Question: Given the distances computed, we can find the closest centroid for each data point. We store this information in a 1m array, and each element
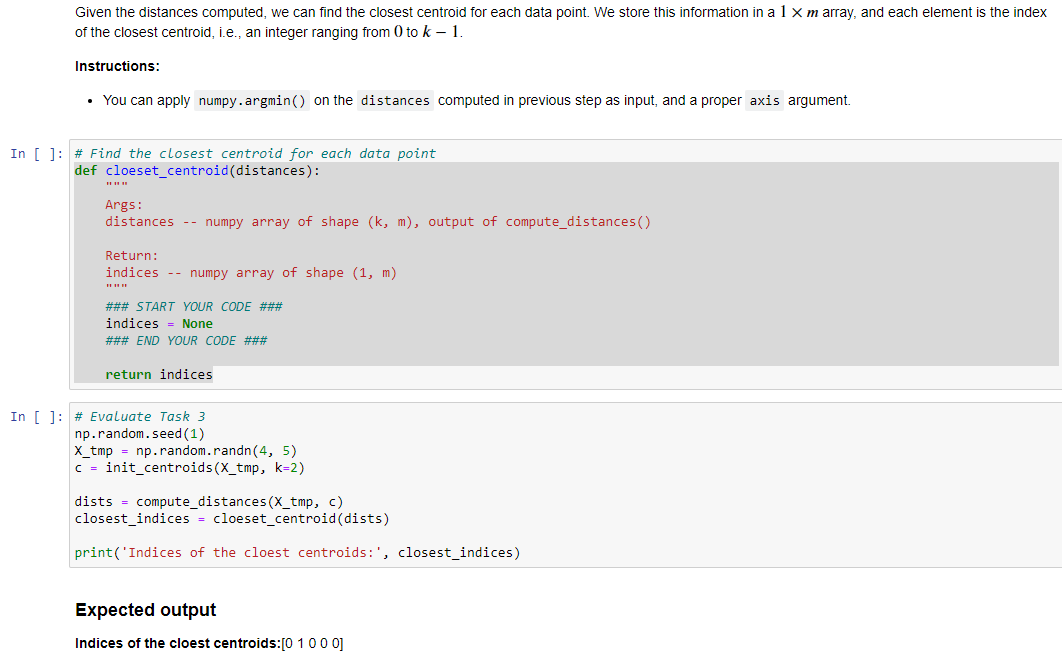
Given the distances computed, we can find the closest centroid for each data point. We store this information in a 1m array, and each element is the index of the closest centroid, i.e., an integer ranging from 0 to k1. Instructions: - You can apply numpy.argmin() on the computed in previous step as input, and a proper argument. \# Find the closest centroid for each data point def cloeset_centroid(distances): Args: distances -- numpy array of shape (k,m), output of compute_distances() Return: indices -- numpy array of shape (1,m) \#"\# START YOUR CODE \#\#\# indices = None \#\#\# END YOUR CODE \#\#\# return indices \# Evaluate Task 3 np.random.seed(1) X_tmp = np.random.randn(4, 5) c = init_centroids(X_tmp, k=2) dists = compute_distances(X_tmp, c) closest_indices = cloeset_centroid(dists) print('Indices of the cloest centroids: ', closest_indices) Expected output Indices of the cloest centroids: [01000]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


