Question: For P(harsh) = 0.2, the optimal order size is units for an ex (Round to the nearest whole number as nee For P(harsh) = 0.4,
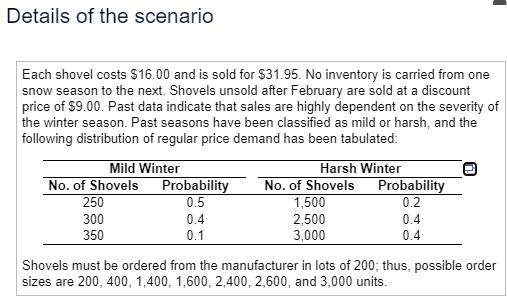
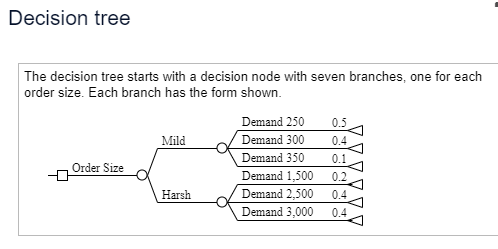
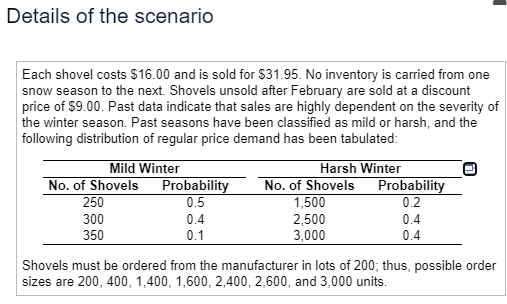
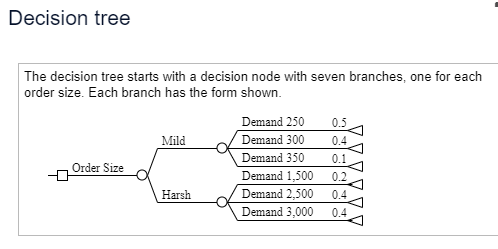
For P(harsh) = 0.2, the optimal order size is units for an ex (Round to the nearest whole number as nee For P(harsh) = 0.4, the optimal order size is in ex (Round to the nearest whole number as nee 200 For P(harsh) = 0.6, the optimal order size is 3,000 in ex (Round to the nearest whole number as nee 1,600 For P(harsh) = 0.8, the optimal order size is in ex (Round to the nearest whole number as nee 400 Choose the correct graph below. 2.600 O A. OB Profit 1.400 30,000- 30.0 a 2,400A hardware store must decide how many snow shovels to order for the coming snow season. Perform a sensitivity analysis and find the optimal order quantity and optimal expected profit for probabilities of a harsh winter ranging from 0.2 to 0.8 in increments of 0.2. Plot optimal expected profit as a function of the probability of a harsh winter. Click here to view the details of the scenario. Click here to view the decision tree. For P(harsh) = 0.2, the optimal order size is units for an expected profit of $ (Round to the nearest whole number as needed.) For P(harsh) = 0.4, the optimal order size is units for an expected profit of $ (Round to the nearest whole number as needed.) For P(harsh) = 0.6, the optimal order size is units for an expected profit of $ (Round to the nearest whole number as needed.) For P(harsh) = 0.8, the optimal order size is units for an expected profit of $ (Round to the nearest whole number as needed.) Choose the correct graph below. O A. OB. O C. OD. A Profit Profit 30.000- O A Profit Profit 30,000- 30.000- 30.000- O P P PDetails of the scenario Each shovel costs $16.00 and is sold for $31.95. No inventory is carried from one snow season to the next. Shovels unsold after February are sold at a discount price of $9.00. Past data indicate that sales are highly dependent on the severity of the winter season. Past seasons have been classified as mild or harsh, and the following distribution of regular price demand has been tabulated: Mild Winter Harsh Winter No. of Shovels Probability No. of Shovels Probability 250 0.5 1,500 0.2 300 0.4 2,500 0.4 350 0.1 3,000 0.4 Shovels must be ordered from the manufacturer in lots of 200; thus, possible order sizes are 200, 400, 1,400, 1,600, 2,400, 2,600, and 3,000 units.Decision tree The decision tree starts with a decision node with seven branches, one for each order size. Each branch has the form shown. Demand 250 0.5 Mild Demand 300 0.4 Demand 350 0.1 Order Size Demand 1,500 0.2 Harsh Demand 2,500 0.4 Demand 3,000 0.4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


