Question: Given an undirected graph and its spanning tree T and starting node 0 , return true if the spanning tree T is a valid traversal
Given an undirected graph and its spanning tree T and starting node return true if the spanning tree T is a valid traversal tree by some DFS on G from starting node otherwise return false.
Input:
Line number of nodes Vnumber of edges E
The following V lines: each line contains a space separated numbers indicating adjacency list of node
line: the starting node label
V lines: the V tree edges.
Output:
true if the spanning tree is valid DFS traversal tree
false otherwise
Example
Input:
Output: false
Explanation: For this small problem there is only two valid DFS traversal tree starting from node The given tree is not one of the the two.
Example
Input:
Output: true
Example
Input:
Output: true
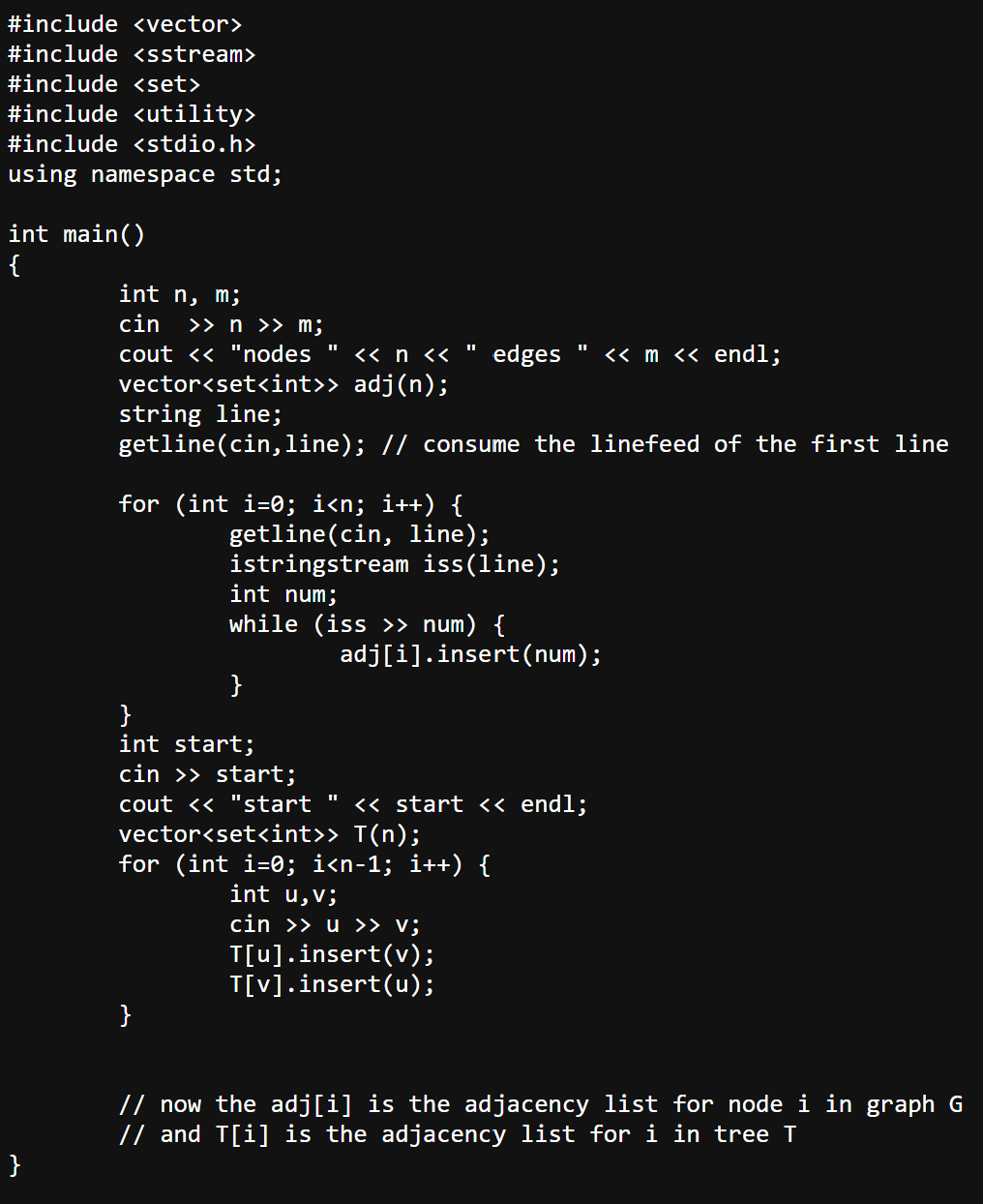
Starter code in the image
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main
int n m;
cin n m;
cout "nodes n edges m endl;
vector adjn;
string line;
getlinecinline; consume the linefeed of the first line
for int i; i num
adjiinsertnum;
int start;
cin start;
cout "start start endl;
vector Tn;
for int i; i u v;
Tuinsertv;
Tvinsertu;
now the adji is the adjacency list for node i in graph G
and Ti is the adjacency list for i in tree T
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


