Question: f(x) = 2 sin(x) + 2 cos(x), 0x 2 Exercise (a) Find the interval on which f is increasing. Find the interval on which
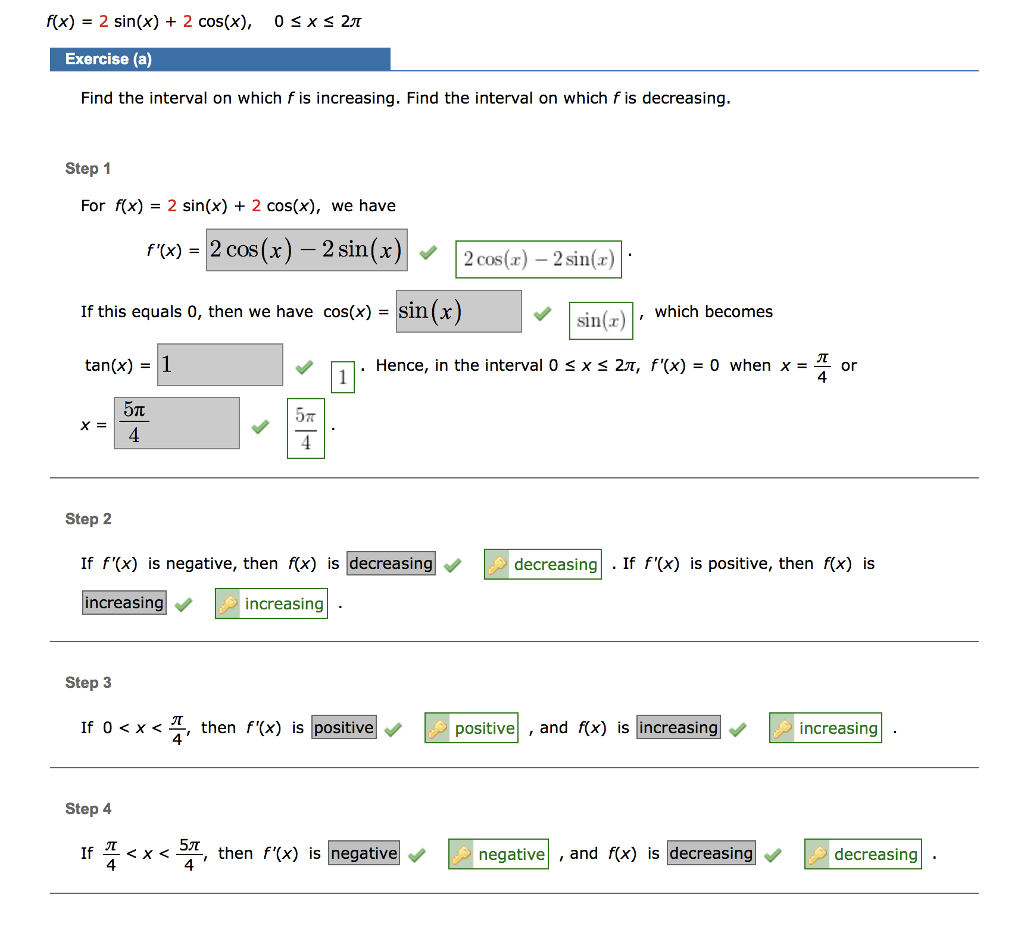
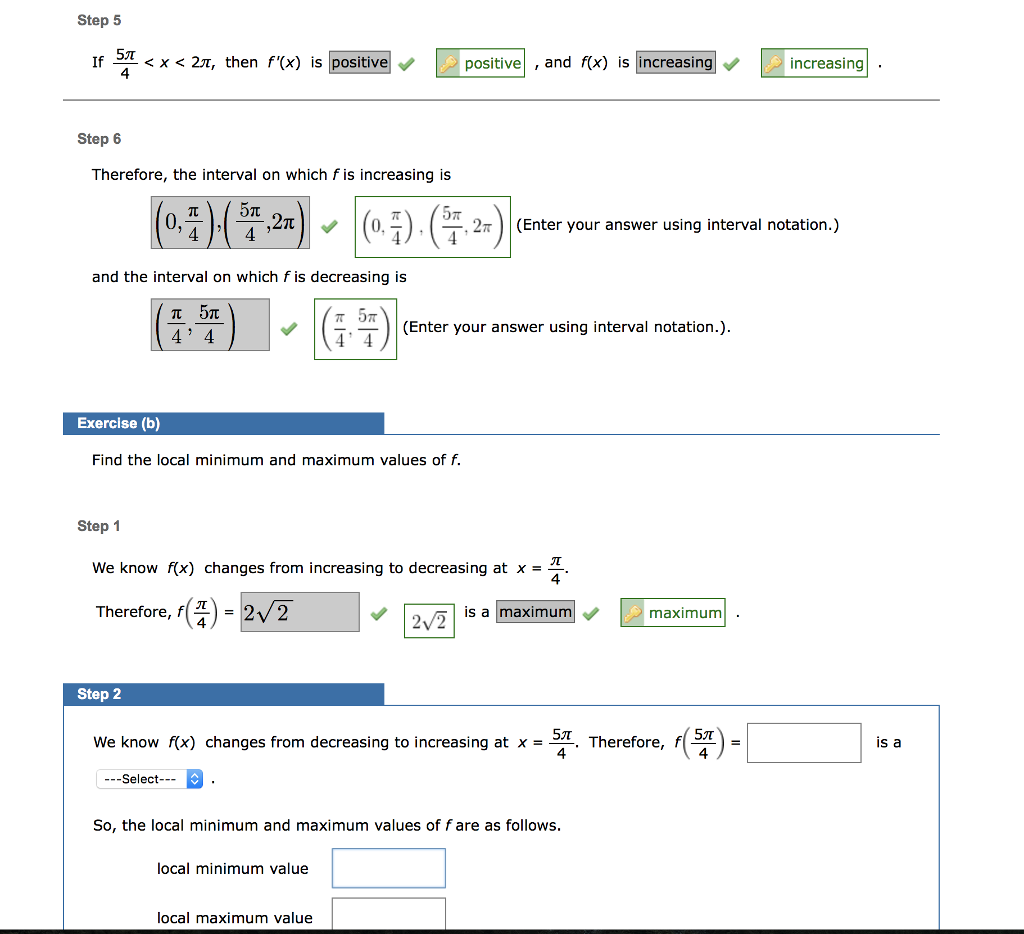
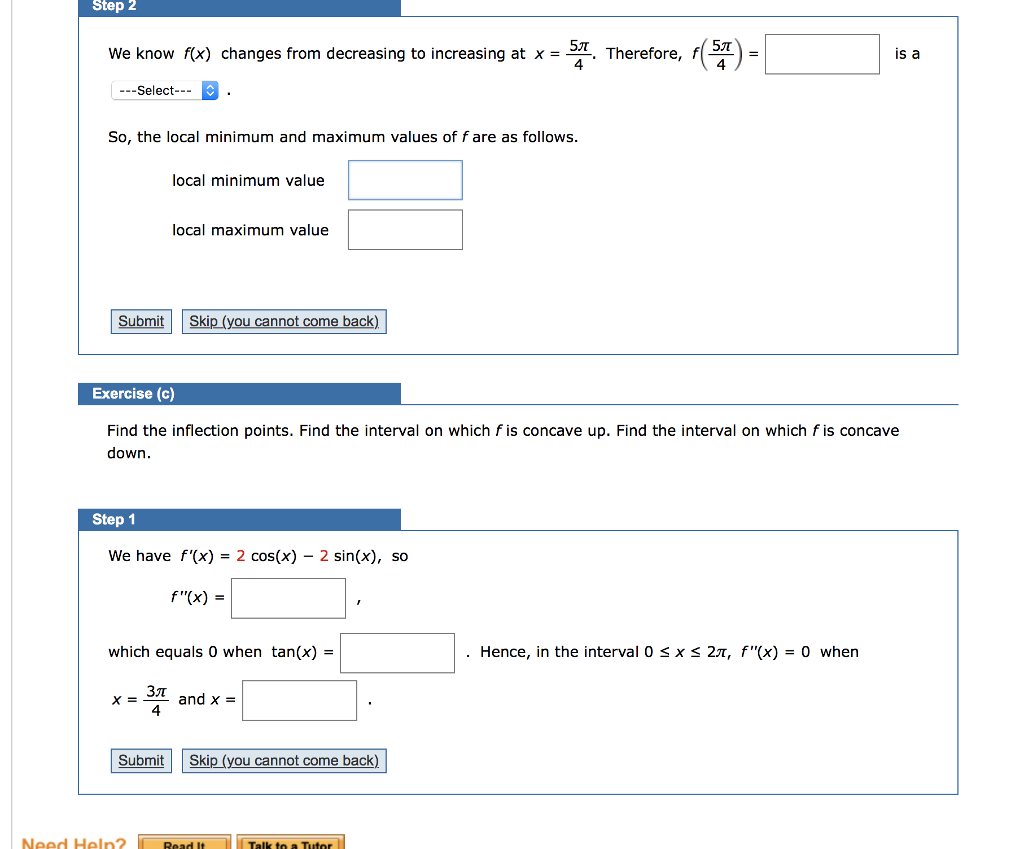
f(x) = 2 sin(x) + 2 cos(x), 0x 2 Exercise (a) Find the interval on which f is increasing. Find the interval on which f is decreasing. Step 1 For f(x) = 2 sin(x) + 2 cos(x), we have If this equals 0, then we have cos(x) = sin(x) tan(x) = 1 5 4 X = f'(x) = 2 cos(x) - 2 sin(x) 2 cos(x) - 2 sin(x) Step 3 Step 2 If f'(x) is negative, then f(x) is decreasing increasing increasing If 0 < x < Step 4 If I Step 5 If 5 < x < 2, then f'(x) is positive 4 Step 6 Therefore, the interval on which f is increasing is (0,4).( 54,2x) 27 and the interval on which fis decreasing is 5 4' 4 Therefore, f(1) Exercise (b) Find the local minimum and maximum values of f. Step 2 = ---Select--- Step 1 We know f(x) changes from increasing to decreasing at x = 4 is a maximum 22 (0,7). (7,2 2 5 (77) 4' 4 local minimum value positive, and f(x) is increasing local maximum value (Enter your answer using interval notation.). 22 (Enter your answer using interval notation.) We know f(x) changes from decreasing to increasing at x = Therefore, f(5) 5 4 So, the local minimum and maximum values of f are as follows. maximum increasing is a Step 2 5 We know f(x) changes from decreasing to increasing at x = 4 ---Select--- So, the local minimum and maximum values of f are as follows. Submit Skip (you cannot come back) local minimum value Step 1 We have f'(x) = 2 cos(x) - 2 sin(x), so f"(x) = X = local maximum value Exercise (c) Find the inflection points. Find the interval on which f is concave up. Find the interval on which f is concave down. which equals 0 when tan(x) = 3 4 Submit Need Help? and x = Skip (you cannot come back) Read It Therefore, f(5) = Talk to a Tutor is a Hence, in the interval 0 x 2, f"(x) = 0 when
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (168 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


