Question: For example, in cell D21 enter the formula = D14. Notes: In the text, variances are always displayed as positive numbers. To accomplish this, you
For example, in cell D21 enter the formula "= D14".
Notes:
In the text, variances are always displayed as positive numbers. To accomplish this, you can use the ABS() function in Excel. For example, the formula in cell B25 would be "=ABS(F21F22)".
- Cells C25 through C27, C34 through C36, and C43 through C45 already contain formulas to compute and display whether variances are Favorable or Unfavorable. Do not enter data or formulas into those cellsif you do, you will overwrite these formulas.
- After entering formulas in all of the cells that contained question marks, verify that the amounts match the numbers in the example in the text.
Check your worksheet by changing the direct materials standard quantity in cell B6 to 2.9 pounds, the direct labor standard quantity in cell B7 to 0.6 hours, and the variable manufacturing overhead in cell B8 to 0.6 hours. The materials spending variance should now be $1,500 U, the labor spending variance should now be $3,720 F, and the variable overhead spending variance should now be $60 F. If you do not get these answers, find the errors in your worksheet and correct them.
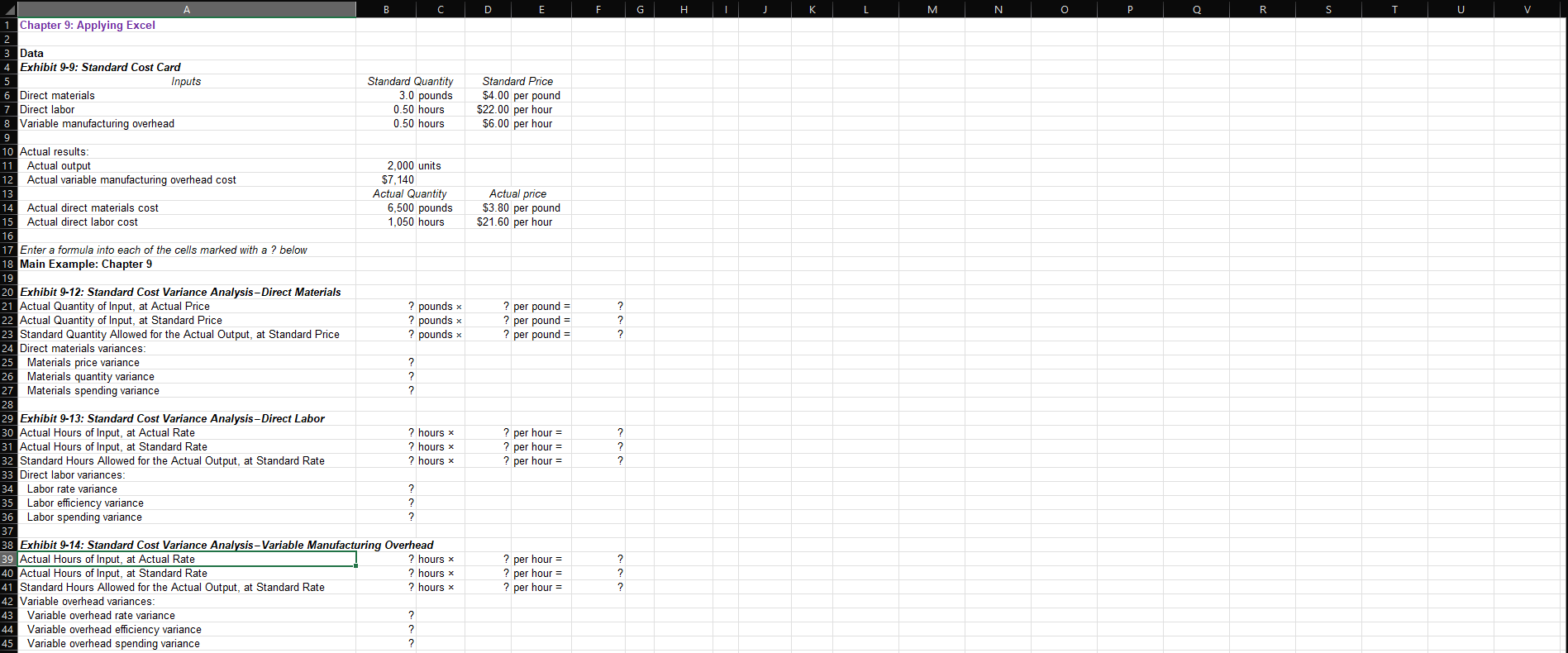
B D F G H O Q R Chapter 9: Applying Excel Data Exhibit 9-9: Standard Cost Card Inputs Standard Quantity Standard Price Direct materials 3.0 pounds $4.00 per pound Direct labor 0.50 hours $22.00 per hour Variable manufacturing overhead 0.50 hours $6.00 per hour Actual results: Actual output 2,000 units Actual variable manufacturing overhead cost $7, 140 Actual Quantity Actual price Actual direct materials cost 6,500 pounds $3.80 per pound Actual direct labor cost 1,050 hours $21.60 per hour Enter a formula into each of the cells marked with a ? below Main Example: Chapter 9 Exhibit 9-12: Standard Cost Variance Analysis-Direct Materials Actual Quantity of Input, at Actual Price ? pounds x ? per pound = Actual Quantity of Input, at Standard Price ? pounds x ? per pound = Standard Quantity Allowed for the Actual Output, at Standard Price ? pounds x ? per pound = Direct materials variances Materials price variance Materials quantity variance Materials spending variance Exhibit 9-13: Standard Cost Variance Analysis-Direct Labor Actual Hours of Input, at Actual Rate ? hours x ? per hour = Actual Hours of Input, at Standard Rate ? hours x ? per hour = Standard Hours Allowed for the Actual Output, at Standard Rate ? hours x ? per hour = Direct labor variances: Labor rate variance Labor efficiency variance Labor spending variance Exhibit 9-14: Standard Cost Variance Analysis-Variable Manufacturing Overhead Actual Hours of Input, at Actual Rate ? hours * ? per hour = Actual Hours of Input, at Standard Rate ? hours x ? per hour = Standard Hours Allowed for the Actual Output, at Standard Rate ? hours x ?per hour = Variable overhead variances Variable overhead rate variance ? Variable overhead efficiency variance Variable overhead spending variance
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


