Question: Given the Singly Linked List interface a presented in class, implement the insertAfter function for a null-terminated list. Insert at the beginning of a list
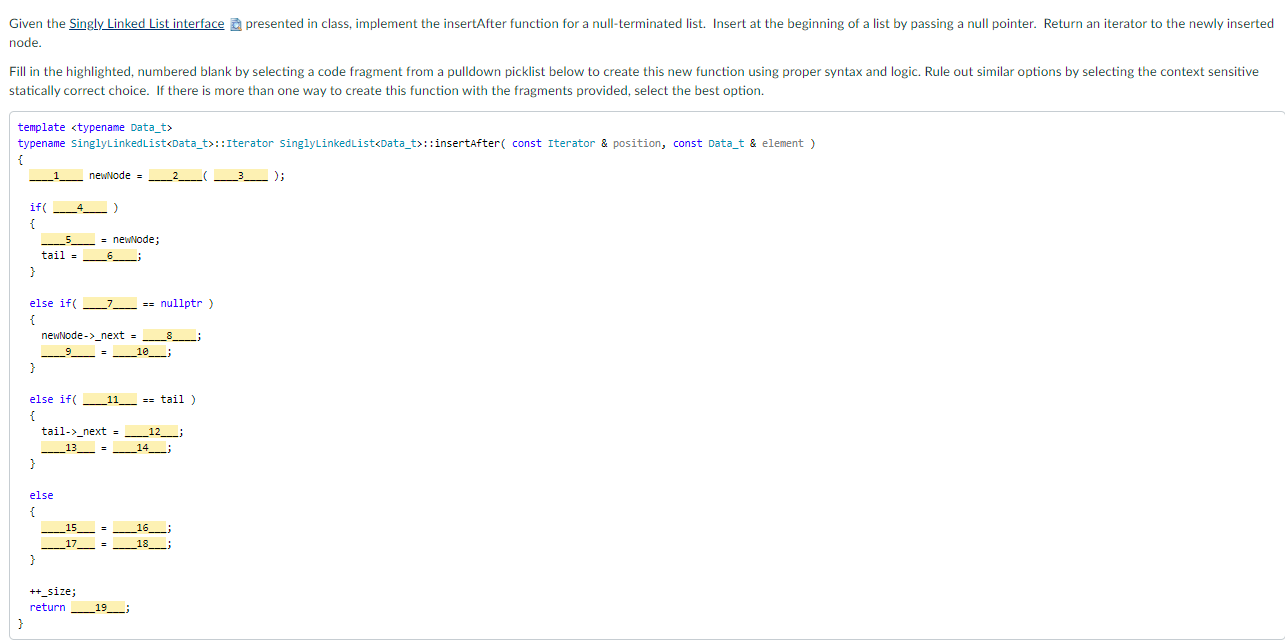
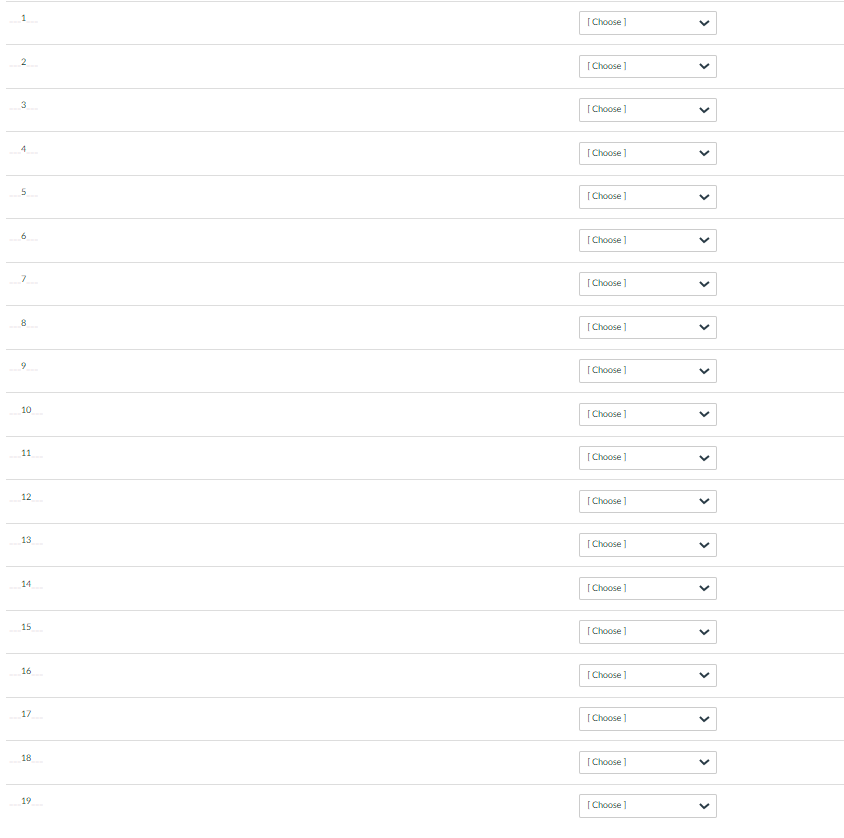

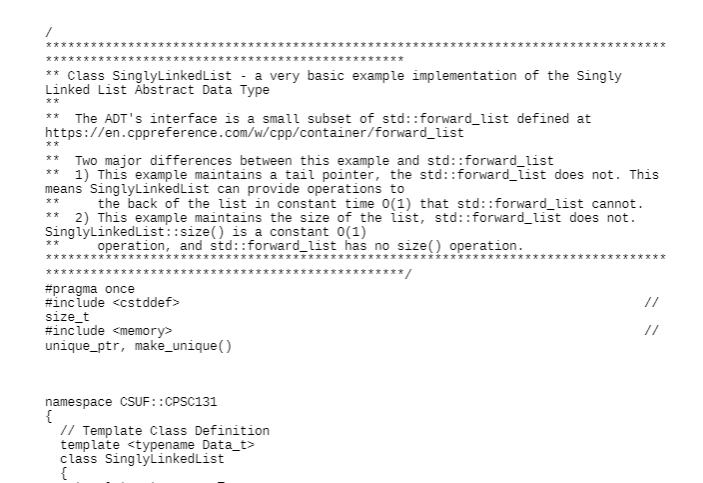




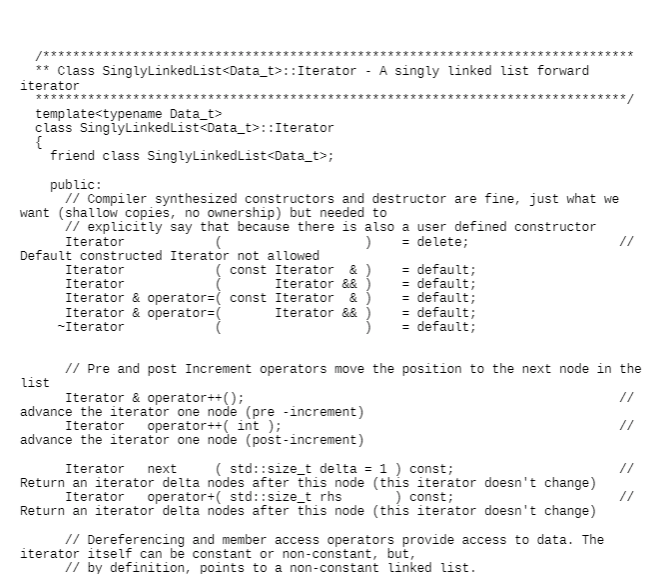

Given the Singly Linked List interface a presented in class, implement the insertAfter function for a null-terminated list. Insert at the beginning of a list by passing a null pointer. Return an iterator to the newly inserted node. Fill in the highlighted, numbered blank by selecting a code fragment from a pulldown picklist below to create this new function using proper syntax and logic. Rule out similar options by selecting the context sensitive statically correct choice. If there is more than one way to create this function with the fragments provided, select the best option. template typename SinglyLinkedList::Iterator SinglyLinkedList:: insertAfter( const Iterator & position, const Data_t & element) { newNode = ( 3___); if { 5_= newNode; tail = } else if == nullptr ) newNode->_next = _____8____ _10__ } else if(__11__ == tail ) { tail->_next = 12___ 13 _14___ } else { _17_ = ___16___ __18___; } ++_size; return ____19_3 } 1 [Choose1 2 Choose1 3 Choose1 next newNode->_next position->_next tail new Node head Node * Element head->next *** ******** ****** *********** ** Class SinglyLinkedlist - a very basic example implementation of the Singly Linked List Abstract Data Type The ADT's interface is a small subset of std::forward_list defined at https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/forward_list Two major differences between this example and std::forward_list ** 1) This example maintains a tail pointer, the std:: forward_list does not. This means SinglyLinkedList can provide operations to the back of the list in constant time 0(1) that std:: forward_list cannot. 2) This example maintains the size of the list, std:: forward_list does not. SinglyLinkedList::size() is a constant 0(1) operation, and std::forward_list has no size() operation. **********/ #pragma once #include // size_t #include unique_ptr, make_unique() **** ************* ******* namespace CSUF::CPSC131 { // Template Class Definition template class SinglyLinkedList { template friend void swap( SinglyLinkedList & lhs, SinglyLinkedList & rhs ); The expected way to make a program-defined type swappable is to provide a non-member function swap in the same namespace as the type. (https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/algorithm/swap) public: // Types class Iterator; A forward iterator // // Constructors, destructor, and assignments SinglyLinkedList(); empty list constructor SinglyLinkedList (const SinglyLinkedList & original ); copy constructor SinglyLinkedList & operator=( SinglyLinkedlist rhs ); copy assignment (rhs intentionally passed by value) -SinglyLinkedList(); destructor // Queries bool empty() const; returns true if list has no items std::size_t size () const; returns the number of elements in the list const Data_t & front const; return List's front element (r-value) const Data_t & back (const; return list's back element (r-value) // Mutators Data_t & front 0; return list's front element (L-value) Data_t & back O; return list's back element (L-value) void clear 0; remove all elements setting size to zero void pushFront (const Data_t & element ); add element to front of list void pushBack (const Data_t & element); add element to back of list void popFront (); remove element at front of list void popBack ( = delete; intentionally not provided - cannot remove a node after the last one Iterator insertAfter( const Iterator & position, const Data_t & element );// Inserts element into list after the one occupied at position and returns an iterator to the newly inserted element Iterator removeAfter{ const Iterator & position );// Removes from list the element after the one occupied at position and returns an iterator to the element after the one removed // Iterators Iterator beforeBegin() const; Returns an Iterator that precedes the list's front element. Do not dereference this Iterator Iterator begin ( const; Returns an Iterator to the list's front element, end() if list is empty Iterator end O const; Returns an Iterator beyond the list's back element. Do not dereference this Iterator private: struct Node; Specific implementations are responsible for defining their node structure struct Private Members; A specific implementation's private members (attributes, functions, etc) std::unique_ptr::Iterator - A singly linked list forward iterator ******** **/ template class SinglyLinkedList::Iterator { friend class SinglyLinkedList; public: 1 Compiler synthesized constructors and destructor are fine, just what we want (shallow copies, no ownership) but needed to 1/ explicitly say that because there is also a user defined constructor Iterator ) = delete; Default constructed Iterator not allowed Iterator (const Iterator & ) =default; Iterator Iterator && ) = default; Iterator & operator= const Iterator & = default; Iterator & operators Iterator && ) = default; Iterator =default; // Pre and post Increment operators move the position to the next node in the list Iterator & operator++(); advance the iterator one node (pre - increment) Iterator operator++ int ); advance the iterator one node (post-increment) Iterator next (std::size_t delta = 1 ) const; Return an iterator delta nodes after this node (this iterator doesn't change) Iterator operator+( std::size_t rhs const; Return an iterator delta nodes after this node (this iterator doesn't change) // Dereferencing and member access operators provide access to data. The iterator itself can be constant or non-constant, but, // by definition, points to a non-constant linked list. Data_t & operator const; Data_t * operator-> const; // Equality operators bool operator==( const Iterator & rhs ) const; bool operator != const Iterator & rhs ) const; private: Node * _nodePtr = nullptr; Iterator( Node * position); Implicit conversion constructor from pointer-to-Node to Iterator-to-Node Node * operator const; Convenience function to return the node pointed at (i.e., _nodeptr) }; // SinglyLinkedList::Iterator } 1/ namespace CSUF::CPSC131 // Including template definitions here allows a consistent approach of separating interface (header file) from implementation (source file) #include "SinglyLinkedlist.hxx














