Question: FIRST CONDITION OF EQUILIBRIUM USING DYNAMIC KIT STAND OBJECTIVE To verify the first condition of equilibrium. MATERIALS Dynamic kit stand, protractor, weights, pulley system, clamps,
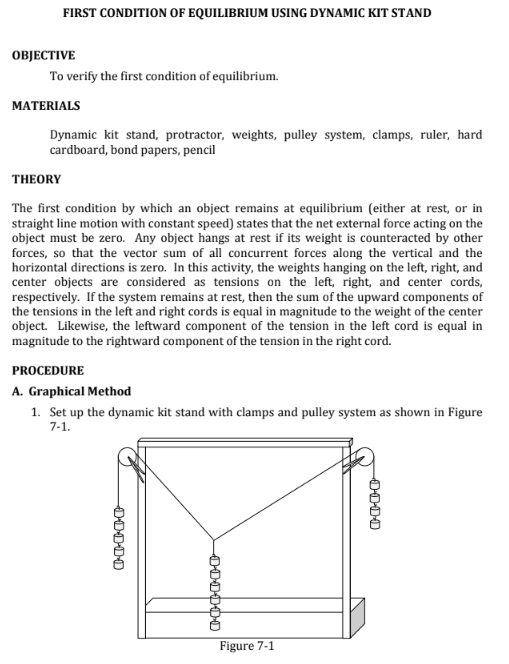
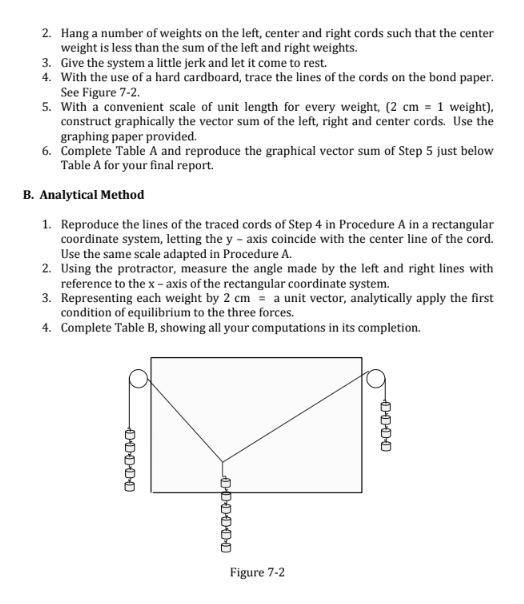
FIRST CONDITION OF EQUILIBRIUM USING DYNAMIC KIT STAND OBJECTIVE To verify the first condition of equilibrium. MATERIALS Dynamic kit stand, protractor, weights, pulley system, clamps, ruler, hard cardboard, bond papers, pencil THEORY The first condition by which an object remains at equilibrium (either at rest, or in straight line motion with constant speed) states that the net external force acting on the object must be zero. Any object hangs at rest if its weight is counteracted by other forces, so that the vector sum of all concurrent forces along the vertical and the horizontal directions is zero. In this activity, the weights hanging on the left, right, and center objects are considered as tensions on the left, right, and center cords, respectively. If the system remains at rest, then the sum of the upward components of the tensions in the left and right cords is equal in magnitude to the weight of the center object. Likewise, the leftward component of the tension in the left cord is equal in magnitude to the rightward component of the tension in the right cord. PROCEDURE A. Graphical Method 1. Set up the dynamic kit stand with clamps and pulley system as shown in Figure 7-1. Figure 7-12. Hang a number of weights on the left, center and right cords such that the center weight is less than the sum of the left and right weights. 3. Give the system a little jerk and let it come to rest. 4. With the use of a hard cardboard, trace the lines of the cords on the bond paper. See Figure 7-2. 5. With a convenient scale of unit length for every weight, (2 cm = 1 weight), construct graphically the vector sum of the left, right and center cords. Use the graphing paper provided. 6. Complete Table A and reproduce the graphical vector sum of Step 5 just below Table A for your final report. B. Analytical Method 1. Reproduce the lines of the traced cords of Step 4 in Procedure A in a rectangular coordinate system, letting the y - axis coincide with the center line of the cord. Use the same scale adapted in Procedure A. 2. Using the protractor, measure the angle made by the left and right lines with reference to the x - axis of the rectangular coordinate system. 3. Representing each weight by 2 cm = a unit vector, analytically apply the first condition of equilibrium to the three forces. 4. Complete Table B, showing all your computations in its completion. 000040 Figure 7-2\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


