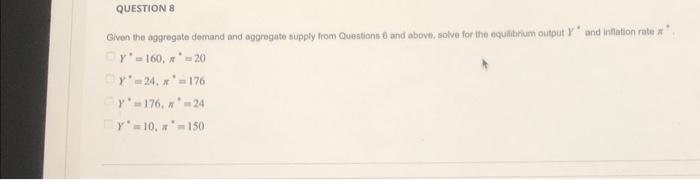
Question: Given the aggregate demand and aggregate supply from Questions 6 and above, solve for the equalibium output ( Y^{*} ) and inflation rate ( pi


![Y^{*}=176, \\pi^{*}=24 \\\\ Y^{*}=10, \\pi^{*}=150 \\end{array} \\] Given the information from Question](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/10/670111bb5de81_323670111bb0cac0.jpg)

Given the aggregate demand and aggregate supply from Questions 6 and above, solve for the equalibium output \\( Y^{*} \\) and inflation rate \\( \\pi \\) \" \\[ \\begin{array}{l} Y^{*}=160, \\pi^{*}=20 \\\\ Y^{*}=24, \\pi^{*}=176 \\\\ Y^{*}=176, \\pi^{*}=24 \\\\ Y^{*}=10, \\pi^{*}=150 \\end{array} \\] Given the information from Question 6.9 above, Which statement best accurately describes a position which a central bank could take when comparing the short-run and long-ran scenarios that the economy is facing? The economy in producing above its potential eutput and is experiencing unemployment below its natural level. The centrai bank could take a tighter monetary policy and sell more bonds in order to cool down the economy and avold higher levels of inliation in the future. The economy is producing above its potental output and is experiencing unemployment aboht its natural level. The central bank could take a Bighter monetary policy by selling more bonds in order to slow down the economy and bring if back to lorng-ruri equiliturium. The economy is producing below its potential output and is experiencing unemployment above its naturn level. The central bank could take a looser monetary policy by buying more bonds in order to stimulate the economy and bring it out of recesalon. The economy is producing below its potential oulput and is experiencing unemployment above its natural ievel. The central bank could take a tighter monetary policy by seling more bonds in order to cool down the econormy in order to avoid higher levels of infation in the future. Suppose that the is curve and monetary policy curve are given, respectively, by \\[ Y=200-4 r \\] and \\[ r=\\frac{1}{4} \\pi . \\] Solve for the aggregate demand curve. \\[ \\begin{array}{l} \\pi=100-\\frac{1}{2} Y \\\\ \\pi=200-Y \\\\ \\pi=200-\\frac{1}{2} Y \\\\ \\pi=400-\\frac{1}{4} Y \\end{array} \\] Suppose that the Phillp's curve and Okur's law are gwen, respectively, by \\[ \\pi=\\pi^{t}-\\frac{1}{2}\\left(U-U^{n}\ ight) \\] and \\[ U-U^{n}=-\\frac{1}{2}\\left(Y-Y^{n}\ ight) \\] Where \\( \\pi^{e} \\) is expected infation, \\( U^{n} \\) is the natural rate of unemployment, and \\( Y^{\\prime \\prime} \\) is potantal Kutput. Supposing that \\( \\pi^{e}=5, U^{n}=40 \\), and \\( \\gamma^{F}=100 \\), solve for the agoregate supply curve \\[ \\begin{array}{l} \\pi=-20+\\frac{1}{4} Y \\\\ \\pi=20+\\frac{1}{4} Y \\\\ \\pi=-20+\\frac{1}{2} Y \\\\ \\pi=20+\\frac{1}{2} Y \\end{array} \\] Based on your answers from \\( 6-8 \\) abovo, what is the unemployment rate in the economy? \\( U=0 \\) \\( U=2 \\) \\( U=4 \\) \\( U=6 \\) Given the aggregate demand and aggregate supply from Questions 6 and above, solve for the equalibium output \\( Y^{*} \\) and inflation rate \\( \\pi \\) \" \\[ \\begin{array}{l} Y^{*}=160, \\pi^{*}=20 \\\\ Y^{*}=24, \\pi^{*}=176 \\\\ Y^{*}=176, \\pi^{*}=24 \\\\ Y^{*}=10, \\pi^{*}=150 \\end{array} \\] Given the information from Question 6.9 above, Which statement best accurately describes a position which a central bank could take when comparing the short-run and long-ran scenarios that the economy is facing? The economy in producing above its potential eutput and is experiencing unemployment below its natural level. The centrai bank could take a tighter monetary policy and sell more bonds in order to cool down the economy and avold higher levels of inliation in the future. The economy is producing above its potental output and is experiencing unemployment aboht its natural level. The central bank could take a Bighter monetary policy by selling more bonds in order to slow down the economy and bring if back to lorng-ruri equiliturium. The economy is producing below its potential output and is experiencing unemployment above its naturn level. The central bank could take a looser monetary policy by buying more bonds in order to stimulate the economy and bring it out of recesalon. The economy is producing below its potential oulput and is experiencing unemployment above its natural ievel. The central bank could take a tighter monetary policy by seling more bonds in order to cool down the econormy in order to avoid higher levels of infation in the future. Suppose that the is curve and monetary policy curve are given, respectively, by \\[ Y=200-4 r \\] and \\[ r=\\frac{1}{4} \\pi . \\] Solve for the aggregate demand curve. \\[ \\begin{array}{l} \\pi=100-\\frac{1}{2} Y \\\\ \\pi=200-Y \\\\ \\pi=200-\\frac{1}{2} Y \\\\ \\pi=400-\\frac{1}{4} Y \\end{array} \\] Suppose that the Phillp's curve and Okur's law are gwen, respectively, by \\[ \\pi=\\pi^{t}-\\frac{1}{2}\\left(U-U^{n}\ ight) \\] and \\[ U-U^{n}=-\\frac{1}{2}\\left(Y-Y^{n}\ ight) \\] Where \\( \\pi^{e} \\) is expected infation, \\( U^{n} \\) is the natural rate of unemployment, and \\( Y^{\\prime \\prime} \\) is potantal Kutput. Supposing that \\( \\pi^{e}=5, U^{n}=40 \\), and \\( \\gamma^{F}=100 \\), solve for the agoregate supply curve \\[ \\begin{array}{l} \\pi=-20+\\frac{1}{4} Y \\\\ \\pi=20+\\frac{1}{4} Y \\\\ \\pi=-20+\\frac{1}{2} Y \\\\ \\pi=20+\\frac{1}{2} Y \\end{array} \\] Based on your answers from \\( 6-8 \\) abovo, what is the unemployment rate in the economy? \\( U=0 \\) \\( U=2 \\) \\( U=4 \\) \\( U=6 \\)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


