Question: Given an empty parameter object, copy all elements of the calling object into the parameter object. Note: - Doubly Linked List. C++ - PARAMETER: Another
Given an empty parameter object, copy all elements of the calling object into the parameter object.
Note:
- Doubly Linked List. C++
- PARAMETER: Another list
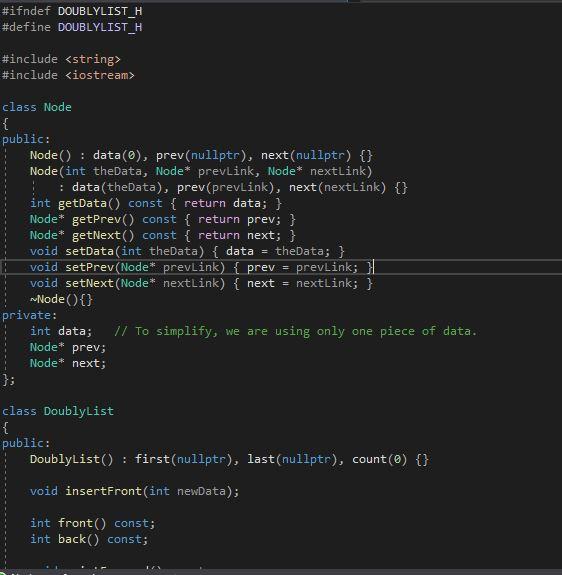
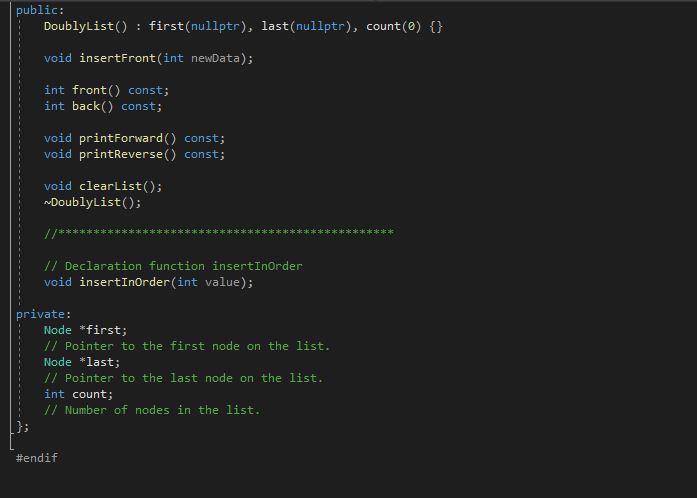
#ifndef DOUBLYLIST_H #define DOUBLYLIST_H #include #include class Node { public: Node() : data(), prev(nullptr), next(nullptr) {} Node(int theData, Node* prevLink, Node* nextLink) : data(theData), prev(prevLink), next(nextLink) {} int getData() const { return data; } Node* getPrev() const { return prev; } Node* getNext() const { return next; } void setData(int theData) { data = theData; } void setPrev(Node* prevlink) { prev= prevlink; }| void setNext (Node* nextLink) { next = nextLink; } Node(){} private: int data; // To simplify, we are using only one piece of data. Node* prev; Node* next; }; class DoublyList { public: DoublyList(): first(nullptr), last(nullptr), count() {} void insertFront(int newData); int front const; int back() const; public: DoublyList(): first(nullptr), last(nullptr), count() {} void insertFront(int newData); int front) const; int back() const; void printForward() const; void printReverse() const; void clearlist(); DoublyList(); ***** // Declaration function insertInOrder void insertInOrder(int value); private: Node *first; // Pointer to the first node on the list. Node *last; // Pointer to the last node on the list. int count; // Number of nodes in the list. Fendif #ifndef DOUBLYLIST_H #define DOUBLYLIST_H #include #include class Node { public: Node() : data(), prev(nullptr), next(nullptr) {} Node(int theData, Node* prevLink, Node* nextLink) : data(theData), prev(prevLink), next(nextLink) {} int getData() const { return data; } Node* getPrev() const { return prev; } Node* getNext() const { return next; } void setData(int theData) { data = theData; } void setPrev(Node* prevlink) { prev= prevlink; }| void setNext (Node* nextLink) { next = nextLink; } Node(){} private: int data; // To simplify, we are using only one piece of data. Node* prev; Node* next; }; class DoublyList { public: DoublyList(): first(nullptr), last(nullptr), count() {} void insertFront(int newData); int front const; int back() const; public: DoublyList(): first(nullptr), last(nullptr), count() {} void insertFront(int newData); int front) const; int back() const; void printForward() const; void printReverse() const; void clearlist(); DoublyList(); ***** // Declaration function insertInOrder void insertInOrder(int value); private: Node *first; // Pointer to the first node on the list. Node *last; // Pointer to the last node on the list. int count; // Number of nodes in the list. Fendif





