Question: Hello, Can you please answer #5 in excel using solver? we provider to co straints should t ed Cost f 195 Application 4: A Drinking
Hello, Can you please answer #5 in excel using solver?
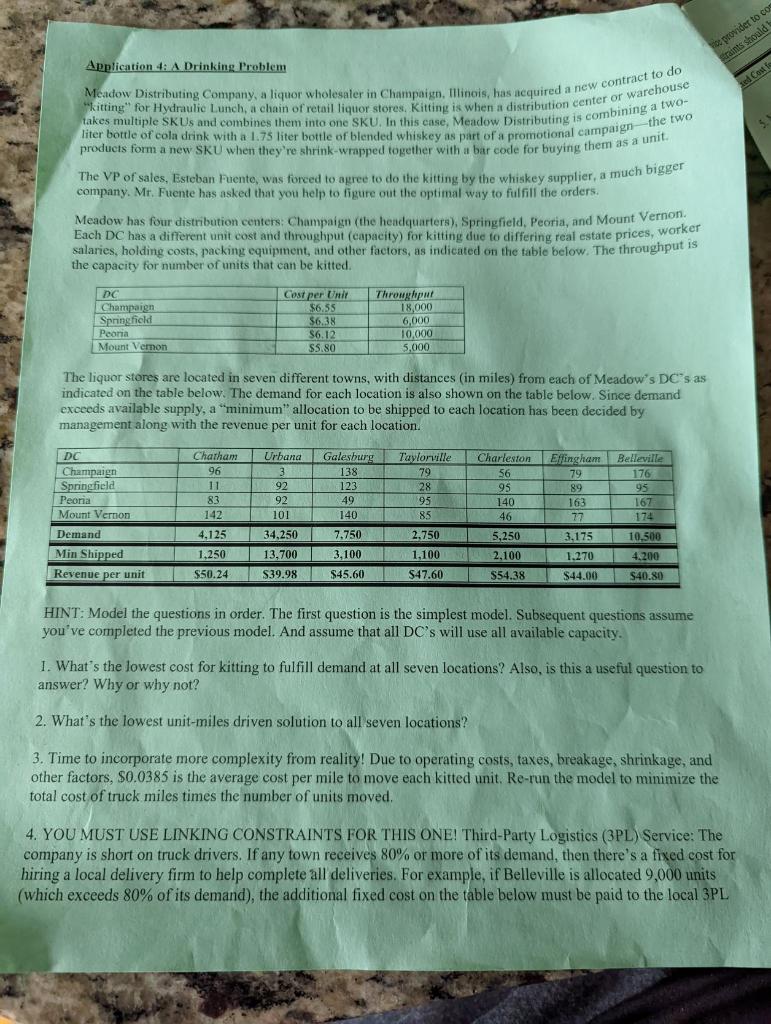

we provider to co straints should t ed Cost f 195 Application 4: A Drinking Problem "kitting" for Hydraulic Lunch, a chain of retail liquor stores, Kitting is when a distribution center or warehouse Meadow Distributing Company, a liquor wholesaler in Champaign, Illinois, has acquired a new contract to do liter bottle of cola drink with a 1.75 liter bottle of blended whiskey as part of a promotional campaign-the two takes multiple SKUs and combines them into one SKU. In this case, Meadow Distributing is combining a two- products form a new SKU when they're shrink-wrapped together with a bar code for buying them as a unit. The VP of sales, Esteban Fuente, was forced to agree to do the kitting by the whiskey supplier, a much bigger company. Mr. Fuente has asked that you help to figure out the optimal way to fulfill the orders. Meadow has four distribution centers: Champaign (the headquarters), Springfield, Peoria, and Mount Vernon, Each DC has a different unit cost and throughput (capacity) for kitting due to differing real estate prices, worker salaries, holding costs, packing equipment, and other factors, as indicated on the table below. The throughput is the capacity for number of units that can be kitted. DC Cost per Unit Throughput 18,000 $6.55 Champaign Springfield Peoria $6.38 6,000 $6.12 10,000 Mount Vernon $5.80 5,000 The liquor stores are located in seven different towns, with distances (in miles) from each of Meadow's DC's as indicated on the table below. The demand for each location is also shown on the table below. Since demand exceeds available supply, a "minimum" allocation to be shipped to each location has been decided by management along with the revenue per unit for each location. DC Chatham Urbana Galesburg Taylorville Charleston Effingham Belleville 96 3 138 79 56 79 176 Champaign Springfield Peoria 11 92 123 28 95 89 95 83 92 49 140 163 167 Mount Vernon 142 101 140 85 46 77 174 Demand 4,125 34,250 7.750 2.750 5,250 3,175 10,500 Min Shipped 1,250 13.700 3,100 1,100 2,100 1,270 4,200 Revenue per unit $50.24 $39.98 $45.60 $47.60 $54.38 $44.00 $40.80 HINT: Model the questions in order. The first question is the simplest model. Subsequent questions assume you've completed the previous model. And assume that all DC's will use all available capacity. 1. What's the lowest cost for kitting to fulfill demand at all seven locations? Also, is this a useful question to answer? Why or why not? 2. What's the lowest unit-miles driven solution to all seven locations? 3. Time to incorporate more complexity from reality! Due to operating costs, taxes, breakage, shrinkage, and other factors, $0.0385 is the average cost per mile to move each kitted unit. Re-run the model to minimize the total cost of truck miles times the number of units moved. 4. YOU MUST USE LINKING CONSTRAINTS FOR THIS ONE! Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Service: The company is short on truck drivers. If any town receives 80% or more of its demand, then there's a fixed cost for hiring a local delivery firm to help complete deliveries. For example, if Belleville is 19,000 units (which exceeds 80% of its demand), the additional fixed cost on the table below must be paid to the local 3PL tract to do rehouse wo- 2 service provider to complete the delivery. BIG HINT: The second of the construction company problem side constraints should help with this one... What is the lowest cost solution? Urbana Galesburg Taylorville Charleston Effingham Belleville Chatham $1,100 Fixed Cost for 3PL $4,700 $1,500 $1,000 $1,200 $1,000 $1,700 5. Mr. Fuentes reminds you that the purpose of business is to make a profit. Re-run your model with the linking constraints and 3PL's. What's the highest profit solution (profit = revenue - expenses)? 6. Mr. Fuentes is disappointed by all the unfulfilled demand. He asks what the numbers would look like if he bumped up throughput capacity by 25% at all DC's. What is the optimal profitability in this scenario? we provider to co straints should t ed Cost f 195 Application 4: A Drinking Problem "kitting" for Hydraulic Lunch, a chain of retail liquor stores, Kitting is when a distribution center or warehouse Meadow Distributing Company, a liquor wholesaler in Champaign, Illinois, has acquired a new contract to do liter bottle of cola drink with a 1.75 liter bottle of blended whiskey as part of a promotional campaign-the two takes multiple SKUs and combines them into one SKU. In this case, Meadow Distributing is combining a two- products form a new SKU when they're shrink-wrapped together with a bar code for buying them as a unit. The VP of sales, Esteban Fuente, was forced to agree to do the kitting by the whiskey supplier, a much bigger company. Mr. Fuente has asked that you help to figure out the optimal way to fulfill the orders. Meadow has four distribution centers: Champaign (the headquarters), Springfield, Peoria, and Mount Vernon, Each DC has a different unit cost and throughput (capacity) for kitting due to differing real estate prices, worker salaries, holding costs, packing equipment, and other factors, as indicated on the table below. The throughput is the capacity for number of units that can be kitted. DC Cost per Unit Throughput 18,000 $6.55 Champaign Springfield Peoria $6.38 6,000 $6.12 10,000 Mount Vernon $5.80 5,000 The liquor stores are located in seven different towns, with distances (in miles) from each of Meadow's DC's as indicated on the table below. The demand for each location is also shown on the table below. Since demand exceeds available supply, a "minimum" allocation to be shipped to each location has been decided by management along with the revenue per unit for each location. DC Chatham Urbana Galesburg Taylorville Charleston Effingham Belleville 96 3 138 79 56 79 176 Champaign Springfield Peoria 11 92 123 28 95 89 95 83 92 49 140 163 167 Mount Vernon 142 101 140 85 46 77 174 Demand 4,125 34,250 7.750 2.750 5,250 3,175 10,500 Min Shipped 1,250 13.700 3,100 1,100 2,100 1,270 4,200 Revenue per unit $50.24 $39.98 $45.60 $47.60 $54.38 $44.00 $40.80 HINT: Model the questions in order. The first question is the simplest model. Subsequent questions assume you've completed the previous model. And assume that all DC's will use all available capacity. 1. What's the lowest cost for kitting to fulfill demand at all seven locations? Also, is this a useful question to answer? Why or why not? 2. What's the lowest unit-miles driven solution to all seven locations? 3. Time to incorporate more complexity from reality! Due to operating costs, taxes, breakage, shrinkage, and other factors, $0.0385 is the average cost per mile to move each kitted unit. Re-run the model to minimize the total cost of truck miles times the number of units moved. 4. YOU MUST USE LINKING CONSTRAINTS FOR THIS ONE! Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Service: The company is short on truck drivers. If any town receives 80% or more of its demand, then there's a fixed cost for hiring a local delivery firm to help complete deliveries. For example, if Belleville is 19,000 units (which exceeds 80% of its demand), the additional fixed cost on the table below must be paid to the local 3PL tract to do rehouse wo- 2 service provider to complete the delivery. BIG HINT: The second of the construction company problem side constraints should help with this one... What is the lowest cost solution? Urbana Galesburg Taylorville Charleston Effingham Belleville Chatham $1,100 Fixed Cost for 3PL $4,700 $1,500 $1,000 $1,200 $1,000 $1,700 5. Mr. Fuentes reminds you that the purpose of business is to make a profit. Re-run your model with the linking constraints and 3PL's. What's the highest profit solution (profit = revenue - expenses)? 6. Mr. Fuentes is disappointed by all the unfulfilled demand. He asks what the numbers would look like if he bumped up throughput capacity by 25% at all DC's. What is the optimal profitability in this scenario






