Question: Given the following, solve the Page Table: Any help would be appreciated! Problem 2 (Page Table Implementation 29 pts) In a paging system, the process'
Given the following, solve the Page Table:

Any help would be appreciated!
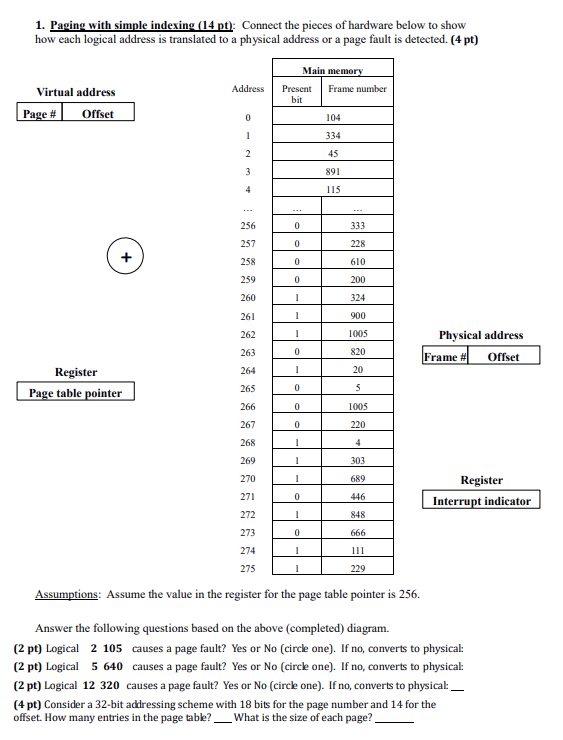
Problem 2 (Page Table Implementation 29 pts) In a paging system, the process' space is divided into consecutive pages of fixed length: Page 0, Page I, Page 2, etc. As such, a logical address (also called a virtual address) consists of Virtual address . A page number . An offset within that page Page # Offset In a paging system, main memory is divided into consecutive frames of fixed length (same length as the pages) Frame 0, Frame 1, Frame 2, etc. Some of the logical pages are placed in the physical frames. For example, pages 3, 8 and 10 might be placed in frames 104, 87 and 378, respectively, with the other pages of the process in virtual memory, i.e., on disk (or other form of secondary memory) The goal of this exercise is to help you understand the Simple indexing and Multi-level indexing for converting a logical address (page number+ offset) to a physical address (frame number offset, or a page fault if the page is not in main memory) Throughout this exercise, logical addresses and physical addresses are written as pairs of numbers (page number offset for logical addresses, frame number/offset for physical addresses). Problem 2 (Page Table Implementation 29 pts) In a paging system, the process' space is divided into consecutive pages of fixed length: Page 0, Page I, Page 2, etc. As such, a logical address (also called a virtual address) consists of Virtual address . A page number . An offset within that page Page # Offset In a paging system, main memory is divided into consecutive frames of fixed length (same length as the pages) Frame 0, Frame 1, Frame 2, etc. Some of the logical pages are placed in the physical frames. For example, pages 3, 8 and 10 might be placed in frames 104, 87 and 378, respectively, with the other pages of the process in virtual memory, i.e., on disk (or other form of secondary memory) The goal of this exercise is to help you understand the Simple indexing and Multi-level indexing for converting a logical address (page number+ offset) to a physical address (frame number offset, or a page fault if the page is not in main memory) Throughout this exercise, logical addresses and physical addresses are written as pairs of numbers (page number offset for logical addresses, frame number/offset for physical addresses)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


