Question: Given an arithmetic expression in infix or postfix notation, the goal of this assignment is to: 1. Write a program that converts the expression to

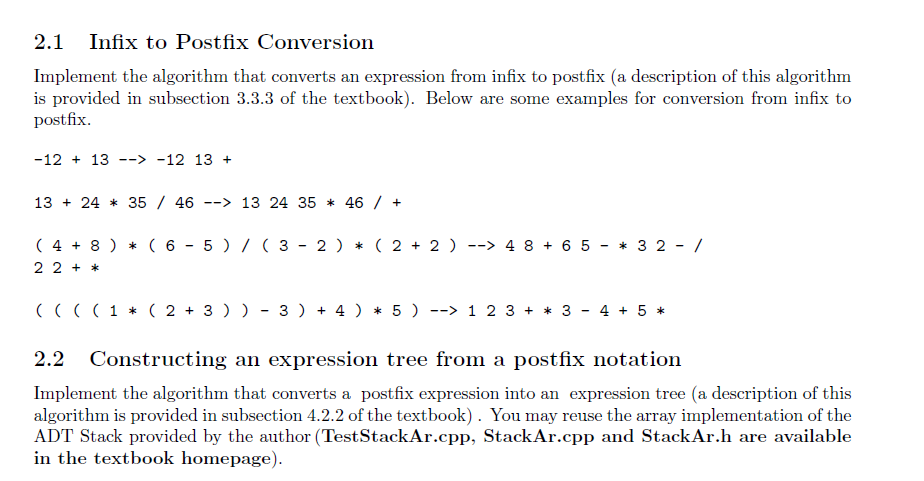

Given an arithmetic expression in infix or postfix notation, the goal of this assignment is to: 1. Write a program that converts the expression to another notation using expression trees. 2. Evaluate the expression. The main idea consists of the following steps: 1. Convert the given (input) expression into a postfix notation (if it is not the case). 2. Construct the expression tree from the postfix representation. 3. Evaluate the expression tree or print it into another notation. The expression contains only the arithmetic operators +, *, - and /, integers and (,) if the expression is in infix form. and / have more priority than + and -- You should leave at least 1 space between operators, operands and symbols (the minus sign("-") for negative numbers should however be attached to the number, -23 for instance). 2.1 Infix to Postfix Conversion Implement the algorithm that converts an expression from infix to postfix (a description of this algorithm is provided in subsection 3.3.3 of the textbook). Below are some examples for conversion from infix to postfix. -12 + 13 --> -12 13 + 13 + 24 * 35 / 46 --> 13 24 35 * 46 / + ( 4 + 8 ) * ( 6 - 5)/ (3 - 2 ) * ( 2 + 2 ) --> 4 8 + 6 5 - * 3 2 - / 2 2 + * (((( 1 * ( 2 + 3)) - 3) + 4) * 5) --> 1 2 3+ * 3 - 4 + 5 * 2.2 Constructing an expression tree from a postfix notation Implement the algorithm that converts a postfix expression into an expression tree (a description of this algorithm is provided in subsection 4.2.2 of the textbook). You may reuse the array implementation of the ADT Stack provided by the author (TestStackAr.cpp, StackAr.cpp and StackAr.h are available in the textbook homepage). 2.3 Printing an arithmetic expression from the expression tree Using the following tree traversal algorithms, write a program that prints an arithmetic expression in a given notation (prefix, infix or postfix) from an expression tree. 2.3.1 Inorder traversal An overly parenthesized infix expression can be produced by recursively producing parenthesized left expression, then printing out the operator at the root, and finally recursively producing parenthesized right expression. This general strategy (left,node,right) is known as an inorder traversal. 2.3.2 Postorder traversal The algorithm consists in recursively print out the left subtree, the right subtree, and then the operator. 2.3.3 Preorder traversal This method consists in printing out the operator first and then recursively print out the left and the right subtrees. 2.4 Evaluating an arithmetic expression from the expression tree Write a program that evaluates an arithmetic expression represented by an expression tree. Given an arithmetic expression in infix or postfix notation, the goal of this assignment is to: 1. Write a program that converts the expression to another notation using expression trees. 2. Evaluate the expression. The main idea consists of the following steps: 1. Convert the given (input) expression into a postfix notation (if it is not the case). 2. Construct the expression tree from the postfix representation. 3. Evaluate the expression tree or print it into another notation. The expression contains only the arithmetic operators +, *, - and /, integers and (,) if the expression is in infix form. and / have more priority than + and -- You should leave at least 1 space between operators, operands and symbols (the minus sign("-") for negative numbers should however be attached to the number, -23 for instance). 2.1 Infix to Postfix Conversion Implement the algorithm that converts an expression from infix to postfix (a description of this algorithm is provided in subsection 3.3.3 of the textbook). Below are some examples for conversion from infix to postfix. -12 + 13 --> -12 13 + 13 + 24 * 35 / 46 --> 13 24 35 * 46 / + ( 4 + 8 ) * ( 6 - 5)/ (3 - 2 ) * ( 2 + 2 ) --> 4 8 + 6 5 - * 3 2 - / 2 2 + * (((( 1 * ( 2 + 3)) - 3) + 4) * 5) --> 1 2 3+ * 3 - 4 + 5 * 2.2 Constructing an expression tree from a postfix notation Implement the algorithm that converts a postfix expression into an expression tree (a description of this algorithm is provided in subsection 4.2.2 of the textbook). You may reuse the array implementation of the ADT Stack provided by the author (TestStackAr.cpp, StackAr.cpp and StackAr.h are available in the textbook homepage). 2.3 Printing an arithmetic expression from the expression tree Using the following tree traversal algorithms, write a program that prints an arithmetic expression in a given notation (prefix, infix or postfix) from an expression tree. 2.3.1 Inorder traversal An overly parenthesized infix expression can be produced by recursively producing parenthesized left expression, then printing out the operator at the root, and finally recursively producing parenthesized right expression. This general strategy (left,node,right) is known as an inorder traversal. 2.3.2 Postorder traversal The algorithm consists in recursively print out the left subtree, the right subtree, and then the operator. 2.3.3 Preorder traversal This method consists in printing out the operator first and then recursively print out the left and the right subtrees. 2.4 Evaluating an arithmetic expression from the expression tree Write a program that evaluates an arithmetic expression represented by an expression tree
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


