Question: Fill in the following code to implement a Naive Bayes Classifier that implements the SKlearn classifier API with fit, predict and score methods code transcript:
Fill in the following code to implement a Naive Bayes Classifier that implements the SKlearn classifier API with fit, predict and score methods
code transcript:
from functools import partial
import numpy as np
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from scipy.stats import norm
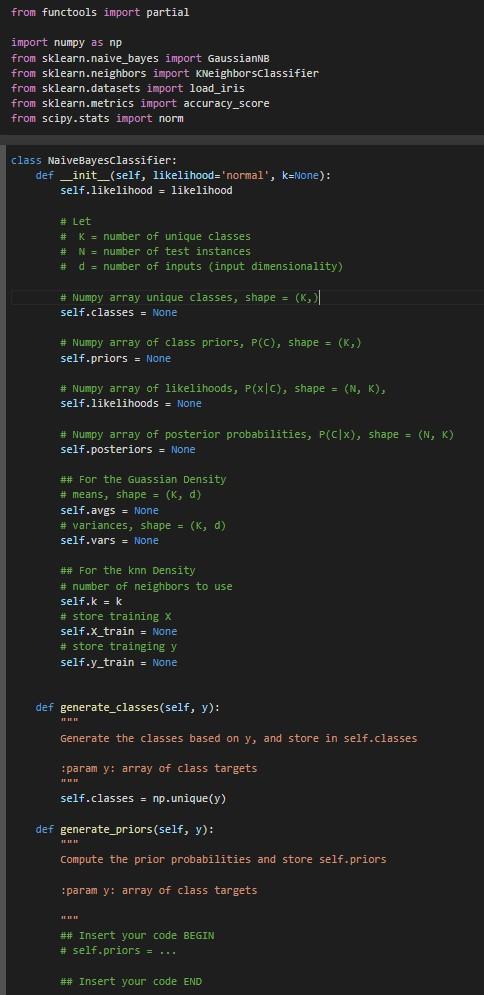
class NaiveBayesClassifier:
def __init__(self, likelihood='normal', k=None):
self.likelihood = likelihood
# Let
# K = number of unique classes
# N = number of test instances
# d = number of inputs (input dimensionality)
# Numpy array unique classes, shape = (K,)
self.classes = None
# Numpy array of class priors, P(C), shape = (K,)
self.priors = None
# Numpy array of likelihoods, P(x|C), shape = (N, K),
self.likelihoods = None
# Numpy array of posterior probabilities, P(C|x), shape = (N, K)
self.posteriors = None
## For the Guassian Density
# means, shape = (K, d)
self.avgs = None
# variances, shape = (K, d)
self.vars = None
## For the knn Density
# number of neighbors to use
self.k = k
# store training X
self.X_train = None
# store trainging y
self.y_train = None
def generate_classes(self, y):
"""
Generate the classes based on y, and store in self.classes
:param y: array of class targets
"""
self.classes = np.unique(y)
def generate_priors(self, y):
"""
Compute the prior probabilities and store self.priors
:param y: array of class targets
"""
## Insert your code BEGIN
# self.priors = ...
## Insert your code END
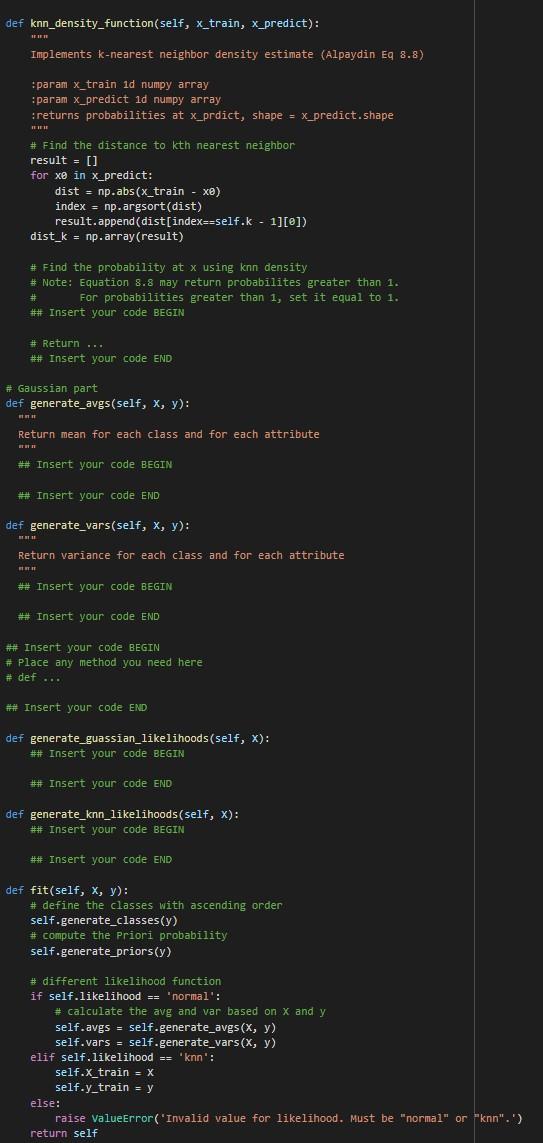
def knn_density_function(self, x_train, x_predict):
"""
Implements k-nearest neighbor density estimate (Alpaydin Eq 8.8)
:param x_train 1d numpy array
:param x_predict 1d numpy array
:returns probabilities at x_prdict, shape = x_predict.shape
"""
# Find the distance to kth nearest neighbor
result = []
for x0 in x_predict:
dist = np.abs(x_train - x0)
index = np.argsort(dist)
result.append(dist[index==self.k - 1][0])
dist_k = np.array(result)
# Find the probability at x using knn density
# Note: Equation 8.8 may return probabilites greater than 1.
# For probabilities greater than 1, set it equal to 1.
## Insert your code BEGIN
# Return ...
## Insert your code END
# Gaussian part
def generate_avgs(self, X, y):
"""
Return mean for each class and for each attribute
"""
## Insert your code BEGIN
## Insert your code END
def generate_vars(self, X, y):
"""
Return variance for each class and for each attribute
"""
## Insert your code BEGIN
## Insert your code END
## Insert your code BEGIN
# Place any method you need here
# def ...
## Insert your code END
def generate_guassian_likelihoods(self, X):
## Insert your code BEGIN
## Insert your code END
def generate_knn_likelihoods(self, X):
## Insert your code BEGIN
## Insert your code END
def fit(self, X, y):
# define the classes with ascending order
self.generate_classes(y)
# compute the Priori probability
self.generate_priors(y)
# different likelihood function
if self.likelihood == 'normal':
# calculate the avg and var based on X and y
self.avgs = self.generate_avgs(X, y)
self.vars = self.generate_vars(X, y)
elif self.likelihood == 'knn':
self.X_train = X
self.y_train = y
else:
raise ValueError('Invalid value for likelihood. Must be "normal" or "knn".')
return self
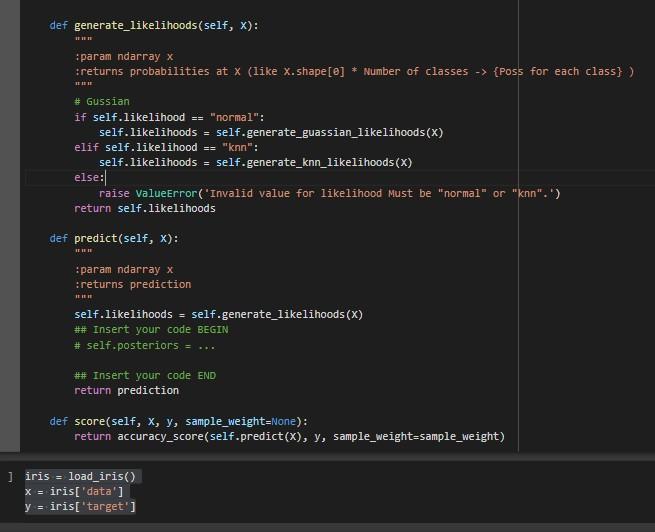
def generate_likelihoods(self, X):
"""
:param ndarray x
:returns probabilities at X (like X.shape[0] * Number of classes -> {Poss for each class} )
"""
# Gussian
if self.likelihood == "normal":
self.likelihoods = self.generate_guassian_likelihoods(X)
elif self.likelihood == "knn":
self.likelihoods = self.generate_knn_likelihoods(X)
else:
raise ValueError('Invalid value for likelihood Must be "normal" or "knn".')
return self.likelihoods
def predict(self, X):
"""
:param ndarray x
:returns prediction
"""
self.likelihoods = self.generate_likelihoods(X)
## Insert your code BEGIN
# self.posteriors = ...
## Insert your code END
return prediction
def score(self, X, y, sample_weight=None):
return accuracy_score(self.predict(X), y, sample_weight=sample_weight)
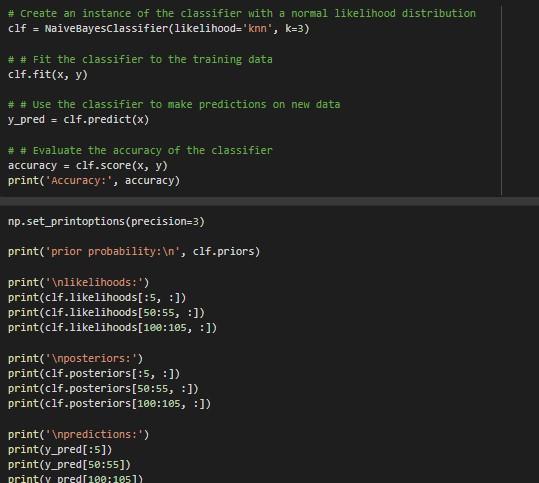
def generate_likelihoods(self, x ): in n iparam ndarray x unu \# Gussian if self.likelihood == "normal": self.likelihoods = self.generate_guassian_likelihoods (X) elif self.likelihood == "knn": self.likelihoods = self.generate_knn_likelihoods (X) else: raise valueError ('Invalid value for likelihood Must be "normal" or "knn". ') return self.likelihoods def predict(self, x) : mun :param ndarray x ireturns prediction nin self.likelihoods = self.generate_likelihoods (X) \#\# Insert your code BEGIN # self.posteriors =. \#\# Insert your code END return prediction def score(self, x,y, sample_weight=None): return accuracy_score(self.predict (x),y, sample_weight=sample_weight) ] iris = load_iris () x= iris ['data'] y= iris ['target']
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


