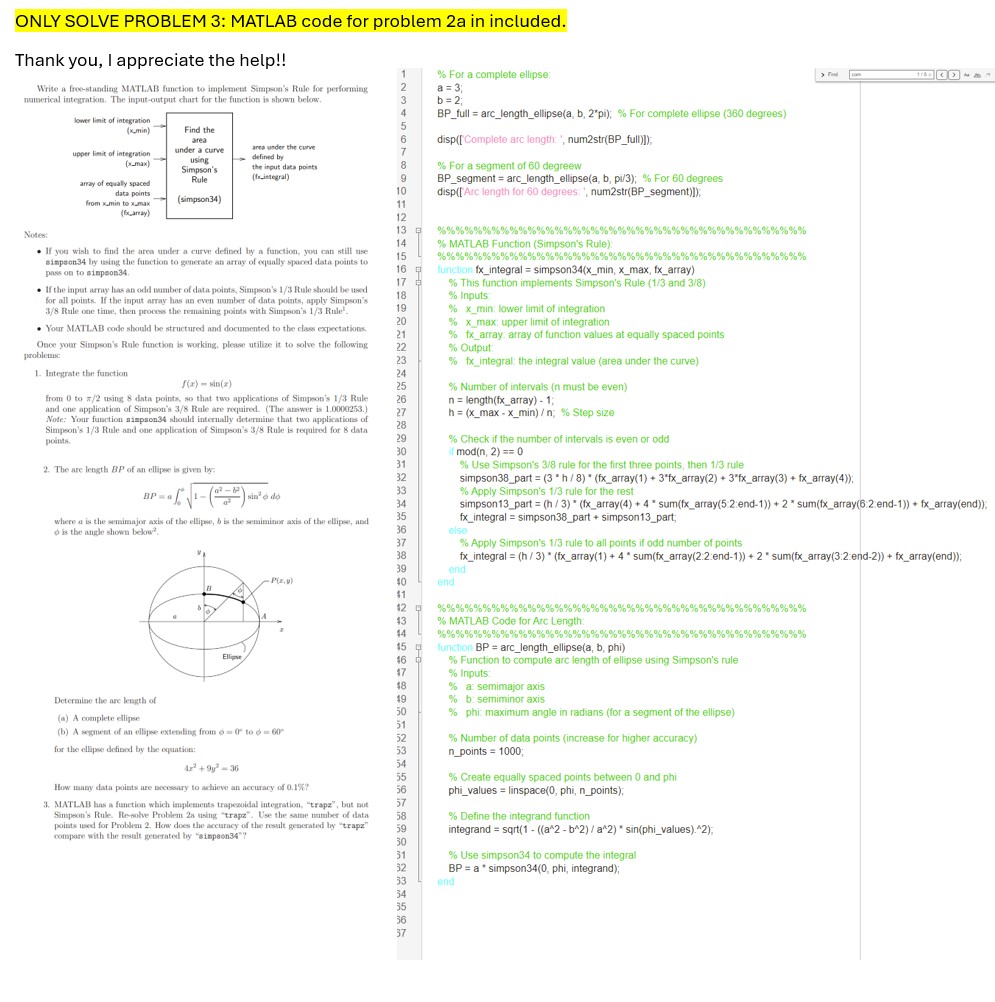
Question: % For a complete ellipse: a = 3 ; b = 2 ; BP _ full = arc _ length _ ellipse ( a ,
For a complete ellipse:
a ;
b ;
BPfull arclengthellipsea bpi; For complete ellipse degrees
dispComplete arc length: numstrBPfull;
For a segment of degreew
BPsegment arclengthellipsea b pi; For degrees
dispArc length for degrees: numstrBPsegment;
MATLAB Function Simpsons Rule:
function fxintegral simpsonxmin, xmax, fxarray
This function implements Simpson's Rule and
Inputs:
xmin: lower limit of integration
xmax: upper limit of integration
fxarray: array of function values at equally spaced points
Output:
fxintegral: the integral value area under the curve
Number of intervals n must be even
n lengthfxarray;
h xmax xmin n; Step size
Check if the number of intervals is even or odd
if modn
Use Simpson's rule for the first three points, then rule
simpsonpart h fxarrayfxarrayfxarray fxarray;
Apply Simpson's rule for the rest
simpsonpart h fxarray sumfxarray::end sumfxarray::end fxarrayend;
fxintegral simpsonpart simpsonpart;
else
Apply Simpson's rule to all points if odd number of points
fxintegral h fxarray sumfxarray::end sumfxarray::end fxarrayend;
end
end
MATLAB Code for Arc Length:
function BP arclengthellipsea b phi
Function to compute arc length of ellipse using Simpson's rule
Inputs:
a: semimajor axis
b: semiminor axis
phi: maximum angle in radians for a segment of the ellipse
Number of data points increase for higher accuracy
npoints ;
Create equally spaced points between and phi
phivalues linspace phi, npoints;
Define the integrand function
integrand sqrta b a sinphivalues;
Use simpson to compute the integral
BP a simpson phi, integrand;
end
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


