Question: Graphical Relationship between Work Done and Kinetic Eneriy Abstract: This experiment aimed to explow the relationship between the work done on an object moving on

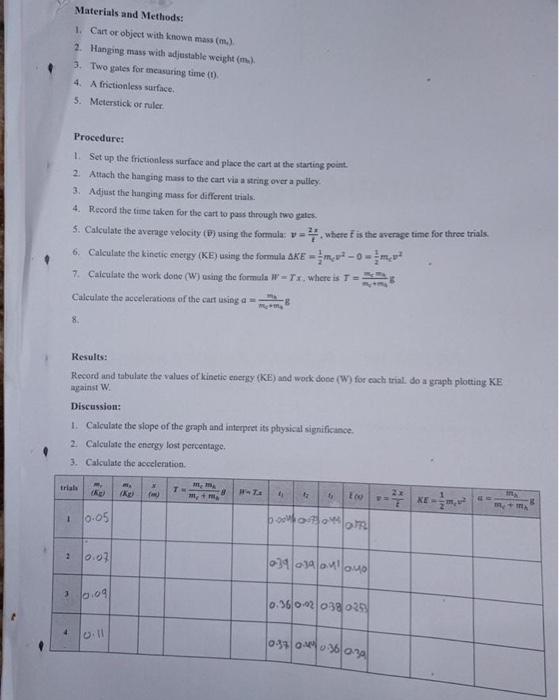
Graphical Relationship between Work Done and Kinetic Eneriy Abstract: This experiment aimed to explow the relationship between the work done on an object moving on a frictionleas wurface and the resulting kinetic encrysy. Introduction: The conkept of energy uanafer is fundamental in physics, and understanding the relatioaship between work Jone and kinetic energy is crucial. In this experincat, we itvestigated the graphical relationship between the work done on an object and the ftualting kinetic eneng. Work is defined as W=F,x, where F is the force acting oo the object x is the displacement of the object, and tho dot product between force F and displacement x prodoces WFF x sisce they are in the same direction, where F is the T which is equal to T=n, wherea is the group acselention. The kinetic energy for the cart is KE=21mev2 with the absence of the frictional force. Furthermore, according to the conservation of enerzy #KE if thene is no friction, then we can rewrite it again as the following: Tx=21m1y2 But from the hanging mas, wo can find the value of T as follows: butTmema................eqn1 by solving equation land 2 we can calculate T as follows: T=mc+mNmcmNg Note that the average velocity will be used instead of the velocity since the object starts moving from rest (v=0) and reacher the final velocity (y=v), so p=20+v,s0v=2F And the desplacement x=0t, so D=t2x Enerylost=WWKE The coergy lost percentage can be calculated by plotting a graph ( KE vs W) where W will be on the x axis, using the formula. Energylosipercentage=(Islope)100% Objective: The primary objective of this experimeat was to analyze the relationship between work done and kinetic energy, using a cart moving on a frictionless surface and a hanging mass to provide the force necessary for the motion. Materials and Methods: 1. Cart or object with known mass (m4) 2. Hanging mass with adjustable weight (mu) 3. Two gates for measuring time (1) 4. A frictionless surface. 5. Metersick or ruler: Procedure: 1. Set up the frictionless surface and place the cart at the starting point. 2. Attach the hanging mass to the cart via a string over a pulley. 3. Adjust the hunging mass for different trials. 4. Record the time taken for the cart to pas through two gates. 5. Calculate the avenge velocity (D) using the formula: v=t2x, whete f is the arerage time for three trials: 6. Calculate the Kinetic enetuy (KE) asiag the formala KE=21my20=21m1y2 Calculate the accelerations of the cart using a=m5m4Bm4g 8. Results: Record and tubulate the values of kinetic energy (KE) and work doee (W) for each trial. do a graph plotting KE: against W. Discussion: 1. Calculate the stope of the graph and interpret its physical signifisance. 2. Calculate the energy lost perceatage. 3. Cakculate the aceclerition
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


