Question: #from ..exceptions import Empty class LinkedQueue: FIFO queue implementation using a singly linked list for storage. #-------------------------- nested _Node class -------------------------- class _Node: Lightweight, nonpublic
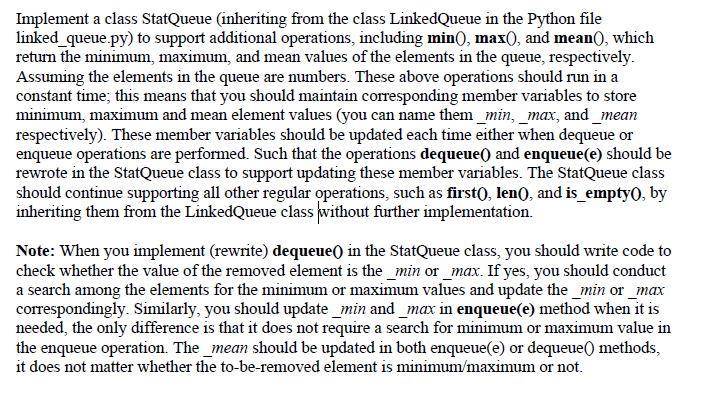
#from ..exceptions import Empty
class LinkedQueue:
"""FIFO queue implementation using a singly linked list for storage."""
#-------------------------- nested _Node class --------------------------
class _Node:
"""Lightweight, nonpublic class for storing a singly linked node."""
__slots__ = '_element', '_next' # streamline memory usage
def __init__(self, element, next):
self._element = element
self._next = next
#------------------------------- queue methods -------------------------------
def __init__(self):
"""Create an empty queue."""
self._head = None
self._tail = None
self._size = 0 # number of queue elements
def __len__(self):
"""Return the number of elements in the queue."""
return self._size
def is_empty(self):
"""Return True if the queue is empty."""
return self._size == 0
def first(self):
"""Return (but do not remove) the element at the front of the queue.
Raise Empty exception if the queue is empty.
"""
if self.is_empty():
print('Queue is empty')
return ""
#raise Empty('Queue is empty')
return self._head._element # front aligned with head of list
def dequeue(self):
"""Remove and return the first element of the queue (i.e., FIFO).
Raise Empty exception if the queue is empty.
"""
if self.is_empty():
print('Queue is empty')
return ""
#raise Empty('Queue is empty')
answer = self._head._element
self._head = self._head._next
self._size -= 1
if self.is_empty(): # special case as queue is empty
self._tail = None # removed head had been the tail
return answer
def enqueue(self, e):
"""Add an element to the back of queue."""
newest = self._Node(e, None) # node will be new tail node
if self.is_empty():
self._head = newest # special case: previously empty
else:
self._tail._next = newest
self._tail = newest # update reference to tail node
self._size += 1
def disp(self): #by XJ
next = self._head
while next != None:
print(next._element)
next = next._next
if __name__ == '__main__':
lQueue = LinkedQueue()
print(lQueue.is_empty())
lQueue.enqueue(1)
lQueue.enqueue(2)
lQueue.enqueue(3)
print(lQueue.is_empty())
lQueue.disp()
Implement a class StatQueue inheriting from the class LinkedQueue in the Python file linked_queue.py) to support additional operations, including min(), max(), and mean(), which return the minimum, maximum, and mean values of the elements in the queue, respectively. Assuming the elements in the queue are numbers. These above operations should run in a constant time; this means that you should maintain corresponding member variables to store minimum, maximum and mean element values (you can name them_min, _max, and _mean respectively). These member variables should be updated each time either when dequeue or enqueue operations are performed. Such that the operations dequeue() and enqueue(e) should be rewrote in the StatQueue class to support updating these member variables. The StatQueue class should continue supporting all other regular operations, such as first(), len(), and is_emptyo, by inheriting them from the LinkedQueue class without further implementation. Note: When you implement (rewrite) dequeue() in the StatQueue class, you should write code to check whether the value of the removed element is the_min or_max. If yes, you should conduct a search among the elements for the minimum or maximum values and update the _min or _max correspondingly. Similarly, you should update _min and_max in enqueue(e) method when it is needed, the only difference is that it does not require a search for minimum or maximum value in the enqueue operation. The _mean should be updated in both enqueue(e) or dequeue() methods, it does not matter whether the to-be-removed element is minimum/maximum or not. Implement a class StatQueue inheriting from the class LinkedQueue in the Python file linked_queue.py) to support additional operations, including min(), max(), and mean(), which return the minimum, maximum, and mean values of the elements in the queue, respectively. Assuming the elements in the queue are numbers. These above operations should run in a constant time; this means that you should maintain corresponding member variables to store minimum, maximum and mean element values (you can name them_min, _max, and _mean respectively). These member variables should be updated each time either when dequeue or enqueue operations are performed. Such that the operations dequeue() and enqueue(e) should be rewrote in the StatQueue class to support updating these member variables. The StatQueue class should continue supporting all other regular operations, such as first(), len(), and is_emptyo, by inheriting them from the LinkedQueue class without further implementation. Note: When you implement (rewrite) dequeue() in the StatQueue class, you should write code to check whether the value of the removed element is the_min or_max. If yes, you should conduct a search among the elements for the minimum or maximum values and update the _min or _max correspondingly. Similarly, you should update _min and_max in enqueue(e) method when it is needed, the only difference is that it does not require a search for minimum or maximum value in the enqueue operation. The _mean should be updated in both enqueue(e) or dequeue() methods, it does not matter whether the to-be-removed element is minimum/maximum or not
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


