Question: flud for the threc - dimensional case. 2 . 2 . The container of Fig. 2 . 4 4 holds water and air as shown.
flud for the threcdimensional case.
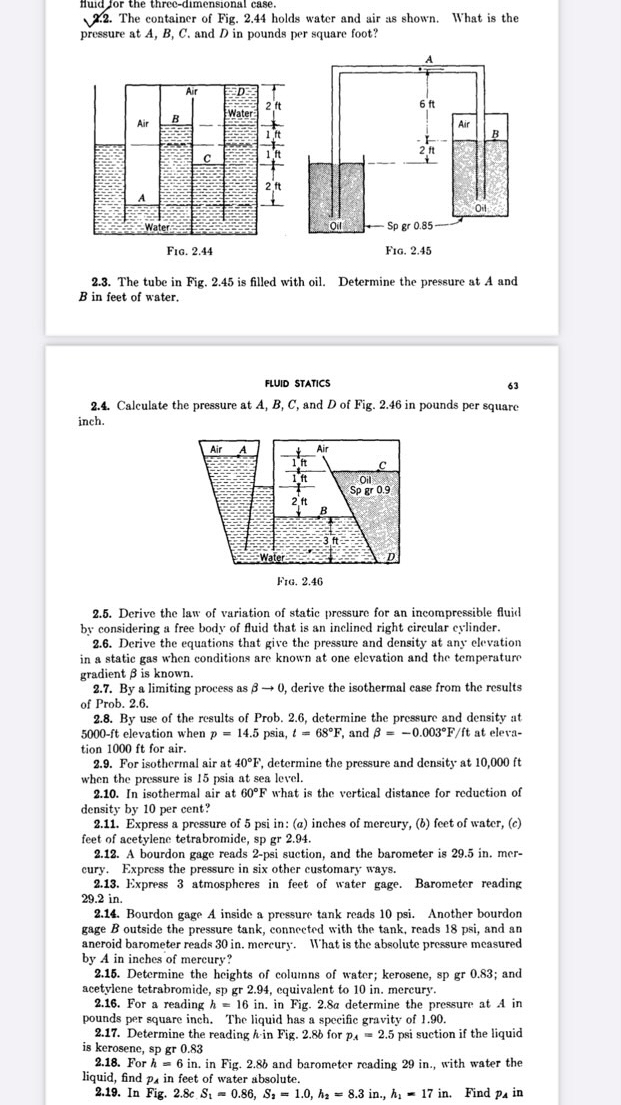
The container of Fig. holds water and air as shown. What is the
pressure at and in pounds per square foot?
The tube in Fig. is flled with oll. Determine the pressure at A and
in feet of water.
FLUID STATICS
Calculate the pressure at and of Fig. in pounds per square
inch.
Derive the law of variation of static pressure for an incompressible fluid
by considering a free body of fluid that is an inclined right circular cylinder.
Derive the equations that give the pressure and density at any elevation
in a static gas when conditions are known at one elevation and the temperature
gradient is known.
By a limiting process as derive the isothermal case from the results
of Prob.
By use of the results of Prob. determine the pressure and density at
ft elevation when and at eleva
tion ft for air.
For isothermal air at determine the pressure and density at
when the pressure is psia at sea level.
In isothermal air at what is the vertical distance for reduction of
density by per cent?
Express a pressure of psi in: a inches of mercury, b feet of water, c
feet of acetylene tetrabromide, sp gr
A bourdon gage reads psi suction, and the barometer is in mer
cury. Express the pressure in six other customary ways.
Express atmospheres in feet of water gage. Barometer reading
in
Bourdon gage A inside a pressure tank reads psi Another bourdon
gage outside the pressure tank, connected with the tank, reads psi and an
aneroid barometer reads in mercury. What is the absolute pressure measured
by in inches of mercury?
Determine the heights of columns of water; kerosene, ; and
acetylene tetrabromide, sp gr equivalent to in mercury.
For a reading in Fig. a determine the pressure at in
pounds per square inch. The liquid has a specific gravity of
Determine the reading in Fig. for psi suction if the liquid
is kerosene, sp gr
For in Fig. and barometer reading in with water the
liquid, find in feet of water absolute
In Fig. in Find in
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


