Question: from the book exploring strategy 9th edition using the case study: Vodafone: developing a total communications strategy in the UK market' identify the following: environmental
from the book exploring strategy "9th edition" using the case study: Vodafone: developing a total communications strategy in the UK market'
identify the following:
environmental factors that impact the industry (based on the PESTEL framework and the 5 forces model of Porter)
the main types of strategies used by Vodafone.

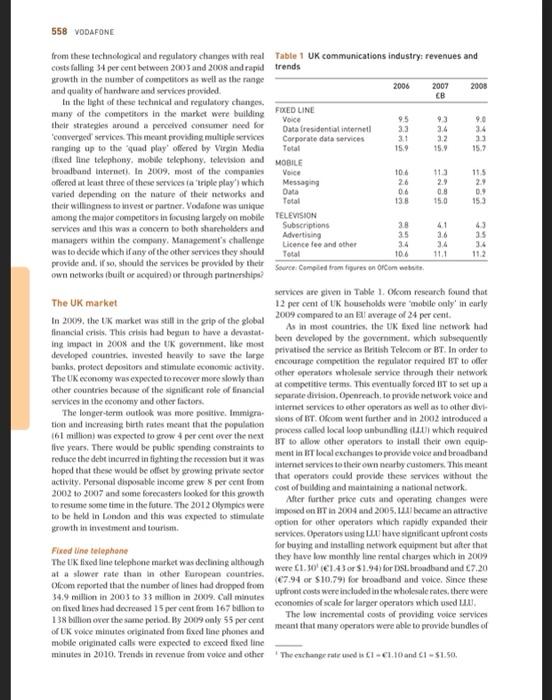
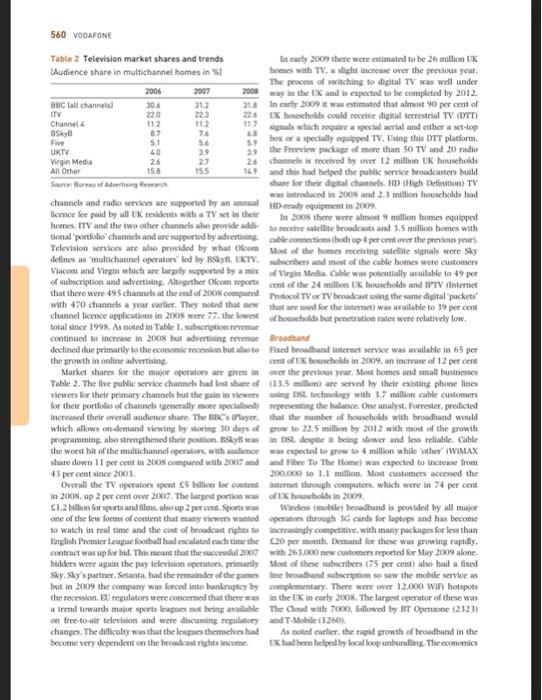
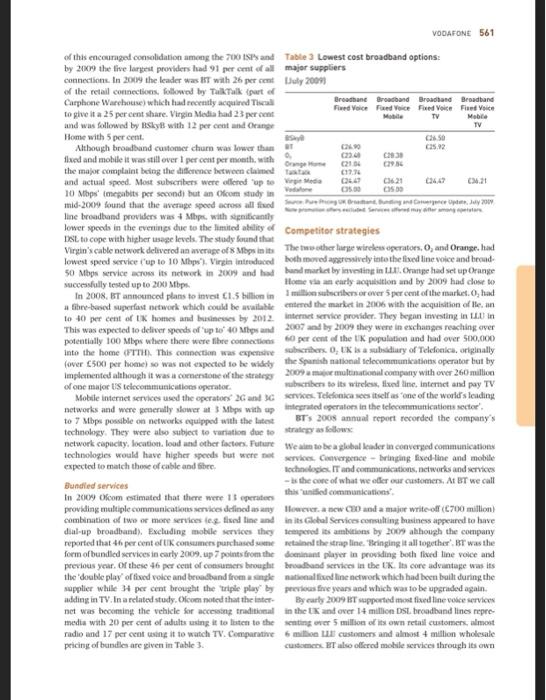
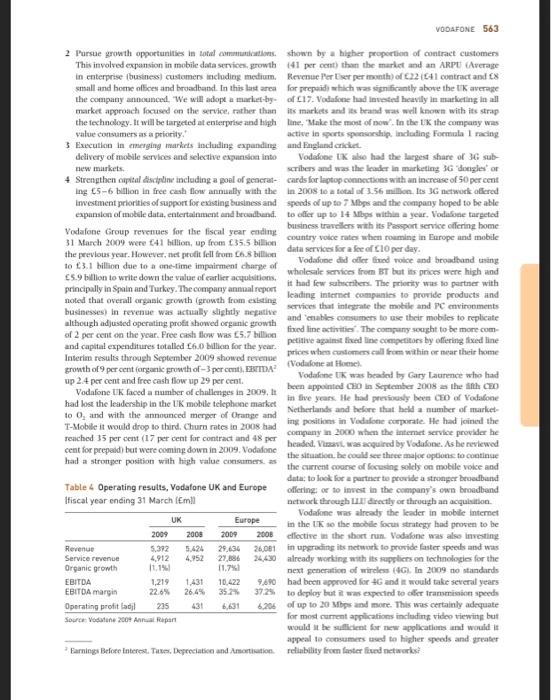
Instructions Students whom are not happy with the number of EVP points obtained so far, are welcome to read this case study and analyze it: 'Vodafone: developing a total communications strategy in the UK market' (p. 557-564 from the course book). In the case study, identify the following: environmental factors that impact the industry (based on the PESTEL framework and the 5 forces model of Porter) the main types of strategies used by Vodafone. CASE STUDY Vodafone: developing a total communications strategy in the UK market Roger A. Strang We will be the communication leader in an incrony comme world Vodafone website 2 In 2009, Vodafone, the world's largest mobile dephone operator by revenue was under increasing pressure develop a strategy to ensure leadership in the rapidly growing market for high speed internet services in its hostie market. The challenge for the company was that the development of new technologies for voice, duta and video transmission was blurring the boundaries among traditional industries and forcing reconsideration of what was required for a strategy of total communications This growth in demand for new services had attracted the interest not only of Vodafone's traditional competitors in the telephone industry, but also from other communica tions companies such as Virgin Media (the largest cable operator in the UX) and Sky Broadcasting which was the UK's largest provider of satellite based television. Other new competitors included the largest UK retailer of mobile phones and services, Carphone Warehouse and suppliers iewing and digital video recording which were challeng such as Apple iTunes and Nokia Ovi which had been ing traditional business models Investing heavily in digital content. Google was also There had been incant regulatory changes Increasingly involved in the communicatie field with the communications industry which had been a new, open, mobile operating system. Android and loved global leader in opening up communications markets to ments in mobile search and advertising competition across the full range of services. These changes In addition to changes in competition, Vodafone and induced ping the national telephone compuy, BT. other operators faced rupid changes in technology with and forcing a to allow access to its network at competitive the growth of IP (Internet protocollowing voice, data rates asing licenses for additional mobile operators and video to be digitised for high-speed distribution over and allowing virtual operators or MVNOs which could multiple networks), the emergence of new broadcasting etwork capacity without the capital cost of building technology such as WI-MAX (extended W-FI and the their own and supporting competition in television and continued upgrading of speeds over fixed and mobile Internet services. Ofcom Olice of communications was networks, The UK was also watching to digital television the replace charged with ensuring competition and and operators were offering services such as demand hiery of basic services Consumers had benefited greatly This case was written by Roger A. Strang, Associate Fellow, Sand Business School University of Oxford, based on published information. It is intended as a basis for class discussionstration of good or bad practice Roger A. Strang 2030 Not to be reproduced or quoted without permission 558 VODAFONE 3.4 23 12 157 15. Data 138 15 104 from these technologkat and regulatory changes with real Table 1 UK communications industry: revenues and costs falling 34 per cent between 2005 and 2008 and rapid trends growth in the number of competitors as well as the range and quality of hardware and services provided 2006 2007 2005 In the light of these technical and regulatory changes many of the competitors in the market were building FUEDLINE Voice 95 93 9.6 their strategies around a perceived consumer need for Data Presidential internet 3.3 3.4 converged services. This meant providing multiple services Corporate data services 3.1 ranging up to the quad play offered by Virgin Media Total 15.7 fixed line telephony, mobile telephony, television and MOBILE broadband Internet). In 2009. most of the companies Voice 106 115 offered at least three of these services ta 'triple play' which Messaging 26 2. 24 varied depending on the nature of their networks and 06 0.8 09 Total 150 their willingness to investor partner. Vodafone was unique among the major competitors in focusing largely on mobile TELEVISION Subscriptions 3.8 services and this was a concem to both shareholders and 4.1 Advertising 35 3.6 35 managers within the company, Management's challenge Licence fee and other 3.4 34 3.4 was to decide which iany of the other services they should Total 112 provide and. If so, should the services be providol by their Source: Compiled from fires on Commit own networks built or acquired) or through partnerships? services are given in Table 1. Ofcom research found that The UK market 12 per cent of UK households were mobile only in early In 2009, the UK market was still in the grip of the global 2009 compared to an average of 24 per cent As in most countries, the UK fixed line network had financial crisis. This crisis had begun to have a devastat Ing Inpact in 2008 and the UK government like most privatised the service as British Telecom or BT. In order to been developed by the government, which subsequently bank, protect depositors and stimulate economic activity encourage competition the regulator required BT to offer The UK economy was expected to recover more slowly than other operators wholesale service through their network other countries because of the significant role of financial at competitive terms. This eventually forced IT to set up a separate division, Openreach, to provide network voice and services in the economy and other factors The longer term outlook was more positive. Immigra internet services to other operators as well as to other dit Nons of Br. Ofcom went further and in 2002 introduced a tion and increasing birth rates meant that the population 161 million) was expected to grow 4 per cent over the next process called local loop unbundling which required five years. There would be public spending constraints to BT to allow other operators to install their own cquis reduce the debt incurred in fighting the recession but it was mentin T local exchanges to provide voice and broadband hoped that these would be offset by growing private sector that operators could provide these services without the internet services to their own nearly customers. This meant activity. Personal disposable income grew percent from cost of building and maintaining a national network 2002 to 2007 and some forecasters looked for this growth to resume some time in the future. The 2012 Olympics were After further price cuts and operating changes were to be held in London and this was expected to stimulate pored on HT 2004 und 2005. I became an attractive prowth in investment and tourism. option for other operators which rapidly expanded their services. Operators using LLU have significant upfront costs Fixed line telephone for buying and installing network equipment but after that The tik fixed line telephone market was declining although they have low monthly line rental charges which in 2009 at a slower rate than in other laropean countries were 130 1.430751.94) for DSt.broadband and c7.20 Ofcom reported that the number of lines had dropped from (07.94 or $10.791 for broadband and voice. Since these 34.9 million in 2003 to 33 million in 2009. Call minutes upfront costs were included in the wholesale rates, there were on fixed lines had decreased 15 per cent from 167 billion to economics of scale for larger operators which used . 138 billion over the same period. By 2009 only 55 per cent The low incremental costs of providing voice services or Uk volce minutes originated from fixed line phones and meant that many operators were able to provide bundles of mobile originated calls were expected to exceed fixed line minutes in 2010. Trends in revenue from voice and other The exchange rates Cl-61.10 and 1 - 51.50. VODAFONE 559 fixed line voice and broadband including Tree broadband would continue to manage their own work they would with voice services. This encouraged the adoption of fixed share ownership of the stones and te broadband services with coc-third of connections in 2008 The large wireless operations prochese handsets under coming from the lines. By the end of 2008, 35 per cent of global contracts with the supplies (Nokia had BT's exchanges had been unbundled and 85 per cent UK 40 per cent of the UK handit market followed by Samsung consumers primarily in urban areas) had a choice of timed at 21 per cent and discount retail prices heavily to attract voler provider. The result was that in 2009. BT's share of new subscribers. In recent yes operations have been able fixed line voice minutes fell below 50 per cent with strong to negotiate with suppliers to introduce their own branded competition from Virgin Media. TalkTalk (a service offered handsets Mobile landet sales in the UK declined in 2009 by retailer. Carphone Warehouse Orange and Sky for the first time UK widesperates have also followed In terms of cross-ownship, BT fixed line subscribers were their low-cost competitors tooder SIM-cell plans which equally likely to save mobile phones from the four largest allow consumers to use their current hunts and pay a operators but less likely to be a Virgin Mobile subscriber significantly lower monthly tart. These plans were 22 per Similarly they were more likely to subscribe to NT partner cent of new subscriptions in the first half of 2009 Sky TV than to Virgin Modia. Virgin Media subscribers a major factor in the first anual decrease in overall UK were also equally likely to subscribe to one of the four major handset sales mobile operators but more likely to subscribe to Virgin Mobile Although everal hundit les were down 3 percent and very much more likely to subscribe to Virgin TV compared with 2005. sales of smartphones with Blackberry and their competits w25 per cent Mobile telephone and reached 16 percent of the market. Apple had need Ofcom reported that at the end of 2005 there were the UK market with the heee in late 2007 der 76.8 million mobile subscriptions in the UK. up 3 million exclusive arrangement with o Demand for the home from the previous year and 24 million from 2003. With meant that Apple became the first handiet supplier to 61 million population this area penetration rate of negotiate = share of the operator's cering revende over 120 per cent similar to other developed markets in although this was later repeated. The iPhone was very Europe. Mobile volce minutes had exceeded 100 billion cessful in the UK, with over 2 mil old in the first and represented over 45 per cent of total call minutes your. The exclusive arrangementended in late 2009 when Mobile revenues in 2005 were estimated at 15.3 billion. Orange began selling the iPhone with Vodafone scheduled up 58 per cent from 2003. Average monthly revenue per to follow in 2010. Less than 15 percent of all mobile phone subscriber was 17. down 2 per cent from the previous owners med internet services but 80 per cent home year due to increasing price competition and regulatory sers accessed the internet. 75 percent accessed call and pressure to reduce certain industry charge 5h per cent linked to social networking sites There were five major network operators in the UK in Average churn customers switching rates in the 2009 and more than 100 virtual network operators MVNOS market had been over 20 per cent annually helped by the which lease network Services and resell them under their introduction of number portably in 2007 and competitive own brand. Ofcom estimated that continued to be the tactics such as subsiding hundets for new cribers market leader in 2008 with 28 per cent share of revenues Some operations, sotably had tried to reduce churn by including the fees paid by the Tesco Mobile MVNO, Vodafone providing a superior customer experience but the best was nest with 26 per cent followed by Oranpe owad by impact came free switching post-gastosto per France Telecom. 22 percent. T-Mobile carrier of the Virgin contracts. By 2009 most contracts were 15 meets with Mobile MVNO and owned by Deutsch Telekom. 17 per cent) 24 months becoming more common. The lowr tarif the and UK (owned by Hutchison Whampo, per cent). Sonly plans had increased the proportion of contract The market share of MVNOs continued to grow.reaching post-guld obscribers to per contin 2009 buruk 12.7 per cent of subscribers at the end of 2008. Virgin mobile we were still on perpaid plans Contact us Mobile was the largest with 62 per cent of subscribers were preferred by operates since they were more boal followed by Tesco Mobile with 2.6 percent. their age rates were four times higher and despite con Wirdess operator margin in the UK were up to 10 points tining price declines, they planted 11 pense per komer than in other Propean countries because of the strong minute compared with pence for prepaid competition. The proti pre was leading to industry consolidation with the merger of Orange and T-Mobile Television agreed for 2010. In early 2009 Vodafone and, announced Television in the UK is donated by the publice a major network sharing agreement covering tive Paropran broadcast channele C 1.c 2. TV 1. Channel 4 countries including the UK. This meant that while they and Five. The channels together with their additional 560 VODAFONE 112 112 Table 2 Television market shares and trends inca 2009 there were estimated to be 26 million UK Audience share in multichannel homes in been with TV. a slighting Over the previous year. The process of switching to digital TV was well under 2006 2007 2006 way in the UK and is expected to be completed by 2012. BBC tatt channels 306 318 in early 2009 it was estimated that almost 90 per cent of ITV 220 223 224 bescholts could receive digital terrestrial TV (UTT Channel 4 Sky 76 signals which require a special serial and either a set-top Five 5.1 58 box or a specially equipped TV. Using this DTT platform, UKTV 40 29 29 the Freeview package of more than 50 TV and 20 radio Virgin Media 26 26 channel is received by over 12 million UK bouseholds All Other 158 155 and this had helped the public service broadcasters build SowerBreas Abertising Research share for their digital channels. HD (High Definition) TV was introduced in 2008 and 2.3 million households had channels and radio services are supported by an annual HD really equipment in 2009 licence lee paid by all UK residents with a TV set in their In 2005 there were almost 9 million homes equipped homes TV and the two other channels we provided to che tellite broadcasts and 3.5 million homes with tional portfolio channels and are supported by advertising able to both upcover the previous year, Television services are also provided by what Of Most of the homes receiving satellite signals were Sky delines as multichannel operates' led by Ray KTV. scribers and most of the cable homes were customers Viscom und Virgin which are largely supported by a mix of Virgin Mediu Calle was potentially able to 49 per of subscription and advertising. Altogether Ocam reportscent of the 24 million UK households and IPTV Internet that there were 495 channels at the end of 2008.com Protocol TV TV broadcast using the same digital packets with 470 channels a year carlier. They noted that now that are used for the internet) was available to 39 percent channel licence applications in 2005 were 77. the lowest of households but penetration rates were relatively low. total since 1998. As noted in Table 1.subscription revende continued to increase in 2008 but advertising revenue Brown declined due primarily to the economic recession but also to ed broadband internet service was available in 65 per the growth in online advertising cont of households in 2009, an increase of 12 per cent Market shares for the major operations are given in over the presious year. Most homes and small businesses Table 2. The five public service channels had lost share of (13.5 in) are served by their existing phone lines viewers for their primary channels but the pain in viewing St. technology with 3.7 million cable customers for their portfolio of channels generally more specialised representing the balance. One analyst. Forrester predicted Increased their overall audience share. The Cayer that the number of households with broadhand would which allows on-demand viewing by storing 30 days of grow to 22.5 million by 2012 with most of the growth programming also strengthened their position Skywatse despite it being slower and less relluble Cable the worst hit of the multichannel operations with audience was expected to grow to million while other' (WIMAX share down 11 per cent in 2005 compared with 2007 and under To The Home) was expected to increase from 43 per cent since 2001 200.000 to 1.1 million. Most customers accessed the Overall the TV operators spent 5 billion for content internet through computers, which were in 74 per cent in 2008, up 2 per cent over 2007. The largest portion of households in 2008 11.2 billion for sports and film aboup 2 percent Sports was Wurdes (de) broadband is provided by all major one of the few forms of content that many viewers wanted operates through 36 cande for laptops and has become to watch in real time and the cost of broadcast rights to creasingly competitive with many packages for less than inglish Premier League football had escalated each time the 20 per month. Demand for there was growing rapidly. contract was up for bid. This meant that the successful 2007 with 263, new customers reported for May 2009 alone. bidders were again the pay teledon operato, primarily Most of these subscribers 175 per cent also had a fixed Sky Sky's partner. Setanta had the remainder of the games the broadband subscription so saw the mobile service as but in 2009 the company was forced into bankruptcy by complementary. There were over 12.000 Win hotspots the Foression. El regulators were concerned that there was the UK in carly 2008. The largest operator of these was a trend towards majorspeiets leagues not being available. The Cod with 7000, followed by BT Opettone (2323) on free-to-air television and were discussing regulatory and T-Mobile (1200) changes. The difficulty was that the leagues themselves had As noted earlier the rapid growth of broadband in the become very dependent on the broadcast rights income UX had bem helped by localloop unbunding. The commic VODAFONE 561 of this encouraged consolidation among the 200 ISI and Table 3 Lowest cost broadband options: by 2009 the live largest providers hd 91 per cent of all major suppliers connection. In 2009 the leader was IT with 26 percent July 2009 of the retail connections, followed by TalkTalk (put of Carphone Warehouse) which had recently acquired Thal Broadhane Broadband Broadband Broadband to give it a 25 per cent share. Virgla Media had 23 percent Fred Voice Fund Voice FeedVoice Find Voice TV and was followed by BSkyB with 12 per cent and Orange TV Home with 5 percent CHO Although broadband customer churn was lower than 5.92 fixed and mobile it was still over 1 per cent per month with Congo 2104 the major complaint being the difference between claimed at 17.30 and actual speed. Most subscribers were offered op to Viro 10 Mbps (megabits per secondi hutan Ofcom studyin 5.00 OS mid-2009 found that the average speed across all . Jay 2009 line broadband providers was Mbps with picantly lower speeds in the evenings due to the limited ability of Competitor strategies ISL to cope with higher usage levels. The study found that Virgin's cable network delivered an average of Mbps in its The two other large wireless operators, O, and Orange hal lowest speed service up to 10 Nhp Virgin introduced both movedressively into the fixed line voice and broad. 50 Mbps vice crows its network in 2009 and had and market by investing in Orange had set up Orange successfully tested up to 200 Mbps Home via an early acquisition and by 2009 had close to In 2008, BT announced plans to invest 1.5 billion in subscribers or over 5percent of the market. had afhe-based superfast network which could be wailable entered the market in 2006 with the acquisition of lean to 40 per cent of UK homes and businesses by 2012. Internet service provider. They began investing in tuin This was expected to deliver speeds of up to 40 Mbps and 2007 and by 2009 they were in exchanges reaching over potentially 100 Mlips where there were the connections to per cent of the population and had over 500,000 into the home (FTTH. This connection was expensive subscribers 0, UK is a subsidiary of Telefonica, originally (over 500 per home so was not expected to be widely the Spanish national telecommunication operator but by Implemented although it was a comenstone of the strategy 2009 mai multinational company with over 260 million of one major US telecommunications operator scribe to it wireless, fed line, Internet and pay TV Mobile internet services used the operators and service. Tdetonica esitself as one of the world's leading networks and were generally lower at Mbps with up Integrated operates in the telecommunication sector to 7 Mbps possible on networks equipped with the latest BT's 2005 annual report recorded the company's technology. They were also subject to variation due to trade as follows network capacity, location. load and other factors. Future Weim to be a global leader in converged communications technologies would have higher speeds but were not sevices. Cvergence-bringing fixed line and mobile expected to match those of cable and he technologies. IT and communications, networks and services Bundled services - the core of what we eller our customers. At BT we call In 2009 Ofcom estimated that there were 15 operates this united communications providing multiple communication services dined as an However, a new CBD and a major write-off (C700 million combination of two or more services tested time and in its Global Services consulting business appeared to have dial-up broadband) Excluding mobile services they empered its ambitions by 2009 although the company reported that 46 per cent of UK consumers purchased me retained the strapline. "Bringing it all together' BT was the form of bundled services in early 2009. up 7 points from the dominant player in providing both fixed line voice and previous year. Of these 46 per cent of consumers brought broadband services in the UK. Its core advantage was its the double play of fixed voice and broadband from a sample satellid line network which had been built during the supplier while per cent brought the triple play by previous fe years and which was to be upgraded again. adding in TV. In a related study. Ofcom noted that the inter By curly 2009 Tupported most fixed line voice services net was becoming the vehicle for accesson traditional in the UK and over 14 million DSL broadband lines repre- media with 20 per cent of adults using it to listen to the enting over 5 million of its own retail customers, almost radio and 17 per cent using it to watch TV. Comparative 6 million customers and almost 4 million wholesale pricing of bundles are plen in Table 3. customer. Talso offered mobile services through its own 562 VODAFONE MVNO which was hosted by Vodafone. Its IPTV service BT leading MVNO, Virgin Mobile. The company is organised Vision offers more than 200,000 customers Television on in three areas: cable including clevision broadband and Your Terms with no monthly subscription, access to a range fixed line voice 177 per cent revenue 37 per cent gross of television and radio channels as well as on-demand margin mobile (14 per cent revenue 44 per cent grows and pay-per-view services which are delivered over BI's margin) and content including its own TV channels as network using IPTV technology well as its joint venture with the BBC, UKTV 9 percent BSkyBar Sky is is a publicly traded UK company but it is revenue 44 per cent gross margin. Overall revenues in 39 per cent owned by News Corp. the global media group, 2009 were expected to be 15 billion with a net loss due to Since 1988 it has allered pay TV services over satellite, acquisition related witralls eventually including a package of 25 of its own channels In 2009. Virgin's cable network passed 12.6 million covering sports news, entertainment. gonbling and special UK households of which 3.7 million were TV subscribers Interests which it alles along with many others. In 2006, 3.8 million broadband and 4.1 million telephone. An adds in partnership with WT. It began offering dised line voice final 225.000 subscribers were served by 11. lines under (Sky Talk and broadband (Sky Broadband. By mid-2009 the Virgin National brand. Virgin's fhe network linked to Sky reported 9.4 million television subscribers. 1.8 million exchanges much closer to customers than the BT network telephone subscribers and 2.2 million broadband. and the final connection was made by coaxial cable supple- The Sky annual report noted that 16 per cent of its mented by copper wires for volce communications. This subscribers purchased a bundle of all three services allowed the company to deliver much higher broadbund an increase from 11 per cent the previous year. Average speeds than any other competitor and to provide a higher monthly revenue per user increased from 136 to 139 and quality on-demand television service. In 2009 cable sub- the annualised chum rade stayed flat at 9.9 percent. Skyscribers were continuing to move to bundled services with offered a limited on-demand package but more than half 60 per cent taking all three services and 25 per cent taking of the TV subscriptions included a digital video recorder two. The average annual revenue per cable subscriber was to allow subscribers to control their viewing Sky relied 370 in 2009 and the annual chum was 15 percent. Virgin on attracting viewers by securing rights to sports, first-run noted that broadband customers were more profitable than movies and popular TV series but in 2009 the company television customers and that triple play customers were was coming under pressure from Ofcom to wholesale more not only more profitable but also more loyal of its channels to other operators Carphone Warehouse announced in 2009 that it would Vodafone strategy split its business into two separate entities in 2010. The retail and distribution business was owned 50 per cent by Vodafone began as Racal Telecom, a division of Racal the US retailer Best Buy and operated 2400 retail outlets lectronics and completed the first UK mobile call in 1985. acros nine Buropean countries as well as Best Buy Europe. Il adopted the name Vodafone Group ple when it became Talk Talk was its communications business which in 2009 an independent public company in 1991. Beginning in had 4.1 million broadband customers and an additional the mid-1990 Vodafone began an aggressive strategy of 1.1 million fixed voice and dial-up subscribers. Talk Talk growth through acquisitions and by September 2009 the had grown with aggressive marketing Including the company operated in 25 countries with partner networks broadband with volce services and acquisitions including in 5 more) and had 123 million customers. The company AOL UK in 2006 and Tiscali in 2009. The Tiscali acquis described itself as the world's leading telecommunications tion cost (236 million and added 1.4 million subscribers company noting that it had operations throughout Europe The company estimated annual savings of 40-50 million the Middle East Africa Asia, the Americas and Australasia particularly from migrating the 50 per cent of Thscall The group primarily focused on mobile telephones but in customers who were not served by us lines onto the 2007 began to acquire or leased fine capacity in a fully unbundled Talk Talk network. Hy September 2009 number of European countries TalkTalk had unbundled 1714 BT exchanges covering Vodafone's recent growth in developing markets bad 81 per cent of the UK population been enthusiastically led by CEO Arun Sarin hut in July In 2008 Virgin Media noted in its annual report that 2008 he was succeeded by Vittorio Cola, who came in the company provided the first quad-play offering of with a strong reputation as a cost cutter. Early in 2009 television, broadband, fixed line telephone and mobile telebe announced a change in corporate strategy to focus on phone services in the UK fogether with the most advanced four objectives TV on demand features available in the UK market. 1 Drive operational performance through value enhance Virgin Media was formed in 2017 when the former NTI. ment('maximising the value of our existing customer rebranded as part of the 2006 acquisition of the UK relationships, not just the revenue and cost reduction VODAFONE 563 2 Pursue growth opportunities in total.com.shown by a higher proportion of contract customers This involved expansion in mobile data services growth (41 per cent than the market and an ARPU (Average in enterprise business customers including medium. Revenue Perliset per month of 22641 contract and 8 small and home offices and broadband. In this last area for prepaid which was significantly above the average the company announced. "We will adopt a market-by- of 117. Vodafone had need heavily in marketing in all market approach focused on the service, rather than its markets and its brand was well known with its strap the fechnology. It will be targeted at enterprise and high tine. Make the most of now. In the UK the company was value consumers as a priority active in sports spendipindading Formula 1 racing Execution in emerging markets including expanding and England nicht delivery of mobile services and selective expansion into Vodafone UK also had the largest share of 3G sub new markets. scribers and was the leader in marketing 3G dongles or 4 Strengthen capital discipline including a poel of gencrat- cards for laptop connections with an increase of 50 percent ing 15-6 billion in free cash flow annually with the in 2008 to a total of 3.56 million. Its 3G network offered investment priorities of support for existing business and speeds of up to 7Mbps and the company hoped to be able expansion of mobile data, entertalement and becadband to clier up to 14 Mbps within a yeur. Vodafone targeted Vodafone Group revenues for the fiscal year codiny business travellers with its esport service offering home 31 March 2009 were 041 billion, up from 355 billion country voice rates when rouming in Europe and mobile the previous year. However, net profit fell from Los billion data services for a fee of clo per day to 3.1 billion due to a me-time impairment charge of wholesale services from BT but its prices were high and Vodafone did oder fred oice and broadband using 5.9 billion to write down the value of earlier acquisitions, it had few subscribers. The priority was to partner with principally in Spain and Turkey. The company annual report noted that overall organic growth growth from existing services that integrate the mobile and environments leading internet companies to provide products and businesses) in revenue was actually slightly negative and cables consumers to use their mobiles to replicate although adjusted operating profit showed organic growth of 2 per cent on the year. Free cash flow was 5.7 billbee fired line activities. The company sought to be more.com and capital expenditures totalled 6.0 Million for the year. petite against fixed line competitors by offering fixed line Interim results through September 2009 showed prices when customers call from within or near their home drevenue (Vodafone at Home growth of 9 percent organic growth of -3 percent), EXIA up 2.4 per cent and free cash flow up 29 per cent. Vodafone UK was beated by Gary Laurence who had Vodafone Lik faced a number of challenges in 2009, been appointed CHO in September 2008 as the fith CHO had lost the leadership in the UK mobile telephone market in five years. He had previously been CEO of Vodafone to 0, and with the announced merper of Orange and Netherlands and before that held a number of market T-Moble it would drop to third Churrates in 2008 had ing positions in Vodafone cewporate. He had joined the reached 15 per cent (17 per cent for contract and 48 per company in 2000 when the internet service provider he cent for prepaid but were coming down in 2009, Vodafone headed. Visst, was acquired by Vodafone. As he reviewed had a stronger position with high value mers as the current course of focusing solely on mobile volce and the situation, he could see three malo opon to continue data: to look for a partner to provide a stronger broadband Table 4 Operating results, Vodafone UK and Europe offering or to invest in the company's own broadband Ifiscal year ending 31 March (Emil network through directly or through an acquisition Vodafone was already the leader in mobile internet UK Europe in the UK the mobile focus strategy had proven to be 2009 2008 2009 2008 effective in the short rum Vodafone was also investing Revenue 5,392 24.081 in upgrading its network to provide faster speeds and was Service revenue 4,912 4.952 27.556 24,430 already working with its suppliers on technologies for the Organic growth 11.741 next generation of wireless (G. In 2009 no standards EBITDA 1,219 1,431 10.422 9,690 had been approved for 4G and it would take sereral years EBITDA margin 22.6% 26.4% 352 37.25 to deploy but it was expected to aber transmission speeds Operating profit adil 235 6,206 of up to 20 Mbps and more. This was certainly adequate Source Youne 2004 Annual Report for most current applications including video viewing but would it be suficient for new applications and would it appeal to consumers used to higher speeds and greater Earnings Before Interest Tues, Depreciation and Amortion reliability from fester und networks 5.424 29.36 564 VODAFONE A partnership would allow Vodafone to gain access to Building or acquiring its own network would involve a network with less capital investment than building or considerable capital expense but it would allow Vodafone acquiring a network. A logical partner would be BT with to integrate horizontally to provide a full range of voice and which Vodafone already had a relationship where it leased data services under its control and with its established fixed line services and in turn hosted BTS MVNO. The two brand. The building costs could be reduced by unbundling companies had also recently announced a partnership to exchanges on a regional basis where Vodafone was provide services to corporations. Vodafone also had a joint strongest. Many of these would be the same exchanges that venture with o, to manage its mobile network so perhaps BT was planning to link with its new high-speed network. this could be extended to the fixed line network. In any Although there had been consolidation among internet partnership there would be questions of control, branding service providers, there were some smaller operators that and the ability to secure a competitive advantage using a could be acquired. Based on the recent price for Tiscali. the shared network cost would be C150-20X) per subscriber