Question: Given the following structure: struct Data { int n; char* name; int* arr[3]; }; n 33 name ? 7 0 0 0 0 arr -
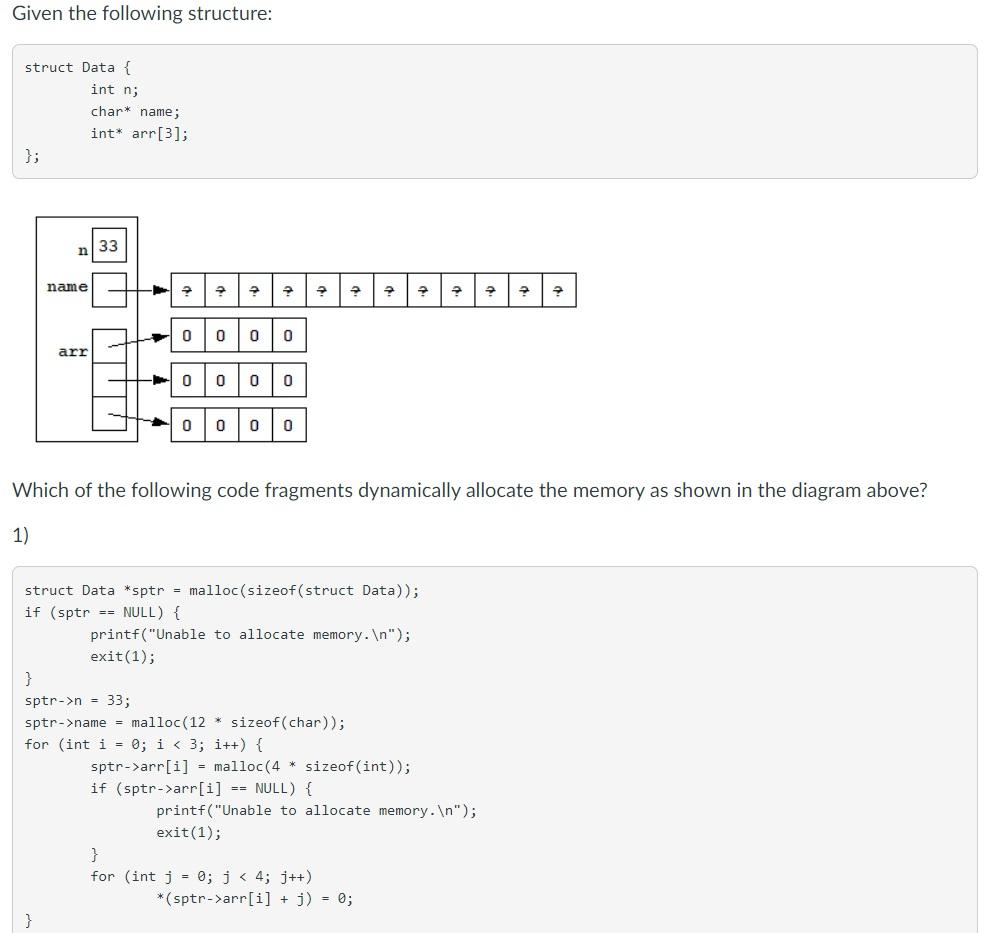
![int* arr[3]; }; n 33 name ? 7 0 0 0 0](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f55753665ce_70766f55753048ba.jpg)
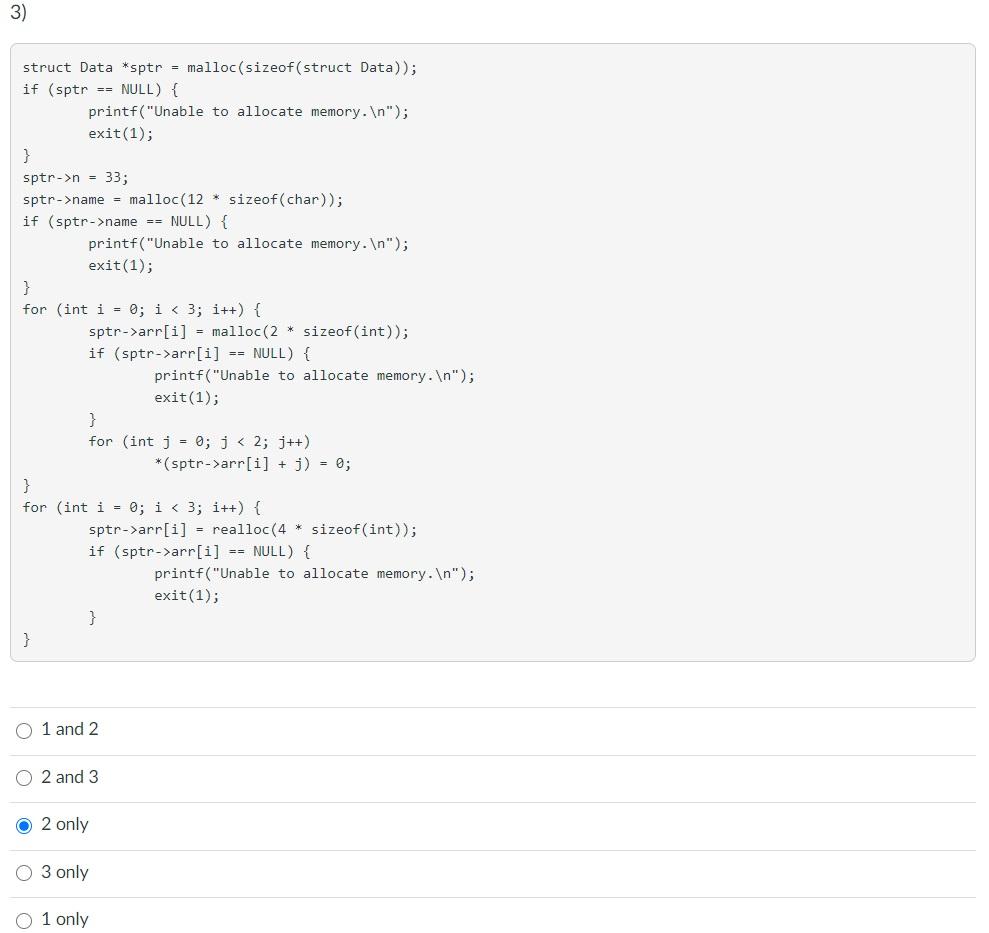
Given the following structure: struct Data { int n; char* name; int* arr[3]; }; n 33 name ? 7 0 0 0 0 arr - 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Which of the following code fragments dynamically allocate the memory as shown in the diagram above? 1) struct Data *sptr = malloc(sizeof(struct Data)); if (sptr == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory. "); exit(1); } sptr->n = 33; sptr->name = malloc(12 * sizeof(char)); for (int i = 0; i arr[i] = malloc(4 * sizeof(int)); if (sptr->arr[i] == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory. "); exit(1); } for (int j = 0; j arr[i] + j) = 0; 2) struct Data *sptr = malloc(sizeof(struct Data)); if (sptr == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory. "); exit(1); } sptr->n = 33; sptr->name = malloc(12 * sizeof(char)); if (sptr->name == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory. "); exit(1); } for (int i = 0; i arr[i] = malloc(4 * sizeof(int)); if (sptr->arr[i] == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory. "); exit(1); } for (int j = 0; j arr[i] + i) = 0; } 3) struct Data *sptr = malloc(sizeof(struct Data)); if (sptr == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory. "); exit(1); } sptr->n = 33; sptr->name = malloc(12 * sizeof(char)); if (sptr->name == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory. "); exit(1); } for (int i = 0; i arr[i] = malloc(2 * sizeof(int)); if (sptr->arr[i] == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory. "); exit(1); } for (int j = 0; j arr[i] + 1) = 0; } for (int i = 0; i arr[i] = realloc(4 * sizeof(int)); if (sptr->arr[i] == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory. In"); exit(1); } } 0 1 and 2 0 2 and 3 O 2 only O 3 only O1 only
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


