Question: Given a data set with Tive transactions, each containing tive items, as shown in the table TID items bought T1 A, H, K, T, T2
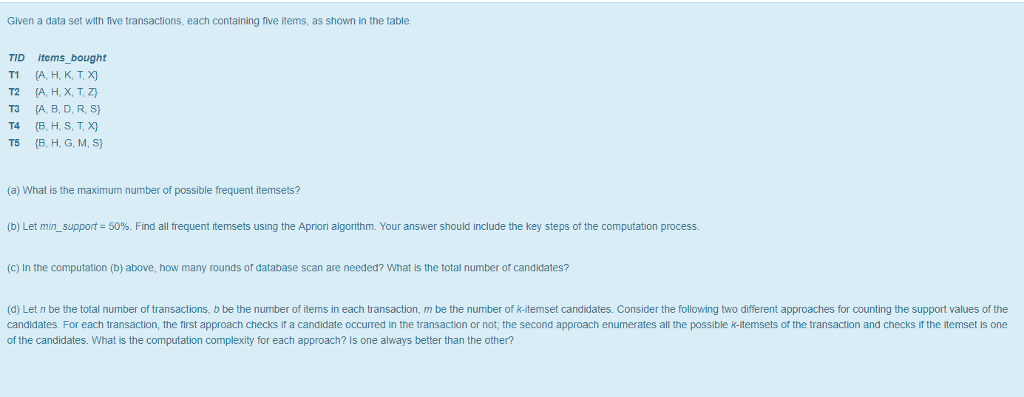
Given a data set with Tive transactions, each containing tive items, as shown in the table TID items bought T1 A, H, K, T, T2 (A, H, X, T, z T3 A, B, D, R, S T4 (B, H, S, T, X) T5 (B, H, G. M, S (a) What is the maximum number of possible frequent itemsets? (b) Let min-support: 50%. Find all frequent itemsets using the Apnon algorithm. Your answer should include the key steps of the computation process. (C) In the computation (b) above, how many rounds of database scan are needed? What is the total number of candidates? (d) Let n be the total number of transactions, b be the number of items in each transaction, m be the number of k-itemset candidates. Consider the following two different approaches for counting the support values of the candidates. For each transaction, the first approach checks if a candidate occurred in the transaction or not, the second approach enumerates all the possible k-Itemsets of the transaction and checks if the itemset is one of the candidates. What is the computation complexity for each approach? Is one always better than the other? Given a data set with Tive transactions, each containing tive items, as shown in the table TID items bought T1 A, H, K, T, T2 (A, H, X, T, z T3 A, B, D, R, S T4 (B, H, S, T, X) T5 (B, H, G. M, S (a) What is the maximum number of possible frequent itemsets? (b) Let min-support: 50%. Find all frequent itemsets using the Apnon algorithm. Your answer should include the key steps of the computation process. (C) In the computation (b) above, how many rounds of database scan are needed? What is the total number of candidates? (d) Let n be the total number of transactions, b be the number of items in each transaction, m be the number of k-itemset candidates. Consider the following two different approaches for counting the support values of the candidates. For each transaction, the first approach checks if a candidate occurred in the transaction or not, the second approach enumerates all the possible k-Itemsets of the transaction and checks if the itemset is one of the candidates. What is the computation complexity for each approach? Is one always better than the other
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


