Question: Functions for parsing time values and determining daylight hours. Both of these functions will be used in the main project. You should
Functions for parsing time values and determining daylight hours.
Both of these functions will be used in the main project. You should hold on to them.
Author: YOUR NAME HERE
Date: DATE FINISHED HERE
from dateutil import parser
from dateutil import tz
import datetime
import pytz
from datetime import datetime, time, timedelta
def strtotimetimestamptzsourceNone:
Returns the datetime object for the given timestamp or None if timestamp is
invalid
This function should just use the parse function in dateutil.parser to
convert the timestamp to a datetime object. If it is not a valid date so
the parser crashes this function should return None.
If the timestamp has a time zone, then it should keep that time zone even if
the value for tzsource is not None. Otherwise, if timestamp has no time zone
and tzsource is not None, then this function will use tzsource to assign
a time zone to the new datetime object.
The value for tzsource can be None, a string, or a datetime object. If it
is a string, it will be the name of a time zone, and it should localize the
timestamp. If it is another datetime, then the datetime object created from
timestamp should get the same time zone as tzsource.
Parameter timestamp: The time stamp to convert
Precondition: timestamp is a string
Parameter tzsource: The time zone to use OPTIONAL
Precondition: tzsource is either None, a string naming a valid time zone,
or a datetime object.
# HINT: Use the code from the previous exercise and add time zone handling.
# Use localize if tzsource is a string; otherwise replace the time zone if not None
try:
final parser.parsetimestamp
except ValueError:
return None
if final.tzinfo is None and tzsource is None:
return final
elif final.tzinfo is None and typetzsource str:
q pytztimezonetzsource
j qlocalizefinal
return j
elif final.tzinfo is not None and tzsource is None:
return final
elif final.tzinfo is None and tzsource is not None:
final final.replacetzinfotzsource.tzinfo
return final
elif final.tzinfo is not None and tzsource is not None:
q final.replace
return q
import pytz
import datetime
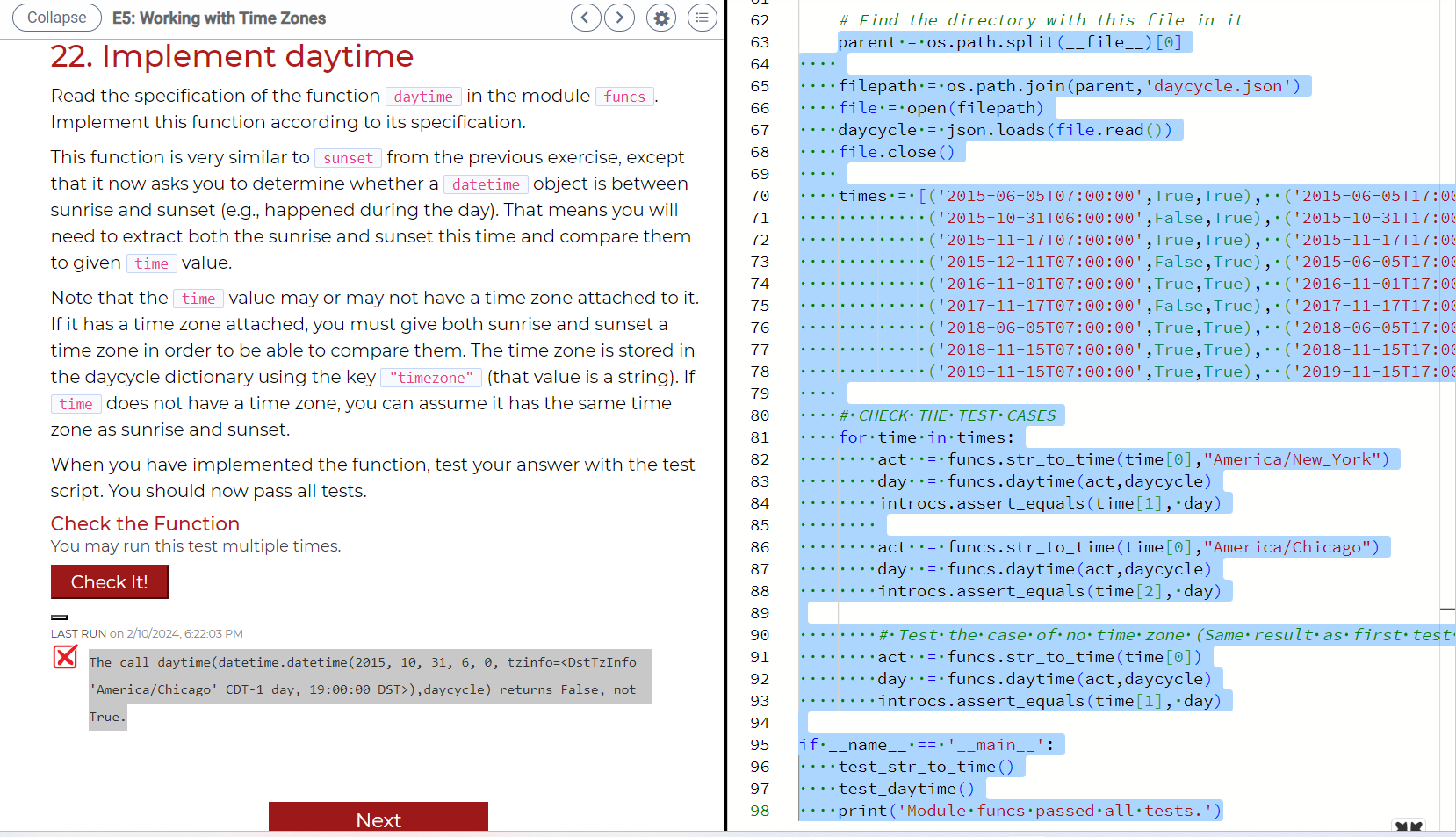
def daytimetimedaycycle:
Returns True if the time takes place during the day, False otherwise and
returns None if a key does not exist in the dictionary
A time is during the day if it is after sunrise but before sunset, as
indicated by the daycycle dictionary.
A daycycle dictionary has keys for several years as strings The value for
each year is also a dictionary, taking strings of the form mmdd The
value for that key is a THIRD dictionary, with two keys "sunrise" and
"sunset". The value for each of those two keys is a string in hour
time format.
For example, here is what part of a daycycle dictionary might look like:
:
:
"sunrise": :
"sunset": :
:
"sunrise": :
"sunset": :
In addition, the daycycle dictionary has a key 'timezone' that expresses the
timezone as a string. This function uses that timezone when constructing
datetime objects using data from the daycycle dictionary. Also, if the time
parameter does not have a timezone, we assume that it is in the same timezone
as the daycycle dictionary.
Parameter time: The time to check
Precondition: time is a datetime object
Parameter daycycle: The daycycle dictionary
Precondition: daycycle is a valid daycycle dictionary, as described above
# HINT: Use the code from the previous exercise to get sunset AND sunrise
# Add a timezone to time if one is missing the one from the daycycle
# Add timezone to time if one is missing
year strtimeyear
if year in daycycle:
monthday :d:dformattimemonth, time.day
if monthday in daycycleyear:
sunrise daycycleyearmonthdaysunrise
sunset daycycleyearmonthdaysunset
sunrisetime datetime.datetime.strptimesunriseH:Mtime
sunsettime datetime.datetime.strptimesunsetH:Mtime
return sunrisetime time.time sunsettime
return None Error in "The call daytimedatetimedatetime tzinfodaycycle returns False, not True." Tests used "def testdaytime:
Test procedure for the function daytime printTesting daytime
parent ospath.splitfile
filepath ospath.joinparent'daycycle.json
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


