Question: first drop down box: with options of : range or specific level second drop down box: with options of :financial or business third drop down
 first drop down box:
first drop down box: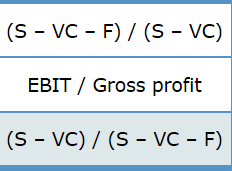 with options of : range or specific level
with options of : range or specific level
second drop down box: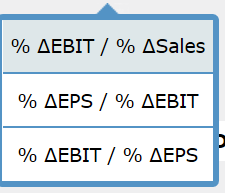 with options of :financial or business
with options of :financial or business
third drop down box: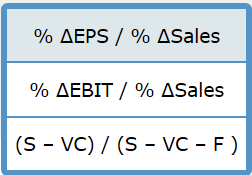 with options of :fixed or variable
with options of :fixed or variable
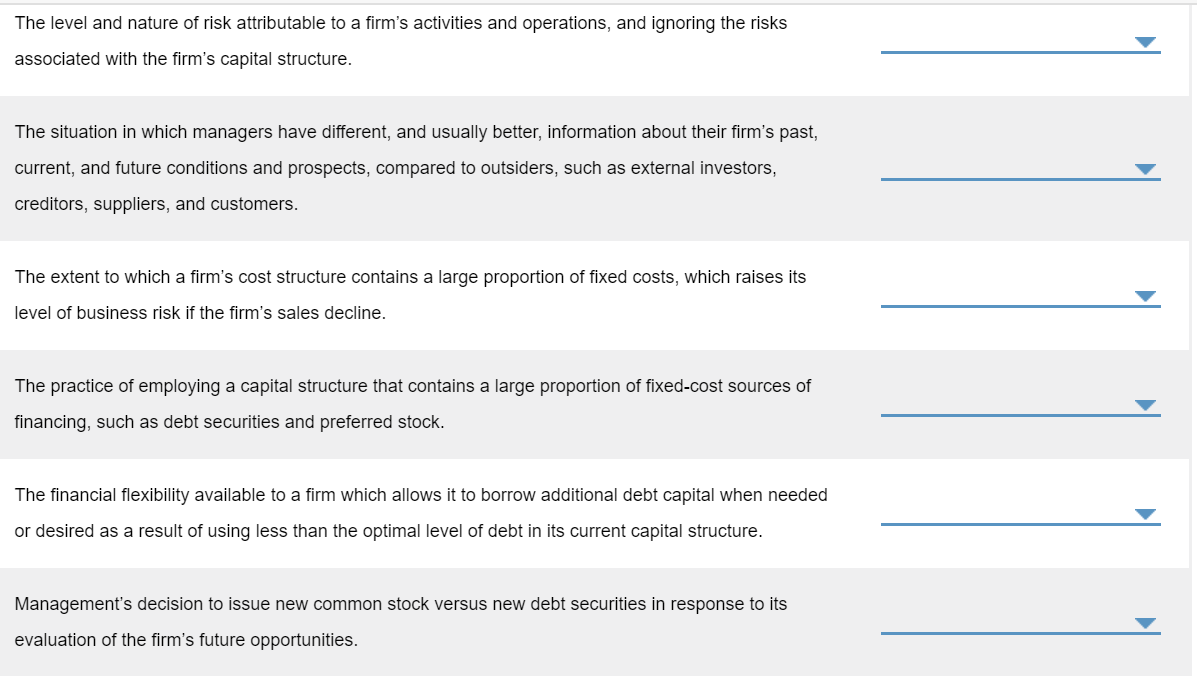
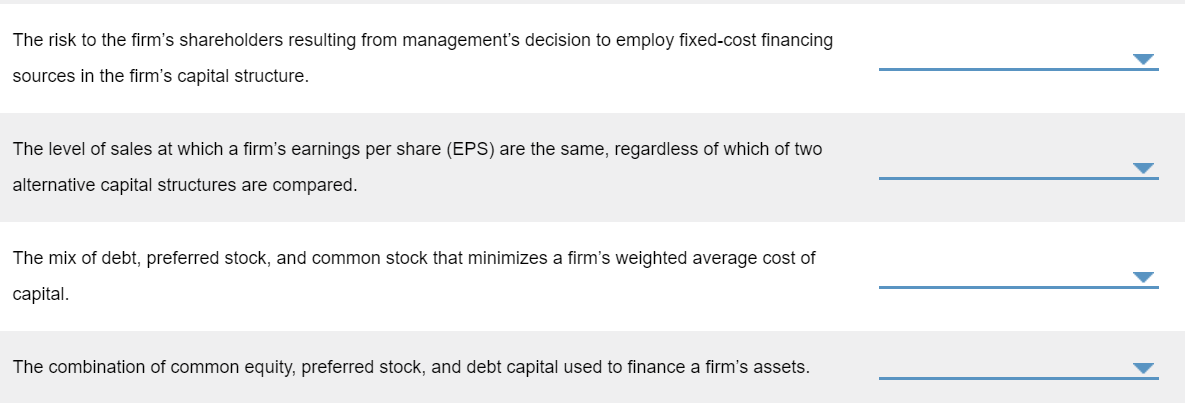
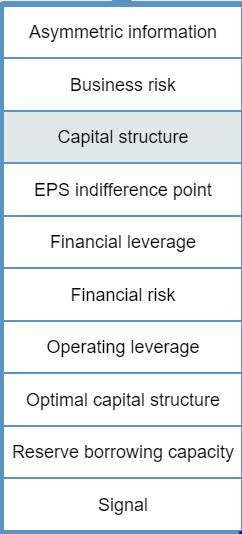
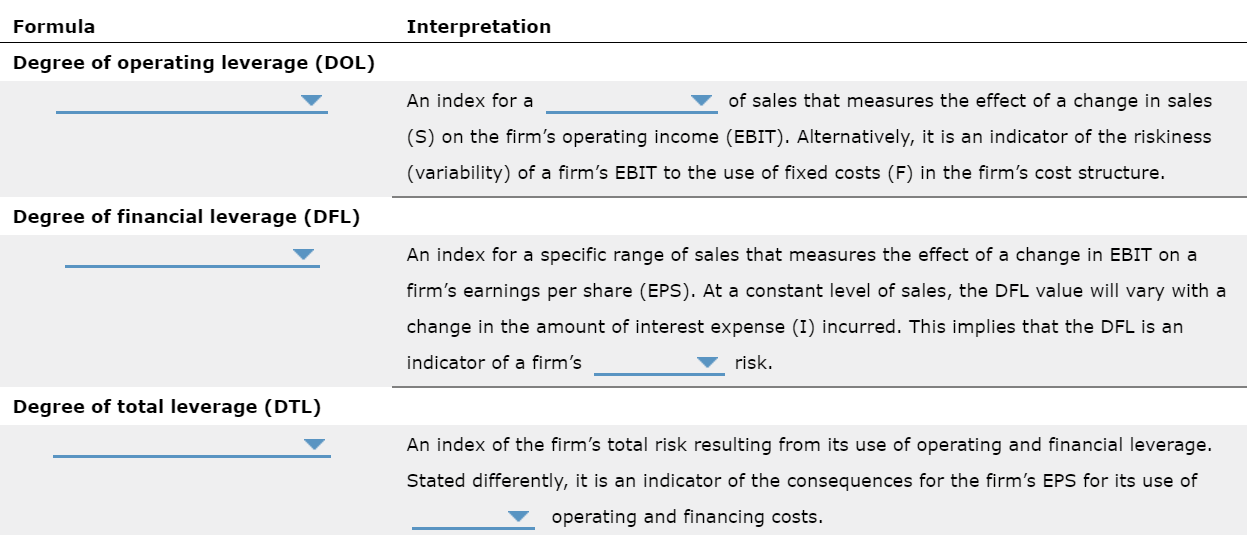
The level and nature of risk attributable to a firm's activities and operations, and ignoring the risks associated with the firm's capital structure. The situation in which managers have different, and usually better, information about their firm's past, current, and future conditions and prospects, compared to outsiders, such as external investors, creditors, suppliers, and customers. The extent to which a firm's cost structure contains a large proportion of fixed costs, which raises its level of business risk if the firm's sales decline. The practice of employing a capital structure that contains a large proportion of fixed-cost sources of financing, such as debt securities and preferred stock. The financial flexibility available to a firm which allows it to borrow additional debt capital when needed or desired as a result of using less than the optimal level of debt in its current capital structure. Management's decision to issue new common stock versus new debt securities in response to its evaluation of the firm's future opportunities. The risk to the firm's shareholders resulting from management's decision to employ fixed-cost financing sources in the firm's capital structure. The level of sales at which a firm's earnings per share (EPS) are the same, regardless of which of two alternative capital structures are compared. The mix of debt, preferred stock, and common stock that minimizes a firm's weighted average cost of capital. The combination of common equity, preferred stock, and debt capital used to finance a firm's assets. Asymmetric information Business risk Capital structure EPS indifference point Financial leverage Financial risk Operating leverage Optimal capital structure Reserve borrowing capacity Signal Formula Interpretation Degree of operating leverage (DOL) An index for a of sales that measures the effect of a change in sales (S) on the firm's operating income (EBIT). Alternatively, it is an indicator of the riskiness (variability) of a firm's EBIT to the use of fixed costs (F) in the firm's cost structure. Degree of financial leverage (DFL) An index for a specific range of sales that measures the effect of a change in EBIT on a firm's earnings per share (EPS). At a constant level of sales, the DFL value will vary with a change in the amount of interest expense (I) incurred. This implies that the DFL is an indicator of a firm's risk. Degree of total leverage (DTL) An index of the firm's total risk resulting from its use of operating and financial leverage. Stated differently, it is an indicator of the consequences for the firm's EPS for its use of operating and financing costs. (S - VC - F) / (S - VC) EBIT / Gross profit (5 - VC) / (S VC F) % / % Sales % PS / % % / % PS % AEPS/ % ASales % AEBIT / % ASales (S - VC)/(5 - VC - F)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


