Question: Given the information on the LP model given above, please fill out and add any additinal information needed to the Excel format of the LP


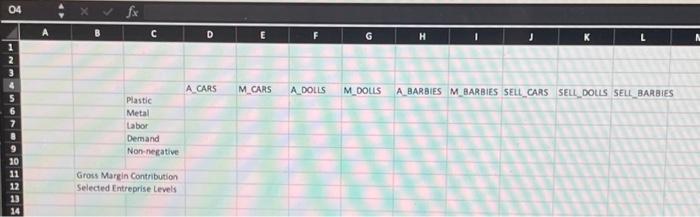
Topic: The management problem I would like to address that can be represented and solved as a linear programming model is production planning. In this scenario, the objective is to maximize the profit by determining the optimal number of units to be produced for each product type, given certain constraints such as available resources and demand. To show this, I will use the example of a toy manufacturer that produces three types of toys, toy cars, dolls, and barbies. The manufacturer will have a limited amount of plastic and metal available to produce the toys, as well as a limited amount of labor hours. These will be used as my constraints. The manufacturer can sell up to 1,000 toy cars, up to 800 dolls per week, and up to 900 barbies per week. The linear programming can be formulated as follows: Decision variables: A_CARS = number of cars produced automatically per week M_CARS = number of toy cars produced manually per week A_DOLLS = number of dolls produced automatically per week M_DOLLS = number of dolls produced manually per week A_BARBIES = number of barbies produced automatically per week M_BARBIES = number of barbies produced manually per week S_CARS = number of car toys sold per week S_DOLLS = number of dolls sold per week S_BARBIES = number of barbies sold per week Objective function: Maximize profit =50 P_CARS +60 P__OLLS +70 P_BARBIES Constraints: - Plastic constraints: 2P_CARS + P_DOLLS + 1.5P_BARBIES =2,000 - Metal constraints: P_CARS + 2P_DOLLS + 1.5p_BARBIES =0 \[ \begin{array}{l} \text { P_DOLLS }>=0 \\ \text { P_BARBIES }>=0 \end{array} \] In this model, the objective function represents the profit, which is calculated as the product of the number of units produced and their respective profit margins. The constraints represent the limitations in the production process, such as availability of raw material and labor hours, as well as the demand for the products. Topic: The management problem I would like to address that can be represented and solved as a linear programming model is production planning. In this scenario, the objective is to maximize the profit by determining the optimal number of units to be produced for each product type, given certain constraints such as available resources and demand. To show this, I will use the example of a toy manufacturer that produces three types of toys, toy cars, dolls, and barbies. The manufacturer will have a limited amount of plastic and metal available to produce the toys, as well as a limited amount of labor hours. These will be used as my constraints. The manufacturer can sell up to 1,000 toy cars, up to 800 dolls per week, and up to 900 barbies per week. The linear programming can be formulated as follows: Decision variables: A_CARS = number of cars produced automatically per week M_CARS = number of toy cars produced manually per week A_DOLLS = number of dolls produced automatically per week M_DOLLS = number of dolls produced manually per week A_BARBIES = number of barbies produced automatically per week M_BARBIES = number of barbies produced manually per week S_CARS = number of car toys sold per week S_DOLLS = number of dolls sold per week S_BARBIES = number of barbies sold per week Objective function: Maximize profit =50 P_CARS +60 P__OLLS +70 P_BARBIES Constraints: - Plastic constraints: 2P_CARS + P_DOLLS + 1.5P_BARBIES =2,000 - Metal constraints: P_CARS + 2P_DOLLS + 1.5p_BARBIES =0 \[ \begin{array}{l} \text { P_DOLLS }>=0 \\ \text { P_BARBIES }>=0 \end{array} \] In this model, the objective function represents the profit, which is calculated as the product of the number of units produced and their respective profit margins. The constraints represent the limitations in the production process, such as availability of raw material and labor hours, as well as the demand for the products.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


