Question: First Set of Sequential Activities - Match the Dunn activities to the activity header of Shi's framework. Activity from Shi:1. Policy Formulation Stage (Agenda Setting
First Set of Sequential Activities - Match the Dunn activities to the activity header of Shi's framework. Activity from Shi:1. Policy Formulation Stage (Agenda Setting and Legislation Development)Match activities From Dunn:
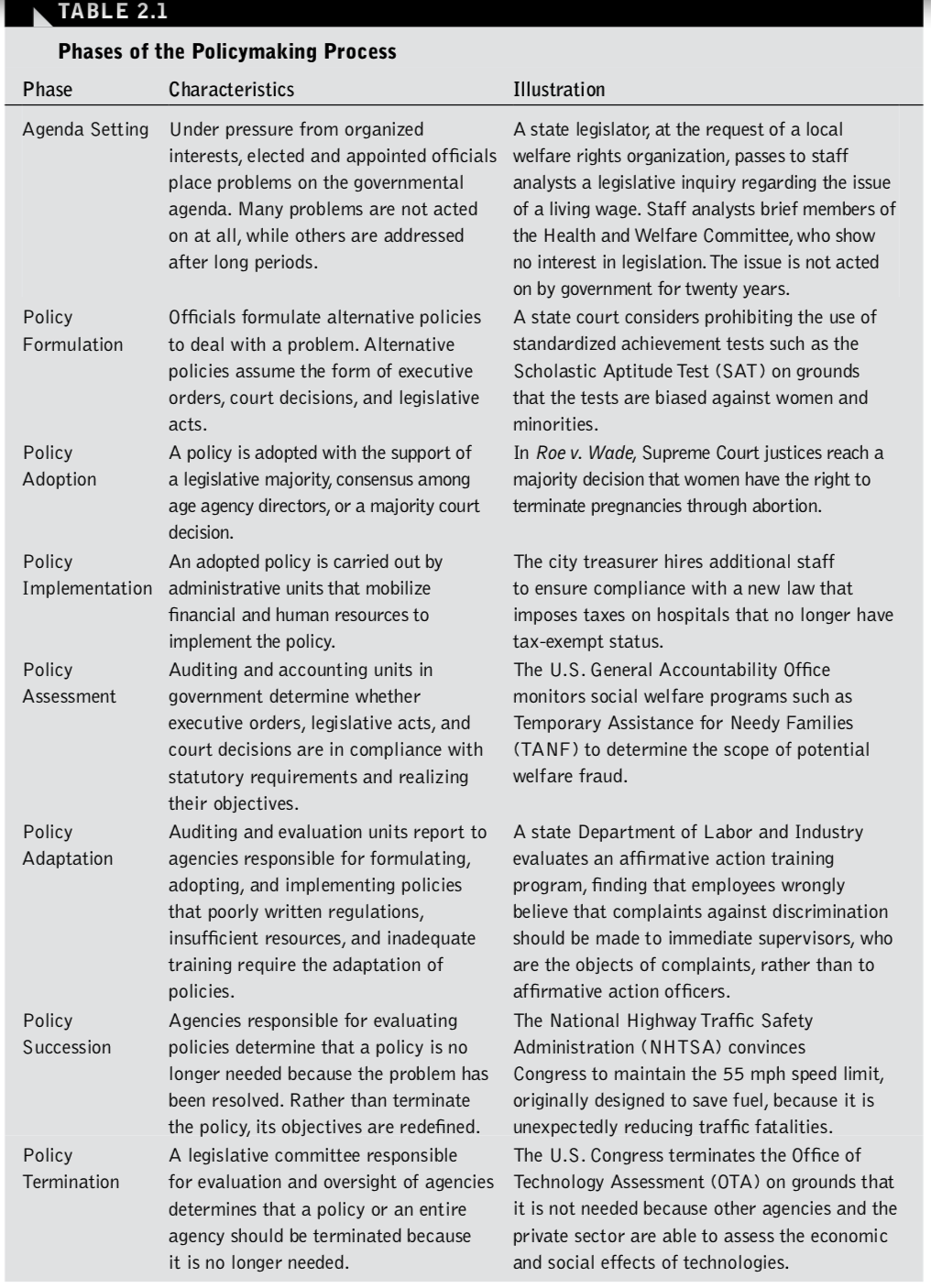
TABLE 2.1 Phases of the Policymaking Process Phase Characteristics Illustration Agenda Setting Policy Formulation Policy Adoption Policy Implementation Policy Assessment Policy Adaptation Policy Succession Policy Termination Under pressure from organized interests, elected and appointed officials place problems on the governmental agenda. Many problems are not acted on at all, while others are addressed after long periods. Officials formulate alternative policies to deal with a problem. Alternative policies assume the form of executive orders, court decisions, and legislative acts. A policy is adopted with the support of a legislative majority, consensus among age agency directors, or a majority court decision. An adopted policy is carried out by administrative units that mobilize financial and human resources to implement the policy. Auditing and accounting units in government determine whether executive orders, legislative acts, and court decisions are in compliance with statutory requirements and realizing their objectives. Auditing and evaluation units report to agencies responsible for formulating, adopting, and implementing policies that poorly written regulations, insufficient resources, and inadequate training require the adaptation of policies. Agencies responsible for evaluating policies determine that a policy is no longer needed because the problem has been resolved. Rather than terminate the policy, its objectives are redefined. A legislative committee responsible for evaluation and oversight of agencies determines that a policy or an entire agency should be terminated because it is no longer needed. A state legislator, at the request of a local welfare rights organization, passes to staff analysts a legislative inquiry regarding the issue of a living wage. Staff analysts brief members of the Health and Welfare Committee, who show no interest in legislation. The issue is not acted on by government for twenty years. A state court considers prohibiting the use of standardized achievement tests such as the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) on grounds that the tests are biased against women and minorities. In Roe v. Wade, Supreme Court justices reach a majority decision that women have the right to terminate pregnancies through abortion. The city treasurer hires additional staff to ensure compliance with a new law that imposes taxes on hospitals that no longer have tax-exempt status. The U.S. General Accountability Office monitors social welfare programs such as Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) to determine the scope of potential welfare fraud. A state Department of Labor and Industry evaluates an affirmative action training program, finding that employees wrongly believe that complaints against discrimination should be made to immediate supervisors, who are the objects of complaints, rather than to affirmative action officers. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) convinces Congress to maintain the 55 mph speed limit, originally designed to save fuel, because it is unexpectedly reducing traffic fatalities. The U.S. Congress terminates the Office of Technology Assessment (OTA) on grounds that it is not needed because other agencies and the private sector are able to assess the economic and social effects of technologies