Question: file 'RecursiveAlgorithms.java' that will implement two recursive algorithms as follows: 1. Implement a static method that calculates the nth Fibonacci number using recursion. Recall
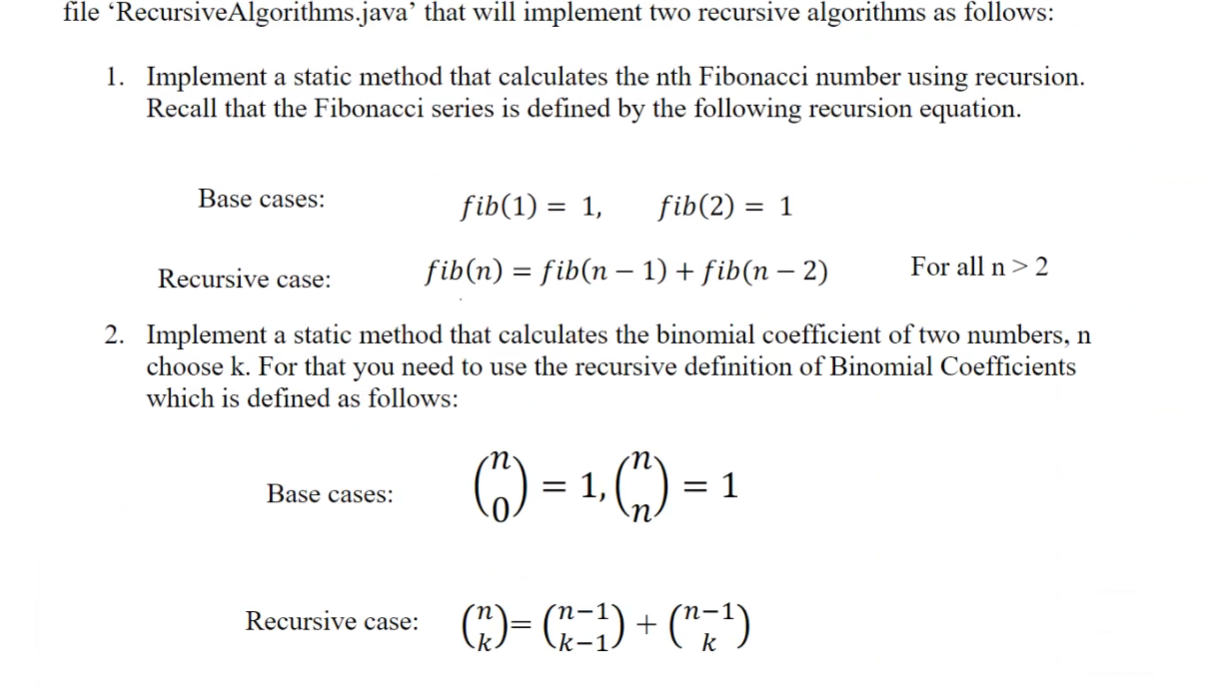


file 'RecursiveAlgorithms.java' that will implement two recursive algorithms as follows: 1. Implement a static method that calculates the nth Fibonacci number using recursion. Recall that the Fibonacci series is defined by the following recursion equation. Base cases: fib(1) = 1, fib(2) = 1 Recursive case: fib(n) = fib(n 1) + fib(n 2) 2. Implement a static method that calculates the binomial coefficient of two numbers, n choose k. For that you need to use the recursive definition of Binomial Coefficients which is defined as follows: Base cases: (1) = 1, = 1 Recursive case: () = (-) + (n=) k-1. For all n > 2 Additional Specification Implement the above functions using recursion. Your implementation must be static methods. Create a Main class that demonstrates the correct use of the recursive methods, on at least 3 non-trivial inputs configurations. Program Requirement Your implementation for the above program should comply with the following requirements and specifications: Your program should implement all the specification outlined above. Your code must be well organized, code must be indented. You must use the data file provided as input to your program. Source code files must be submitted (not the compiled files) You must use the template code provided. Your program must compile and run without errors and generate the expected output. Deliverables: You must submit your implementation of the Recursive Algorithms.java, the Main.java, an output screen showing your code executing and complete the Submission Cover Page for this assignment as listed on the LMS. In this problem set you will practice using the concept of recursion. In the lecture, we saw that we can use recursion to solve problems that their solution can be in terms of smaller occurrences of the same problem. As an example, we saw the problem of calculating the factorial of a number, denoted as n!. By definition, the factorial of a number is given by the following recursive expression. Base case: Recursive case: n! = 0! = 1 (n 1)! * n For all n > 0 We noticed that each recursive problem has one (or more) base cases, which the solution can be evaluated trivially (i.e. 0! = 1), and one or more recursive cases, whose solution requires first to solve a smaller instance of the same problem (i.e. (n-1)!). In the case of the recursive step when programming recursion, we will recursively the current function with the appropriate input. We saw how to implement such algorithms in java. For this problem set you are asked to implement a class called 'Recursive Algorithms' stored in a file 'Recursive Algorithms.java' that will implement two recursive algorithms as follows:
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Below is the implementation of the RecursiveAlgorithms class in ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


