Question: For a linear polymer molecule, the total chain length L depends on the bond length between chain atoms d, the total number of bonds in

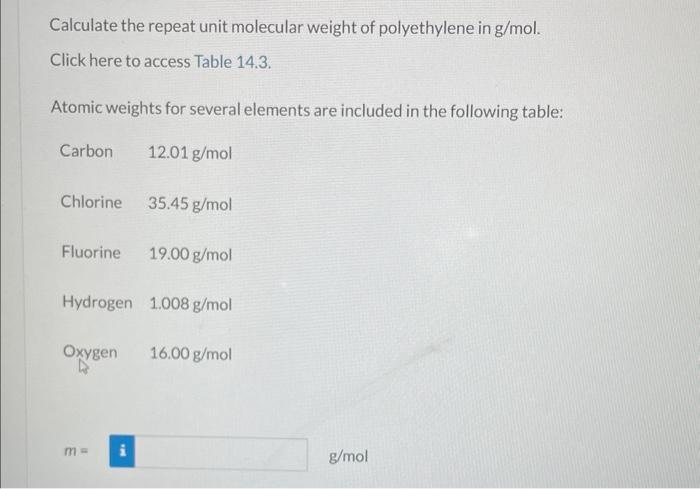

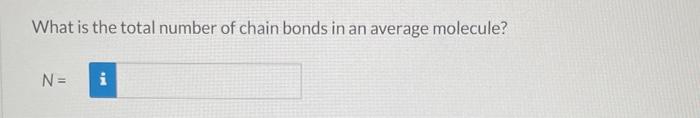
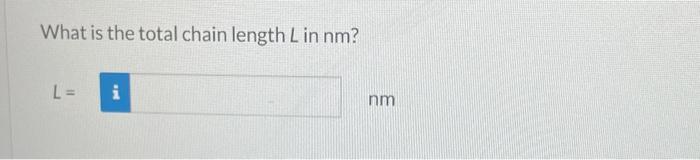
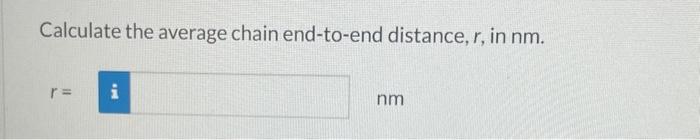
For a linear polymer molecule, the total chain length L depends on the bond length between chain atoms d, the total number of bonds in the molecule N, and the angle between adjacent backbone chain atoms , as follows: L=Ndsin(2) Furthermore, the average end-to-end distance for a series of polymer molecules r in Figure 14.6 is equal to r=dN Calculate the repeat unit molecular weight of polyethylene in g/mol. Click here to access Table 14.3. Atomic weights for several elements are included in the following table: Carbon 12.01g/mol Chlorine 35.45g/mol Fluorine 19.00g/mol Hydrogen 1.008g/mol Oxygen 16.00g/mol m= g/mol What is the degree of polymerization of this polymer if the number-average molecular weight is 400000g/mol ? What is the total number of chain bonds in an average molecule? N= What is the total chain length L in nm ? L= Calculate the average chain end-to-end distance, r, in nm. r=nm
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


