Question: Given the following Java code: public class A { private int x = 30; } public class B extends A{ public void b(){ System.out.print(x); }


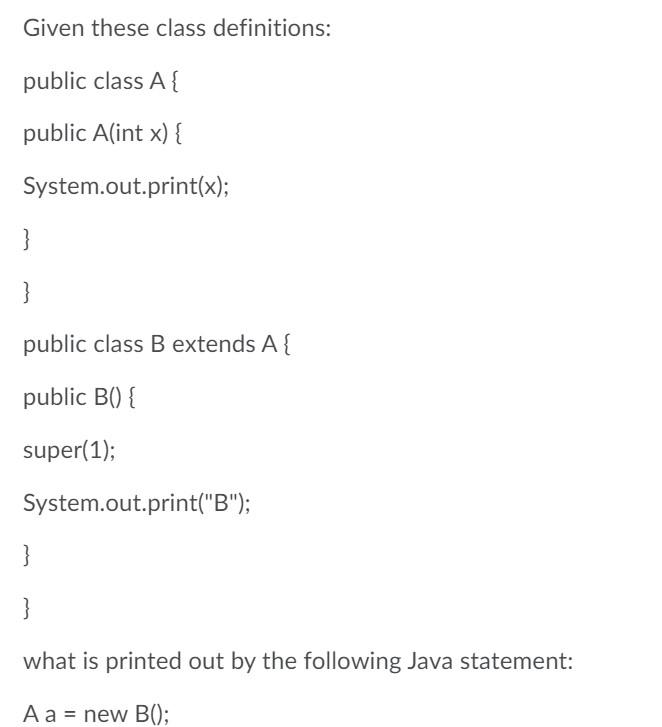
Given the following Java code: public class A { private int x = 30; } public class B extends A{ public void b(){ System.out.print(x); } } what would be the result of the statements: B b = new B(); b.b(); In the following Java code fragment: public class MyClass { public void a() { int p; p = 98; } public void b() { al); /* state of p here?*/ } } Given these class definitions: public class A { public A(int x) { System.out.print(x); } } public class B extends A{ public B() { super(1); System.out.print("B"); } } what is printed out by the following Java statement: A a = new B()
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


