Question: Hello, I could use some help understanding how to answer the fill in portions of the text, I don't believe I filled the first two
Hello, I could use some help understanding how to answer the fill in portions of the text, I don't believe I filled the first two in correctly. Also, I could use help understanding how to answer the bottom two questions. Thank you!

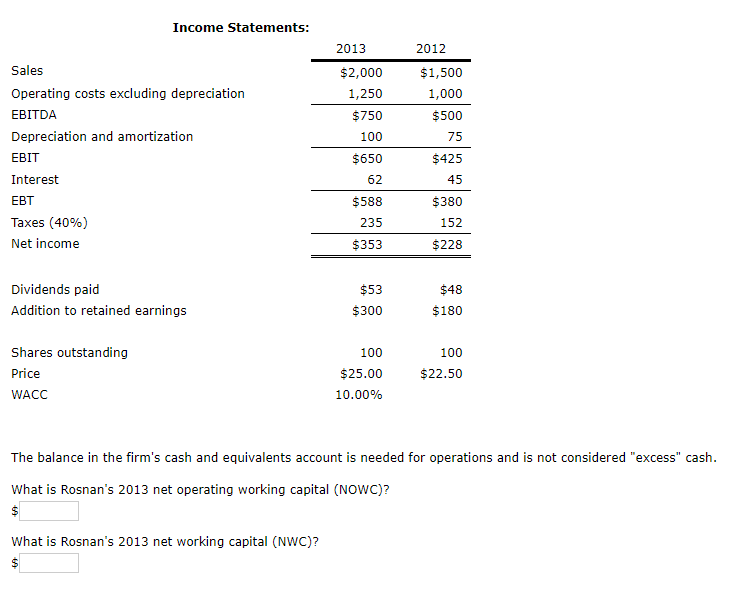
Financial Statements The focus on financial statements in finance is how managers and investors interpret and use them. A firm's annual report contains both verbal and quantitative information. The quantitative information consists of four financial statements: (1) Balance Sheet, (2) Income Statement, (3) Statement of Cash Flows, and (4) Statement of Stockholders' Equity. The balance sheet shows the firm's assets and claims against those assets. In other words, assets are equal to liabilities and equity. Assets are shown in order of their liquidity and claims are listed in the order of when they must be paid. Current assets include cash and their equivalents, accounts receivable, and inventory, while long-term assets are those whose useful lives exceed one year. Liabilities are divided into -Select and long-term debt. We differentiate between total debt and total liabilities. A company's total debt includes both its short-term and long-term -Select- v liabilities. Total liabilities equal -Select- plus the company's "free" liabilities. -Select- is the difference between current assets and current liabilities, while -Select- is equal to current assets less the difference between current liabilities and notes payable. -Select- is capital supplied by common stockholders and represents ownership. The income statement reports on operations over a period of time. Companies' operating performances can be compared by looking at each firm's EBIT, often referred to as -Select . A typical stockholder focuses on the bottom line of the income statement, -Select- The income statement is tied to the -Select- through the retained earnings account. Net income minus -Select paid is equal to the retained earnings for the year, and this amount is added to the cumulative retained earnings from prior years to obtain the year-end retained earnings balance. available to Management's goal is to maximize the firm's stock price. The value of any asset, including a share of stock, is based on the -Select- the asset is expected to produce. Therefore, managers strive to maximize the -Select- investors. The statement of cash flows shows how much -Select- va firm is generating. It is divided into four parts: (1) Operating activities, (2) Long-Term Investing activities, (3) Financing activities, and (4) Summary. Changes in stockholders' equity during an accounting period are reported in the statement of stockholders' equity. Changes in stockholders' equity can come from new stock issues, stock repurchases, net income, and -Select- paid. Quantitative Problem: Rosnan Industries' 2013 and 2012 balance sheets and income statements are shown below. Balance Sheets: 2013 2012 $55 Cash and equivalents Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Net plant and equipment Total assets $70 275 375 $720 2,000 $2,720 300 350 $705 1,490 $2,195 $150 $85 75 50 120 145 $345 Accounts payable Accruals Notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Common stock Retained earnings Total liabilities and equity 450 $280 290 1,225 1,225 700 $2,720 400 $2,195 Income Statements: 2013 2012 $2,000 1,250 $1,500 1,000 $500 75 $750 100 Sales Operating costs excluding depreciation EBITDA Depreciation and amortization EBIT Interest EBT Taxes (40%) Net income $650 62 $425 45 $588 $380 235 152 $353 $228 $48 Dividends paid Addition to retained earnings $53 $300 $180 Shares outstanding Price WACC 100 $25.00 10.00% 100 $22.50 The balance in the firm's cash and equivalents account is needed for operations and is not considered "excess" cash. What is Rosnan's 2013 net operating working capital (NOWC)? S What is Rosnan's 2013 net working capital (NWC)? $ Financial Statements The focus on financial statements in finance is how managers and investors interpret and use them. A firm's annual report contains both verbal and quantitative information. The quantitative information consists of four financial statements: (1) Balance Sheet, (2) Income Statement, (3) Statement of Cash Flows, and (4) Statement of Stockholders' Equity. The balance sheet shows the firm's assets and claims against those assets. In other words, assets are equal to liabilities and equity. Assets are shown in order of their liquidity and claims are listed in the order of when they must be paid. Current assets include cash and their equivalents, accounts receivable, and inventory, while long-term assets are those whose useful lives exceed one year. Liabilities are divided into -Select and long-term debt. We differentiate between total debt and total liabilities. A company's total debt includes both its short-term and long-term -Select- v liabilities. Total liabilities equal -Select- plus the company's "free" liabilities. -Select- is the difference between current assets and current liabilities, while -Select- is equal to current assets less the difference between current liabilities and notes payable. -Select- is capital supplied by common stockholders and represents ownership. The income statement reports on operations over a period of time. Companies' operating performances can be compared by looking at each firm's EBIT, often referred to as -Select . A typical stockholder focuses on the bottom line of the income statement, -Select- The income statement is tied to the -Select- through the retained earnings account. Net income minus -Select paid is equal to the retained earnings for the year, and this amount is added to the cumulative retained earnings from prior years to obtain the year-end retained earnings balance. available to Management's goal is to maximize the firm's stock price. The value of any asset, including a share of stock, is based on the -Select- the asset is expected to produce. Therefore, managers strive to maximize the -Select- investors. The statement of cash flows shows how much -Select- va firm is generating. It is divided into four parts: (1) Operating activities, (2) Long-Term Investing activities, (3) Financing activities, and (4) Summary. Changes in stockholders' equity during an accounting period are reported in the statement of stockholders' equity. Changes in stockholders' equity can come from new stock issues, stock repurchases, net income, and -Select- paid. Quantitative Problem: Rosnan Industries' 2013 and 2012 balance sheets and income statements are shown below. Balance Sheets: 2013 2012 $55 Cash and equivalents Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Net plant and equipment Total assets $70 275 375 $720 2,000 $2,720 300 350 $705 1,490 $2,195 $150 $85 75 50 120 145 $345 Accounts payable Accruals Notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Common stock Retained earnings Total liabilities and equity 450 $280 290 1,225 1,225 700 $2,720 400 $2,195 Income Statements: 2013 2012 $2,000 1,250 $1,500 1,000 $500 75 $750 100 Sales Operating costs excluding depreciation EBITDA Depreciation and amortization EBIT Interest EBT Taxes (40%) Net income $650 62 $425 45 $588 $380 235 152 $353 $228 $48 Dividends paid Addition to retained earnings $53 $300 $180 Shares outstanding Price WACC 100 $25.00 10.00% 100 $22.50 The balance in the firm's cash and equivalents account is needed for operations and is not considered "excess" cash. What is Rosnan's 2013 net operating working capital (NOWC)? S What is Rosnan's 2013 net working capital (NWC)? $
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


