Question: Given starter code: #include /*import standard io header files*/ int n; // global variable int process( int [][n]); int main () { // read input
Given starter code:
#include/*import standard io header files*/ int n; // global variable int process( int [][n]); int main () { // read input from stdin, and create M, and populate M with trees ......... int M[n][n]; ......... printf("............ "); // pass M to process(), and get the return value int resu = ....; printf("............ "); printf("%d ", resu); } int process(int M[][n]){ // create another matrix C, and record max count ....... // display C and return the max value }
![// global variable int process( int [][n]); int main () { //](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f51bc3e1bba_45966f51bc383389.jpg)

![......... int M[n][n]; ......... printf("............ "); // pass M to process(), and](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f51bc548aa8_46066f51bc4bf45a.jpg)
![resu); } int process(int M[][n]){ // create another matrix C, and record](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f51bc6c78d9_46266f51bc66f7f6.jpg)
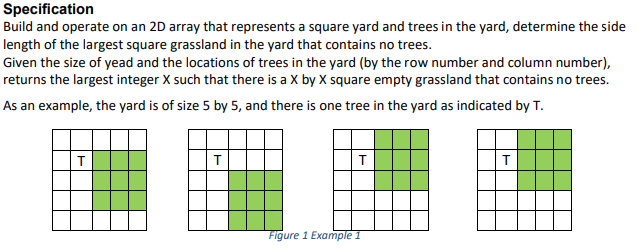
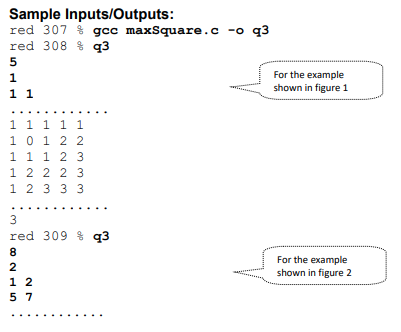
Build and operate on an 2D array that represents a square yard and trees in the yard, determine the side length of the largest square grassland in the yard that contains no trees. Given the size of yead and the locations of trees in the yard (by the row number and column number), returns the largest integer X such that there is a X by X square empty grassland that contains no trees. As an example, the yard is of size 5 by 5 , and there is one tree in the yard as indicated by T. Implementation Download the code maxSquare.c. The program first reads inputs from stdin. There are several lines of input to the program. The first is the width/length of the yard. The second is the number of trees in the yard. This is followed by the locations of the trees, each line for a single tree. For the example shown in figure 1 , the input will be 5 1 1 Based on the inputs, the program then creates a 2D array M that represents the yard, where the locations of trees are marked in the 2D array. Then, passes the 2D array to function process() to calculate the side length of the largest square grassland in the yard that contains no trees. Hint: one brute force solution is to visit each element in the 2D array, treating it as the top-left corner and trying to expand the square until hit a tree. Then we record the max side length and visit next element. The problem with this approach is that there are lots repeated computations. Here we use a more efficient approach: we visit each element in the 2D array row by row. For each element, we consider it as the bottom-right corner of a potential square and try to expand in the up and left directions. Consider several cases: For a cell that is in the first row or the first column of the yard: if it contains a tree, then for this cell we record 0 for it, indicating that no square is possible with this element as bottom-right corner. If there is no tree in this cell, then we record 1 for the cell, as itself is a square (cannot expand up and/or left). For a cell that is not in the first row and first column: if it contains a tree, then for this cell we record 0 for it, indicating that no square is possible. If this cell has no tree, then the largest square with it as bottom-right corner is 1 plus the smallest size among three empty squares: the square above it, above- left of it, and left of it. That is, its expansion is limited by the smallest square from the above, above-left and left squares, plus 1 for itself. As shown in the example below, the cell with ? has above-left cell recorded as 1 , above cell recorded as 2, left cell recorded as 2, so the square size with element ? as right-bottom corner is limited to min{1,2,2}+1=2 as shown in the right figure. Try to convince yourself that this works correctly. By using the information stored for the neighboring cells, the algorithm avoids doing repeated expansions. So, one version of the algorithm for function process() work as follows: - Create another 2D array of same size as M, call it C, to record the length of each element in M. - Visit element in M row by row. For each element M[i][j], if M[i][j] is in first row or first column, then - if M[i][j] contains a tree, then C[i][j] set to 0 , else C[i][j] set to 1 (itself) - if M[i][j] is not in the first row or column, then - if M[i][j] contains a tree, then C[i][j] set to 0 , else C[i][j] set to 1+ min of values stored in the cell above, left, and above-left to C[i][j]. (Since we visit elements row by row, these 3 values must have been available) - Return the max value in C. Sample Inputs/Outputs: red 307 gcc maxsquare.c -o q3 red 308 q3 5 1 For the example 11 shown in figure 1 11111 11123 12223 12333 3 red 309 \& q 3 8 2 For the example 12 shown in figure 2 1111111112222222101233331112344412223455123334561234445612345012
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


