Question: Given the interface of the container class below: // Container with dynamic storage #include #include using namespace std; class container { friend ostream& operator //
Given the interface of the container class below:
// Container with dynamic storage
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class container {
friend ostream& operator
// Postcondition: displays # of values stored in the container, storage capacity of the contianer, and stored values in the container
// in the following format: Array size = 3, capacity = 4, contents = 11, 22, 33 (see below sample program output
public:
container();
// Postcondition: set dynamic storage capacity to 1 and count to -1 where (count + 1) represents the actual values stored
// in the container. Notice that data member count is used as the subscript to access elements (actual values) stored
// in the dynamic array; thus (count + 1) represents the total # of values that are currently stored in the array
container(int n);
// Postcondition: set dynamic storage (data array) capacity to n and count to -1
container(container &);
// Programmer-supplied copy constructor is necessary to avoid memory leak and other side effect
// Postcondition: a new container class object is created which is the same as the one passed to the function
~container();
// Programmer-supplied destructor is necessary to avoid memory leak
// Postcondition: all dynamic memory locations have been returned back to the heap whenever a container object goes out of scope
container& operator=(const container &rhs);
// Programmer-supplied overloaded assignment is necessary to avoid memory leak and other side effect
// Postconditoin: the container object rhs is assigned to the calling object
void insert(int);
// Postcondition: if the container is not full, the value passed to the function is stored in
// the first available element of the dynamic array. Otherwise the function calls the private
// "allocate" member function requesting a new set of dynamic memory with twice the previous storage capacity
// the insert function then increments count by 1 and insert the value into the new and larger array.
void remove();
// Precondition: the data array must not be empty; i.e., count must be greater than or equal to 0.
// Postcondition: if the container is not empty, then remove the most recently stored value ifrom the container and
// decrement count by 1; otherwise, display the message "The container is empty; no action is taken!"
int operator[](int sub);
// Precondition: value passed to the function must be a positive integer including 0
// Postcondition: the value of stored in data[sub] is returned; if sub is out of range, display a message and terminate the program .
bool isFull();
// Postcondition: return true if the container is full; return false otherwise
bool isEmpty();
// Postcondition: return true if the container is empty; return false otherwise
int Capacity();
// Notice uppercase 'C' to avoid conflict with data member named "capacity"
// Postcondition: returns the current storage capacity of the container
int size();
// Postcondition: returns the # of elements (# of objects) currently stored in the container
void resize(int n);
// Postcondition: container (i.e., the dynamic array) is resized to n; contents of existing container have been copied to the new array;
// old array is deleted to avoid memory leak.
private:
void allocate();
// Postcondition: 1) the capacity of the container has been doubled, 2) existing values in the existing array have been copied to
// the new and larger dynamic array, 3) memory of the old array has been deleted (returned to "heap").
int *data;
int capacity; // indicates the storage capcity of the container, i.e., the size of the dynamic array
int count; // used as a subscript to index into the array; size = count + 1
};
Implement all member and friend functions of the class and write a main function to generate an output similar to the following sample output. Make sure the Big-3 are properly coded such that there is no memory leak and any side effect.
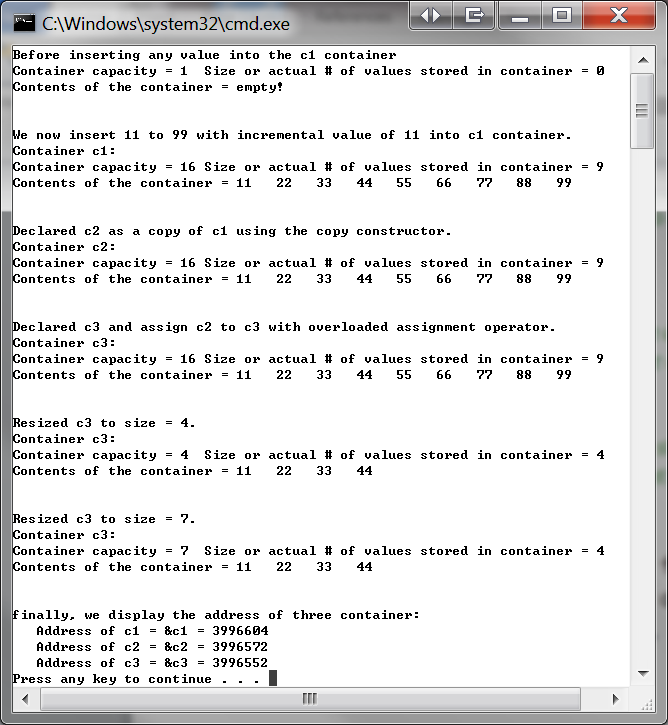
C: Windows system32\cmd.exe efore inserting any value into the cl container ontainer capac ity = 1 Size or actual # of values stored in container ontents of the container - empty! e now insert 11 to 99 with incremental value of 11 into ci container. ontainer c1: ontainer capac ity = 16 Size or actual # of value s stored in container 9 ontents of the container 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 eclared c2 as a copy of c1 using the copy constructor. ontainer c2: ontainer capac ity = 16 Size or actual # of value s stored in container 9 ontents of the container 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 eclared c3 and assign c2 to c3 with overloaded assignment operator. ontainer c3: ontainer capac ity = 16 Size or actual # of value s stored in container 9 ontents of the container 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 esized c3 to size-4. ontainer c3: ontainer capac ity = 4 Size or actual # of values stored in container 4 ontents of the container 11 22 3344 esized c3 to size-7 ontainer c3: ontainer capac ity = ? Size or actual # of values stored in container 4 ontents of the container 11 22 3344 inally. we display the address of three container: Address of c1- &c1 Address of c2- &c2 Address of c3-&c3 3996604 3996572 3996552 ress any key to continue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


