Question: Goal: to implement circular-array-based queues and run a simple simulation. Program structure . The interface of Queue ADT is given in this file: Queue.java .

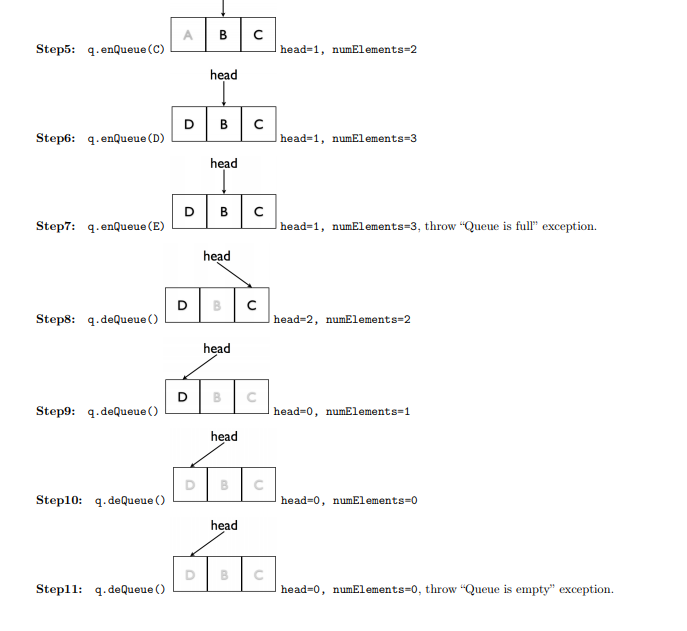

Goal: to implement circular-array-based queues and run a simple simulation. Program structure . The interface of Queue ADT is given in this file: Queue.java . The data structure and constructor of Queue is defined in this file: BasicQueue.java You will need to implement the operations defined in the interface. You will also need to create an application to test the Queue ADT. More specifications on the test driver (QueueingSimulation.java) can be found in the next exercise. . Tip: you should also make a simple test driver (testQueue.java) as how we did in previous labs to test every method as you finish implementing each to correct any compiling errors on time. The program should build an array-based queue ADT, and test out each function to make sure they work. To avoid shifting data in the array, a technique can be used to build circular-array-based queues by using the modulo operation. An example is given as follows to show you the general idea of circular array head Stepl: Instantiate a queue (q) of size 3. head=0, numElements=0 head Step2: q.enQueue(A) head-0, numElements-1 head AB Step3: q.enQueue (B) head-0, numElements-2 ea AB Step4: q.deQueue() head-1, numElements-1 Step5: q.enQueue (C) head-1, numElements-2 head Step6: q.enQueue (D) head-1, numElements-3 ea Step7: q.enQueue (E) head-1, numElements-3, throw Queue is full exception. ea Step8: q.deQueueO) head-2, numElements-2 ea Step9: q.deQueueO) head-0, numElements-1 head Step10: q.deQueue ) head-0, numElements-0 head Stepl: q.deQueue ) head-0, numElements-0, throw "Queue is empty" exception. Build the following program to test out the queue, name it as QueueingSimulation.java. . The goal is to model a counter that appears in many services with a lineup. Every person "takes and when a new position is available a "next number is called". The number is incremented by on one is taken . Create a queue of size 5, which is the maximum size of the store/ineup. . Continually ask the user to "enter t to take a number, c to call a number or q to quit" .If they enter 't', t should add the next number to the queue and display the number to the screen .If they enter 'c', t should remove the last number from the queue and display it to the screen. . If they enter 'q' t should terminate the program. . If the queue is empty, it should not be possible to leave the lineup . If the queue is full, it should not be possible to take a number Below is a sample run: > run QueueingSimulation Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit: You have number 1 Current line up is: 1 Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit: The number 1 should leave the line Current line up is Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit: The queue is empty already Current line up is Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit: You have number 2 Current line up is: 2 Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit: Goal: to implement circular-array-based queues and run a simple simulation. Program structure . The interface of Queue ADT is given in this file: Queue.java . The data structure and constructor of Queue is defined in this file: BasicQueue.java You will need to implement the operations defined in the interface. You will also need to create an application to test the Queue ADT. More specifications on the test driver (QueueingSimulation.java) can be found in the next exercise. . Tip: you should also make a simple test driver (testQueue.java) as how we did in previous labs to test every method as you finish implementing each to correct any compiling errors on time. The program should build an array-based queue ADT, and test out each function to make sure they work. To avoid shifting data in the array, a technique can be used to build circular-array-based queues by using the modulo operation. An example is given as follows to show you the general idea of circular array head Stepl: Instantiate a queue (q) of size 3. head=0, numElements=0 head Step2: q.enQueue(A) head-0, numElements-1 head AB Step3: q.enQueue (B) head-0, numElements-2 ea AB Step4: q.deQueue() head-1, numElements-1 Step5: q.enQueue (C) head-1, numElements-2 head Step6: q.enQueue (D) head-1, numElements-3 ea Step7: q.enQueue (E) head-1, numElements-3, throw Queue is full exception. ea Step8: q.deQueueO) head-2, numElements-2 ea Step9: q.deQueueO) head-0, numElements-1 head Step10: q.deQueue ) head-0, numElements-0 head Stepl: q.deQueue ) head-0, numElements-0, throw "Queue is empty" exception. Build the following program to test out the queue, name it as QueueingSimulation.java. . The goal is to model a counter that appears in many services with a lineup. Every person "takes and when a new position is available a "next number is called". The number is incremented by on one is taken . Create a queue of size 5, which is the maximum size of the store/ineup. . Continually ask the user to "enter t to take a number, c to call a number or q to quit" .If they enter 't', t should add the next number to the queue and display the number to the screen .If they enter 'c', t should remove the last number from the queue and display it to the screen. . If they enter 'q' t should terminate the program. . If the queue is empty, it should not be possible to leave the lineup . If the queue is full, it should not be possible to take a number Below is a sample run: > run QueueingSimulation Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit: You have number 1 Current line up is: 1 Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit: The number 1 should leave the line Current line up is Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit: The queue is empty already Current line up is Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit: You have number 2 Current line up is: 2 Enter t to take a number, or c call next number or q to quit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


