Question: Header File - // ************************************ // * SPECIFICATION FILE (Animal.h) * // ************************************ #ifndef Animal_H #define Animal_H #include #include using namespace std; class Animal {
![Animal(); Animal(int,char[],double); //******************************************* //* Return the value of the private members *](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f016b2e1718_48266f016b2364ed.jpg)
Header File -
// ************************************
// * SPECIFICATION FILE (Animal.h) *
// ************************************
#ifndef Animal_H
#define Animal_H
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Animal
{
//members of the class
public:
//****************
//* Constructors *
//****************
Animal();
Animal(int,char[],double);
//*******************************************
//* Return the value of the private members *
//*******************************************
//**************************************************************************
//* By adding the "const" modifier following a member function declaration *
//* the member function is prevented from modifying any data in the class *
//**************************************************************************
int GetTrackingNumber()const;
char* GetAnimalType()const; //referring to an array
double GetCharge()const;
//*********************************************
//* Display Information Concerning Animal *
//*********************************************
void Display()const;
private:
int TrackingNumber;
double Charge;
//**************************************************************
//* Only class data members can be declared "mutable" *
//* The purpose of "mutable" is to specify which data members *
//* can be modified by const member functions *
//*Normally, a const member function cannot modify data members*
//**************************************************************
mutable char AnimalType[34]; //making array more secure
};
#endif
--------------------------------
Implemention file ---
// ***************************************
// * Implementation File (Animal.cpp) *
// ***************************************
#include "Animal.h"
//****************
//* Constructors *
//****************
Animal::Animal()
{
TrackingNumber = 0;
AnimalType[24] = '\0';
Charge = 0;
}
Animal::Animal( int InitTrackingNumber, char InitAnimalType[],
double InitCharge )
{
TrackingNumber = InitTrackingNumber;
strcpy_s(AnimalType, InitAnimalType);
Charge = InitCharge;
}
//*************************************************
//* Return the value of the private class members *
//*************************************************
int Animal::GetTrackingNumber() const
{
return(TrackingNumber);
}
char* Animal::GetAnimalType() const
{
return(AnimalType);
}
double Animal::GetCharge() const
{
return(Charge);
}
//*********************************************
//* Display Information Concerning Animal *
//*********************************************
void Animal::Display() const
{
char Separator[50] = "_____________________________________________";
//*******************************************
//* Display header for Animal information *
//*******************************************
cout
cout
cout
cout
//*****************************
//* Display data for Animal *
//*****************************
cout
cout
cout
cout
cout
}
---------------------
Client Code-
#include "Animal.h"
int main( )
{
int InitTrackingNumber = 0;
char InitAnimalType[25] = "\0";
double InitCharge = 0;
char NextChar = '\0';
char ContinuationFlag = 'Y';
//*********************************************************
//* The "ContinuationFlag" is a control variable used *
//* in creating a loop. The loop mechanism that is *
//* employed is a "do while" where the flag is checked *
//* at the end of the loop. *
//*********************************************************
//************************************************
//* The "toupper" function returns the upper *
//* case value of the argument passed. *
//************************************************
while(toupper(ContinuationFlag)=='Y')
{
cout
cout
cin>>InitTrackingNumber;
cout
//*****************************************************
//* The "peek" function returns the next character *
//* without extracting it from the input stream *
//*****************************************************
NextChar = cin.peek();
//*************************************************************
//* If the next character is a " " (the carriage *
//* return character), then the "ignore" function *
//* is called. The "ignore" function, without input *
//* arguments, will cause the next character to be skipped *
//*************************************************************
if (NextChar ==' ')
{
cin.ignore();
}
cin.get(InitAnimalType, 30);
cout
cin>>InitCharge;
//**************************
//* Create Animal Object *
//**************************
Animal TrackingItem(InitTrackingNumber, InitAnimalType, InitCharge);
//*******************************************
//* Display Information Concerning Animal *
//*******************************************
TrackingItem.Display();
cout
cout
cin>> ContinuationFlag;
}
return 0;
}
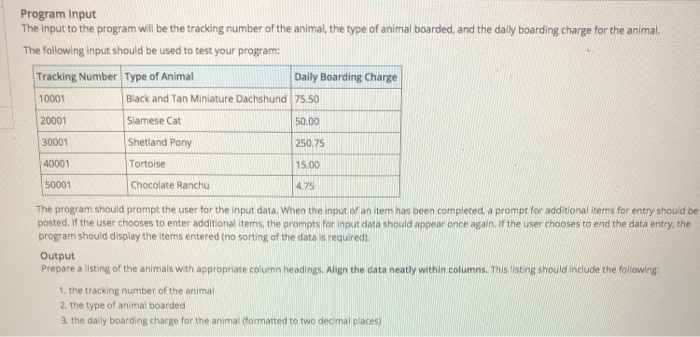
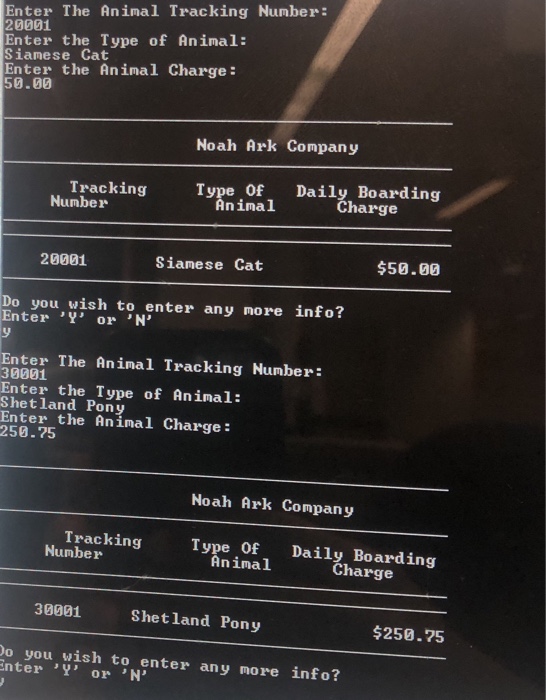
Program Input The input to the program will be the tracking number of the animal, the type of animal boarded, and the daily boarding charge for the animal. The following input should be used to test your program: Tracking Number Type of Animal Daily Boarding Charge 10001 20001 30001 40001 50001 Black and Tan Miniature Dachshund 75.50 Siamese Cat Shetland Pony Tortoise Chocolate Ranchu 50.00 250.75 15.00 4.75 The program should prompt the user for the input data. When the input of an item has been completed, a prompt for additional tems for entry should be posted. If the user chooses to enter additional items, the prompts for input data should appear once again. If the user chooses to end the data entry, the program should display the items entered (no sorting of the data is required). Output Prepare a listing of the animals with appropriate column headings. Align the data neatly within columns. This listing should include the following: 1. the tracking number of the animal 2. the type of animal boarded 3. the daily boarding charge for the animal (formatted to two decimal places)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


