Question: GESCH Exercise 17-18 Activity-based costing LO P3 Surgery Center is an outpatient surgical clinic that was profitable for many years, but Medicare has cut its
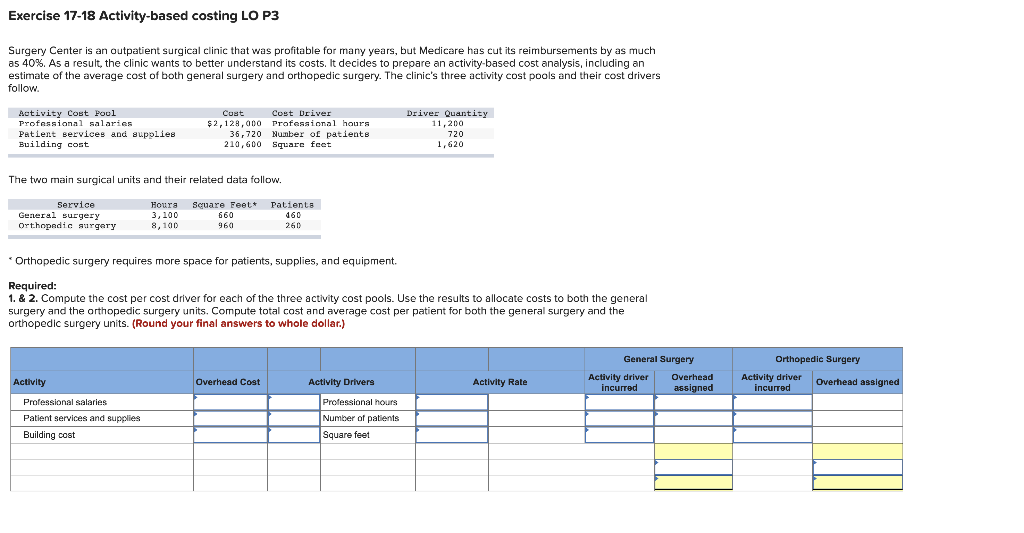
GESCH Exercise 17-18 Activity-based costing LO P3 Surgery Center is an outpatient surgical clinic that was profitable for many years, but Medicare has cut its reimbursements by as much as 40%. As a result, the clinic wants to better understand its costs. It decides to prepare an activity-based cost analysis, including an estimate of the average cost of both general surgery and orthopedic surgery. The clinic's three activity cost pools and their cost drivers follow. Activity Cost Pool Cout Cost Driver Driver Quantity Professional salaries $2,128,000 Professional hours 11,200 Patient services and supplies 36,720 Number of patients 720 Building cost 210,600 square feet 1,620 The two main surgical units and their related data follow. Service Houra Square Feet Patients 3,100 660 160 Orthopedic surgery 8,100 960 260 Orthopedic surgery requires more space for patients, supplies, and equipment. Required: 1. & 2. Compute the cost per cost driver for each of the three activity cost pools. Use the results to allocate costs to both the general surgery and the orthopedic surgery units. Compute total cost and average cost per patient for both the general surgery and the orthopedic surgery units. (Round your final answers to whole dollar.) General Surgery Activity driver Overhead incurred assigned Orthopedic Surgery Activity driver Overhead assigned incurred Activity Overhead Cost Activity Drivers Activity Rate Professional salaries Patient services and supplies Building cost Professional hours Number of patients Square feet
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


