have an MPG of 10 , and would be releasing twice as much carbon. The government's regulations specify that vehicles operate at a certain MPG. The regulation applies to an automobile company's entire "fleet" - in other words, all the types of vehicles it makes and sells. If you assume that a company makes and sells 100,000 sedans that have an MPG of 25 , and 50,000 trucks that have an MPG of 20, the fleet's average MPG would be a weighted average equal to the following: ((100,00025)+(50,00020))/(100,000+50,000)=23.33 In the example, if the government's requirement was a fleet average MPG of 23 , then the company would be in compliance. But, if the requirement were 24 , then the company would have to do something to come into compliance. The company could work to increase the MRG of its vehicles, or it could decide to make and sell more of its higher-rated MPG vehicles and less of its lower-rated MPG models. Or, the company could try some combination of these options. Periodically, the government increases the required MPG, and recently it mandated that a car company's fleet average MPG must improve to 45 five years from now. Achieving this fleet average in five years will be a challenge. The company's trucks, SUVs, sedans, and compact cars all have internal combustion engines that burn gasoline. The company also makes electric vehicles that are battery powered, and the battery emits no carbon Changing Cells section: You will ask the Solver model to compute how many of each type of vehicle to make and sell five vears from now in order to meet the MPG standard and maximize gross profit Start with a value of " 1 "in each cell. Solver will change each value as it computes the answers, You do nor: want Solver to compute the fractional part of a vehicle. You can force Solver to recommend integer values when specifving the constraints. Constants Section - Average Seling Prices-The selling prices expected in five years are given - Average Cost of Mlanuiacture-The costs of manufacture expected in five vears are given Changing Cells section: You will ask the Solver model to compute how many of each type of vehicle to make and sell five years from now in order to meet the MPG standard and maximize gross profit. Start with a value of " 1 " in each cell. Solver will change each value as it computes the answers. You do not want Solver to compute the fractional part of a vehicle. You can force Solver to recommend integer values when specifying the constraints. Constants Section - Average Selling Prices-The selling prices expected in five vears are given - Average Cost of Manufacture-The costs of manufacture expected in five years are given - Average MPG - The expected MPGs for each type of vehicle are given - Max Production Capacity-Upper limits on production are given Calculations Section Revenue - Revenues are a function of the number of vehicles made and sold and the expected selling price. - Cost of Manufacture - Costs are a function of the number of vehicles made and sold and the expected cost of manufacture. - Tota number of autos made-This value is the sum of all the vehicles made and sold. - Fleet MPG - This value is the we ghted average MPG of all the vehicles made and sold. Income Statement Section - Total Revenue - This is the sum of the revenues for allvehicles. These revenues are values from the Calcu ations section. - Tota Cost of Manufacture-This is the sum of the costs for all venicles. Thesie costs of manufacture are values from the Calculations section. - Gross Margin - This is the difference between tote revenue and total cost of manufacture. Calculations Section Revenue-Revenues are a function of the number of vehicles made and sold and the expected selling price. - Cost of Manufacture - Costs are a function of the number of vehicles made and sold and the expected cost of manufacture. - Total number of autos made - This value is the sum of all the vehicles made and sold. - Fleet MPG - This value is the weighted average MPG of all the vehicles made and sold. Income Statement Section - Total Revenue-This is the sum of the revenues for all vehicles. These revenues are values from the Calculations section. - Total Cost of Manufacture-This is the sum of the costs for all vehicles. These costs of manufacture are values from the Calculations section. - Gross Margin-This is the difference between total revenue and total cost of manufacture. - Gross Margin Percentage-This is total revenue divided by total cost of manufacture. The company wants a gross margin of at least 30 percent. Constraints and Running Solver - Next you must determine the constraints. You can assume that the marketing managers think at least 20,000 trucks, 20,000 SUVs, 20,000 sedans, 20,000 compacts, and 8,000 electric yehicles will be made and sold five years from now: - Use Solver to enter the base case constraints. You want to maximize total gross margin. Set Solver for GRG Nonlinear mode. Run Solver and ask for the Answer Report when Solver finds a solution that satisfies the constraints. File Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Rev 116 fx Changing Cells Dptimization Cells 35 Calculations 36 Riverne: 37 Trucks 38 Euvs 39 Sedans 40 Compacts 41 Elearics 42. Costof Marnufacture: 4. Trucks 44 Suvs 45 Fedans 46 Compats Vehicles with an internal combustion engine burn gasoline for propulsion. In this process, carbon-laden fumes are released out of the tailpipe into the air. This release contributes to air pollution. The government requires automobile companies to produce vehicles that are fuel efficient in order to reduce air pollution. A vehicle's fuel efficiency is denoted by its miles per gallon (MPG) - the number of miles that can be covered by burning a gallon of gasoline in the vehicle's engine. For example, if an automobile needs to bum five gallons of gasoline in order to cover 100 miles, the vehicle's MPG would be 100/5=20. A vehicle that needed 10 gallons to cover 100 miles would have an MPG of 10 , and would be releasing twice as much carbon. The government's regulations specify that vehicles operate at a certain MPG. The regulation applies to an automobile company's entire "fleet" - in other words, all the types of vehicles it makes and sells. If you assume that a company makes and sells 100,000 sedans that have an MPG of 25 , and 50,000 trucks that have an MPG of 20, the fleet's average MPG would be a weighted average equal to the following: ((100,00025)+(50,00020))/(100,000+50,000)=23.33 In the example, if the government's requirement was a fleet average MPG of 23 , then the company would be in compliance. But, if the requirement were 24 , then the company would have to do something to come into compliance. The company could work to increase the MRG of its vehicles, or it could decide to make and sell more of its higher-rated MPG vehicles and less of its lower-rated MPG models. Or, the company could try some combination of these options. Periodically, the government increases the required MPG, and recently it mandated that a car company's fleet average MPG must improve to 45 five years from now. Achieving this fleet average in five years will be a challenge. The company's trucks, SUVs, sedans, and compact cars all have internal combustion engines that burn gasoline. The company also makes electric vehicles that are battery powered, and the battery emits no carbon Changing Cells section: You will ask the Solver model to compute how many of each type of vehicle to make and sell five vears from now in order to meet the MPG standard and maximize gross profit Start with a value of " 1 "in each cell. Solver will change each value as it computes the answers, You do nor: want Solver to compute the fractional part of a vehicle. You can force Solver to recommend integer values when specifving the constraints. Constants Section - Average Seling Prices-The selling prices expected in five years are given - Average Cost of Mlanuiacture-The costs of manufacture expected in five vears are given Changing Cells section: You will ask the Solver model to compute how many of each type of vehicle to make and sell five years from now in order to meet the MPG standard and maximize gross profit. Start with a value of " 1 " in each cell. Solver will change each value as it computes the answers. You do not want Solver to compute the fractional part of a vehicle. You can force Solver to recommend integer values when specifying the constraints. Constants Section - Average Selling Prices-The selling prices expected in five vears are given - Average Cost of Manufacture-The costs of manufacture expected in five years are given - Average MPG - The expected MPGs for each type of vehicle are given - Max Production Capacity-Upper limits on production are given Calculations Section Revenue - Revenues are a function of the number of vehicles made and sold and the expected selling price. - Cost of Manufacture - Costs are a function of the number of vehicles made and sold and the expected cost of manufacture. - Tota number of autos made-This value is the sum of all the vehicles made and sold. - Fleet MPG - This value is the we ghted average MPG of all the vehicles made and sold. Income Statement Section - Total Revenue - This is the sum of the revenues for allvehicles. These revenues are values from the Calcu ations section. - Tota Cost of Manufacture-This is the sum of the costs for all venicles. Thesie costs of manufacture are values from the Calculations section. - Gross Margin - This is the difference between tote revenue and total cost of manufacture. Calculations Section Revenue-Revenues are a function of the number of vehicles made and sold and the expected selling price. - Cost of Manufacture - Costs are a function of the number of vehicles made and sold and the expected cost of manufacture. - Total number of autos made - This value is the sum of all the vehicles made and sold. - Fleet MPG - This value is the weighted average MPG of all the vehicles made and sold. Income Statement Section - Total Revenue-This is the sum of the revenues for all vehicles. These revenues are values from the Calculations section. - Total Cost of Manufacture-This is the sum of the costs for all vehicles. These costs of manufacture are values from the Calculations section. - Gross Margin-This is the difference between total revenue and total cost of manufacture. - Gross Margin Percentage-This is total revenue divided by total cost of manufacture. The company wants a gross margin of at least 30 percent. Constraints and Running Solver - Next you must determine the constraints. You can assume that the marketing managers think at least 20,000 trucks, 20,000 SUVs, 20,000 sedans, 20,000 compacts, and 8,000 electric yehicles will be made and sold five years from now: - Use Solver to enter the base case constraints. You want to maximize total gross margin. Set Solver for GRG Nonlinear mode. Run Solver and ask for the Answer Report when Solver finds a solution that satisfies the constraints
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


