Question: fill in anything so i understand how to do it PLEASE AND THANK YOU !!! ASAP 71 SUMMARY OF RESULTS Write the chemical equations corresponding
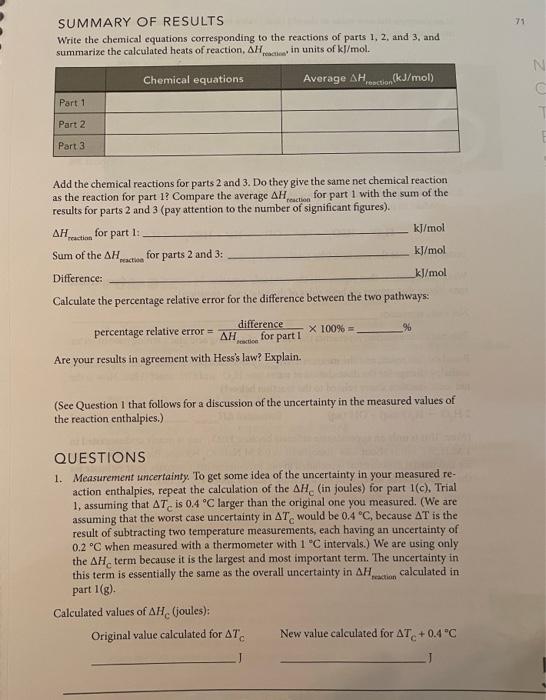

71 SUMMARY OF RESULTS Write the chemical equations corresponding to the reactions of parts 1, 2, and 3, and summarize the calculated heats of reaction, AH ro in units of kJ/mol. N Chemical equations Average AH cction(kJ/mol) ZU Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 peace Add the chemical reactions for parts 2 and 3. Do they give the same net chemical reaction as the reaction for part 1? Compare the average AH, reaction for part 1 with the sum of the results for parts 2 and 3 (pay attention to the number of significant figures). . reaction kJ/mol for part 1 Sum of the . for parts 2 and 3: kJ/mol Difference: kJ/mol Calculate the percentage relative error for the difference between the two pathways: difference percentage relative error = X 100% %6 . for part 1 Are your results in agreement with Hess's law? Explain. to (See Question that follows for a discussion of the uncertainty in the measured values of the reaction enthalpies.) QUESTIONS 1. Measurement uncertainty. To get some idea of the uncertainty in your measured re- action enthalpies, repeat the calculation of the AH (in joules) for part 1(c), Trial 1, assuming that AT, is 0.4 C larger than the original one you measured. (We are assuming that the worst case uncertainty in AT. would be 0.4 C, because AT is the result of subtracting two temperature measurements, each having an uncertainty of 0.2 C when measured with a thermometer with 1 "C intervals. We are using only the AH term because it is the largest and most important term. The uncertainty in this term is essentially the same as the overall uncertainty in AH calculated in part 1(g) Calculated values of AH (joules): Original value calculated for AT New value calculated for AT. +0.4 C reaction Now compare the new value to the old (first) value by calculating the relative percentage uncertainty in AH relative percentage uncertainty = AH (new) - AH (original) -X 100% = AH (original) Typically, this relative percentage uncertainty is about 3%. Also keep in mind that our neglect of the heat losses to the calorimeter biases our results to values that are about 3% too low, + 2. The enthalpy of dissociation of water. The H,SO, and NaOH reactants and the NaHSO, product in part 3 actually exist as dissociated ions, so the equation H,0* +HSO, +Na+ + OH - Na' +HSO, +2H,O better represents the reaction (the total ionic equation). Write the equation that represents the net ionic equation by canceling out the spectator ions (those that appear on both sides of the total ionic equation). Net ionic equation: This net ionic equation represents the reaction of a strong acid and a strong base in water. Based on this result, and the measured AH /mol from part 3, what is the approximate enthalpy change for the dissociation of water into H,O and OH ions? (Hint: How is the net ionic reaction above related to the reaction below?) 2 H,0 --H, O'(aq) + OH(aq) Estimated Action kj/mol (Note: This is only an approximate estimate because HSO, ion is nearly undissociated in 1 MH,SO, but is about 14% dissociated in 0.5 M NaHSO, because the enthalpy change for this partial dissociation is included in our measurements. Compare your estimate for the dissociation of water with the literature value of about +57 kJ/mol.) reactie
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


