Question: Given that lim f(x) = 0 x - a lim g(x) = 0 x - a lim h(x) = 1 x - a lim p(x)
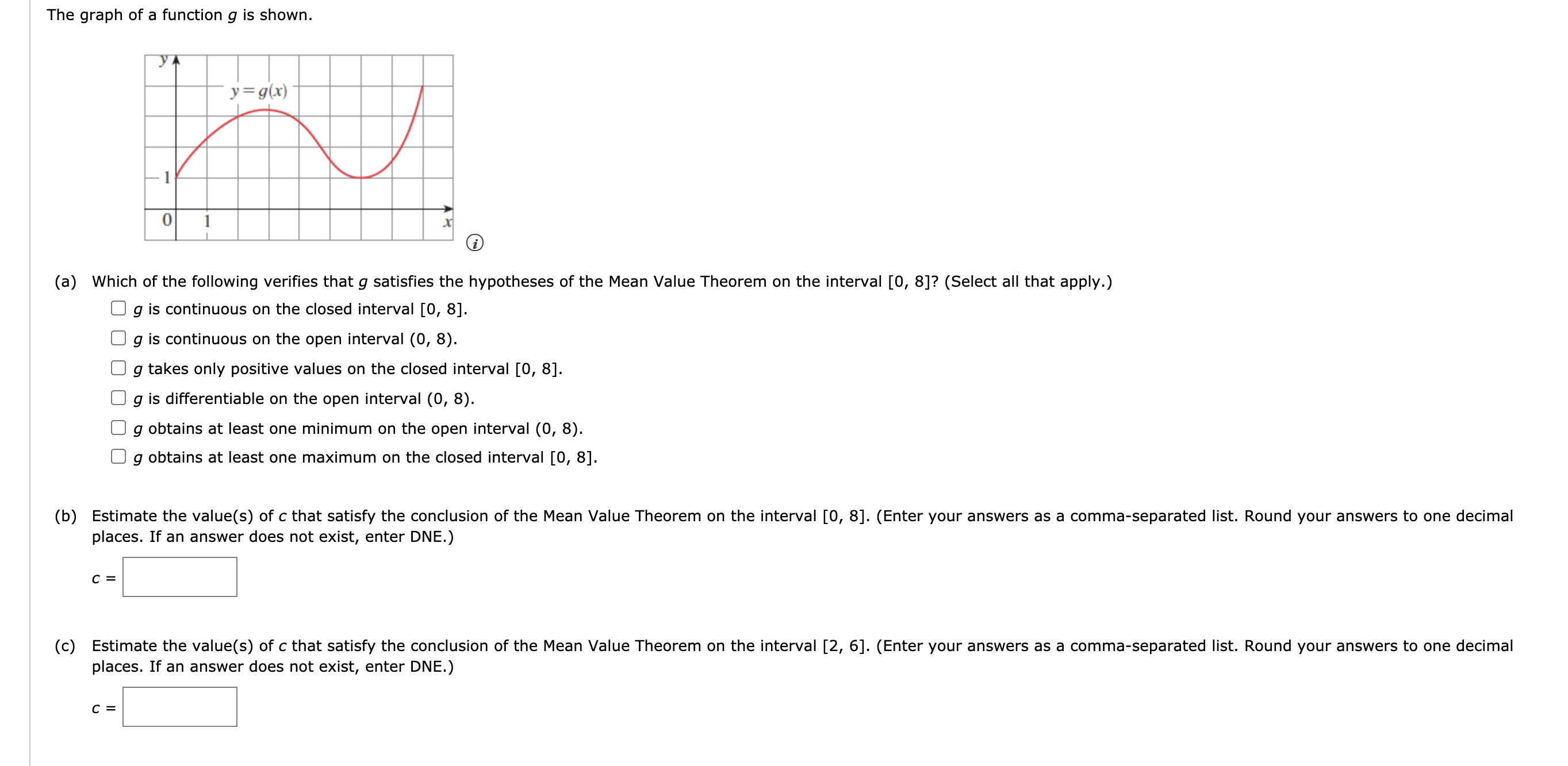
Given that lim f(x) = 0 x - a lim g(x) = 0 x - a lim h(x) = 1 x - a lim p(x) = 0o x- a lim q(x) = 0o, x-a evaluate if the following limits are not indeterminate forms. (If a limit is indeterminate, enter INDETERMINATE.) (a) lim [f(x)p(x)] x - a (b) lim [h(x)p(x)] x- a (c) lim [p(x)q(x)] x - aGiven that lim f(x) = 0 x - a lim g(x) = 0 x- a lim h(x) = 1 X- a lim p(x) = co x - a lim q(x) = 0o, x - a evaluate if the following limits are not indeterminate forms. (If a limit is indeterminate, enter INDETERMINATE.) (a) lim [f(x) - p(x)] x - a (b) lim [p(x) - q(x)] x - a (c) lim [p(x) + q(x)] x - aThe graph of a function g is shown. (a) Which of the following veries that 9 satises the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem on the interval [0, 8]? (Select all that apply.) g is continuous on the closed interval [0, 8]. g is continuous on the open interval (0, 8). 9 takes only positive values on the closed interval [0, 8]. g is differentiable on the open interval (0, 8). g obtains at least one minimum on the open interval (0, 8). g obtains at least one maximum on the closed interval [0, 8]. (b) Estimate the value(s) of c that satisfy the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem on the interval [0, 8]. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list. Round your answers to one decimal places. If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.) C= (c) Estimate the value(s) of c that satisfy the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem on the interval [2, 6]. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list. Round your answers to one decimal places. If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.) c: The graph of a function f is shown. Does f satisfy the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem on the interval [0, 5]? Yes, because f has a maximum on the closed interval [0, 5]. O Yes, because f is continuous on the closed interval [0, 5] and differentiable on the open interval (0, 5). Yes, because f is continuous on the open interval (0, 5) and differentiable on the closed interval [0, 5]. O No, because f is not differentiable on the open interval (0, 5). O No, because f is not continuous on the open interval (0, 5). O No, because f does not have a minimum on the closed interval [0, 5]. X If so, find a value c that satisfies the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem on that interval. (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.)separated list.) Verify that the function satisfies the three hypotheses of Rolle's Theorem on the given interval. Then find all numbers c that satisfy the conclusion of Rolle's Theorem. (Enter your answers as a comma- f (x) = x+ 3 3 C = 4 XDoes the function satisfy the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem on the given interval? f ( x ) =1, X' [1, 2] Yes, it does not matter if f is continuous or differentiable, every function satisfies the Mean Value Theorem. O Yes, f is continuous on [1, 2] and differentiable on (1, 2). O No, f is not continuous on [1, 2]. O No, f is continuous on [1, 2] but not differentiable on (1, 2). There is not enough information to verify if this function satisfies the Mean Value Theorem. If it satisfies the hypotheses, find all numbers c that satisfy the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list. If it does not satisfy the hypotheses, enter DNE).Consider the following. (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.) f(x) = x3 - 3x2 - 24x (a) Find the interval(s) on which f is increasing. (Enter your answer using interval notation.) (b) Find the interval(s) on which f is decreasing. (Enter your answer using interval notation.) (c) Find the local minimum and maximum value of f. local minimum value local maximum valueConsider the equation below. (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.) f ( x) = x2 - x - In(x) (a) Find the interval(s) on which f is increasing. (Enter your answer using interval notation.) Find the interval(s) on which f is decreasing. (Enter your answer using interval notation.) (b) Find the local minimum and maximum value of f. local minimum value local maximum value (c) Find the inflection point. ( x, y ) = Find the interval(s) on which f is concave up. (Enter your answer using interval notation.) Find the interval(s) on which fis concave down. (Enter your answer using interval notation.)Find the local maximum and local minimum values of fusing both the First and Second Derivative Tests. f (x) = x2 X - 8 local maximum value local minimum value
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts






![indeterminate, enter INDETERMINATE.) (a) lim [f(x)p(x)] x - a (b) lim [h(x)p(x)]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/10/671383ba20a59_154671383ba0a714.jpg)
![x- a (c) lim [p(x)q(x)] x - aGiven that lim f(x) =](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/10/671383ba7f29f_154671383ba6165d.jpg)


