Question: For each node u in an undirected graph G = (V, E), let q(u) be the sum of the squares of the degrees of us
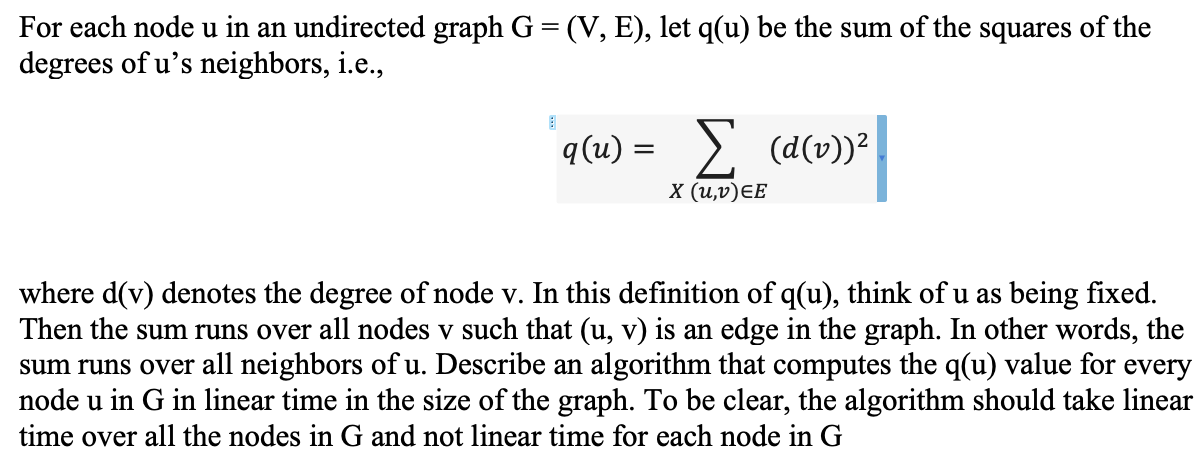
For each node u in an undirected graph G = (V, E), let q(u) be the sum of the squares of the degrees of us neighbors, i.e., q(u) = 2 (d(v))2 X (u,v)EE where d(v) denotes the degree of node v. In this definition of q(u), think of u as being fixed. Then the sum runs over all nodes v such that (u, v) is an edge in the graph. In other words, the sum runs over all neighbors of u. Describe an algorithm that computes the q(u) value for every node u in G in linear time in the size of the graph. To be clear, the algorithm should take linear time over all the nodes in G and not linear time for each node in G For each node u in an undirected graph G = (V, E), let q(u) be the sum of the squares of the degrees of us neighbors, i.e., q(u) = 2 (d(v))2 X (u,v)EE where d(v) denotes the degree of node v. In this definition of q(u), think of u as being fixed. Then the sum runs over all nodes v such that (u, v) is an edge in the graph. In other words, the sum runs over all neighbors of u. Describe an algorithm that computes the q(u) value for every node u in G in linear time in the size of the graph. To be clear, the algorithm should take linear time over all the nodes in G and not linear time for each node in G
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


