Question: = For In-class problem #1, we calculated the minimum temperature of air that could be blown over a sheet of Forming rolls glass that could
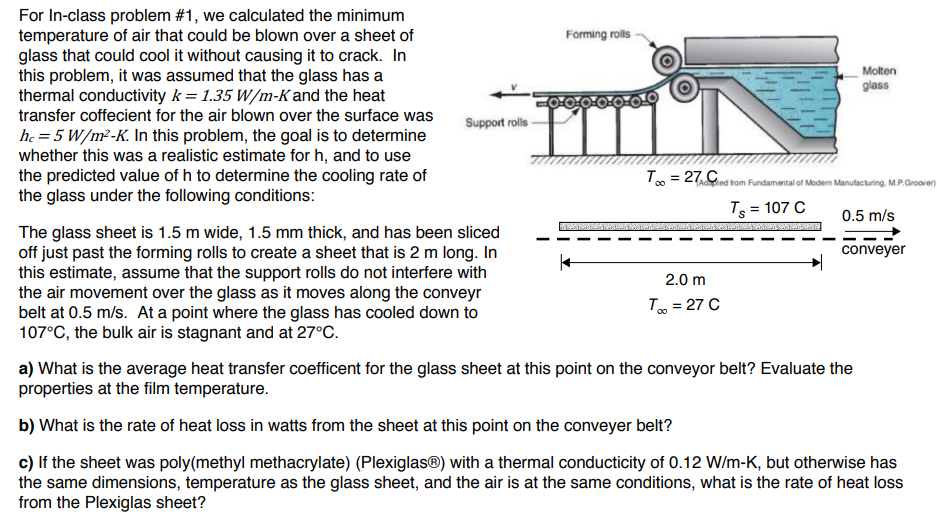
= For In-class problem #1, we calculated the minimum temperature of air that could be blown over a sheet of Forming rolls glass that could cool it without causing it to crack. In this problem, it was assumed that the glass has a Molten glass thermal conductivity k = 1.35 W/m-K and the heat transfer coffecient for the air blown over the surface was Support rolls he = 5 W/m2-K. In this problem, the goal is to determine whether this was a realistic estimate for h, and to use the predicted value of h to determine the cooling rate of To = 27C Adried from Fundamental of Modern Manufacturing, M.P.Groover) the glass under the following conditions: Ts = 107 C 0.5 m/s The glass sheet is 1.5 m wide, 1.5 mm thick, and has been sliced off just past the forming rolls to create a sheet that is 2 m long. In conveyer this estimate, assume that the support rolls do not interfere with 2.0 m the air movement over the glass as it moves along the conveyr belt at 0.5 m/s. At a point where the glass has cooled down to To = 27C 107C, the bulk air is stagnant and at 27C. a) What is the average heat transfer coefficent for the glass sheet at this point on the conveyor belt? Evaluate the properties at the film temperature. b) What is the rate of heat loss in watts from the sheet at this point on the conveyer belt? c) If the sheet was poly(methyl methacrylate) (Plexiglas) with a thermal conducticity of 0.12 W/m-K, but otherwise has the same dimensions, temperature as the glass sheet, and the air is at the same conditions, what is the rate of heat loss from the Plexiglas sheet
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


