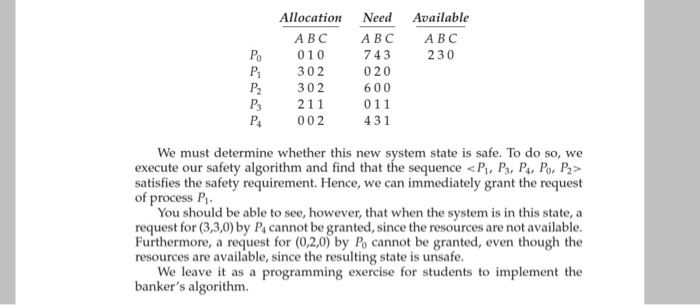
Question: For this project, you will write a multithreaded program that implements the bankers algorithm discussed in Section 7.5.3. Several customers request and release resources from


7.5.3 Banker's Algorithm allocation system with multiple instances of each resounce type. The deadlock avoidance algorithm that we describe next is applicable to such a system but scheme. This algorithm is comsmonly known as the banker's algorithm. The name was chosen because the algorithm could be edin a banking sysbemh to ensure that the bank never Figure 7.8 An unsafe state in a resource-allocation graph allocated its available cash in such a way that it could no longer satisfy the needs of all its castomers When a new process enters the system, it mast declare the maximum number of instances of each nsource type that it may need. This namber may not exceed the total number of resources in the system. When a user reqaests a set of resources, the system must determine whether the allocation of these resources will leave the system in a safe state, If it will, the resources are allocated; otherwise, the process mast wait until some other process releases enough resources Several data structures must be maintained to algorithm. These data structures encode the state of the resource-allocation system. We need the following data structures, where n is the number of processes in the system and m is the namber of resource types: Available. Avector of indicates the umber of availableresources equals k, then instances of resource type R are available . Max An x m matrix defines the maximum demand of each pricess. If MariIA equals k, then process P may request at most k instances of resource type R Allocation. An " m matrix defines the number of resources of each type currently allocated to each process. If Allocation(411 equalsk, then process P is currently allocated k instances of resource type R * * Need. An " matrix indicates the remaining resource need of each process. If Need ul equals k, then process P may need k more instances of resource type Ry to complete its task Note that Needlll equals Max These data structures vary over time in both size and value, To simplify the of the banker's algoeithm, we next establis some notation Lt X and Y be vectors of length n. We say that Xs Y if and only if Xil Yli] for all i : 1, 2 . For example, if X: (1,732) and Y (Q321), then X. In addition, Y X iIY and Y X. We can treat each rove in the matrioes Allocation and Need as vectors and refer to them as Allocation, and Need The vector Allocation specifies the resources currently allocabed to process P, the vector Nend, specises the additional resounces that process P may still request to complete its task We can now present the algorithm for finding out whether or not a system is in a safe state. This algorithm can be described as follows 1 Let work and Finish be vectors of length m and st, respectively. Initialize Work "Anailable and Finish(f]-false for i-0,1,-N-1. 2 Find an index i such that both a. FiniskM=false b. Need, s Work
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


