Question: Hello, I need help solving this problem. Could you please show the formulas and work on an excel file, thank you During the last few
Hello, I need help solving this problem. Could you please show the formulas and work on an excel file, thank you
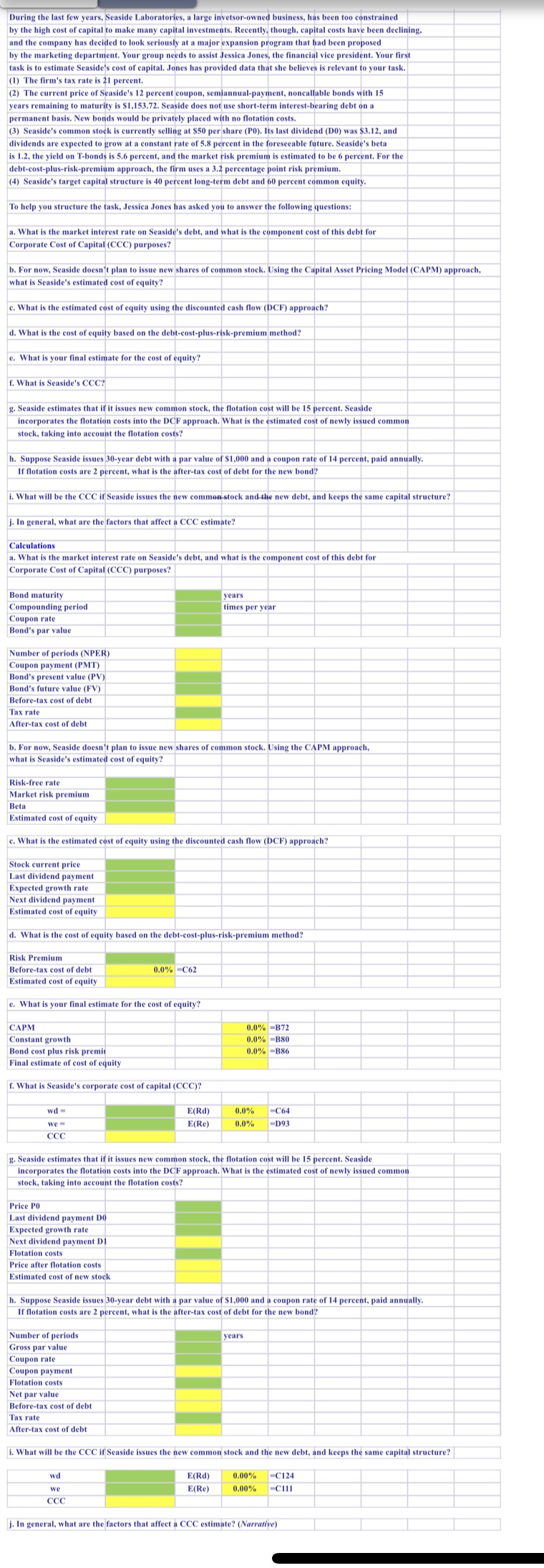
During the last few years, Seaside Laboratories, a large invetsor-owned business, has been too constrained by the high cost of capital to make many capital investments. Recently, though, capital costs have been declining, and the company has decided to look seriously at a major expansion program that had been proposed by the marketing department. Your group needs to assist Jessica Jones, the financial vice president. Your first task is to estimate Seaside's cost of capital. Jones has provided data that she believes is relevant to your task. (1) The firm's tax rate is 21 percent. (2) The current price of Seaside's 12 percent coupon, semiannual-payment, noncallable bonds with 15 years remaining to maturity is $1,153.72. Seaside does not use short-term interest-bearing debt on a permanent basis. New bonds would be privately placed with no flotation costs. (3) Seaside's com selling at $50 per share (PO). Its last dividend (DO) was $3.12, and dividends are expected to grow at e of 5.8 percent in the foreseeable future. Seaside's beta is 1.2, the yield on T-bonds is 5.6 percent, and the market risk premium is estimated to be 6 percent. For the debt-cost-plus-risk-premium approach, the firm uses a 3.2 percentage point risk premium. (4) Seaside's target capital structure is 40 percent long-term debt and 60 percent common equity. To help you structure the task, Jessica Jones has asked you to answer the following questions: a. What is the market interest rate on Seaside's debt, and what is the component cost of this debt for Corporate Cost of Capital (CCC) purposes? b. For now, Seaside doesn't plan to issue new shares of common stock. Using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) approach, what is Seaside's estimated cost of equity? c. What is the estimated cost of equity using the discounted cash flow (DCF) approach? d. What is the cost of equity based on the debt-cost-plus-risk-premium method? e. What is your final estimate for the cost of equity? f. What is Seaside's CCC? g. Seaside estimates that if it issues new common stock, the flotation cost will be 15 percent. Seaside incorporates the flotation costs into the DCF approach. What is the estimated cost of newly issued common stock, taking into account the flotation costs? h. Suppose Seaside issues 30-year debt with a par value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 14 percent, paid annually. If flotation costs are 2 percent, what is the after-tax cost of debt for the new bond? i. What will be the CCC if Seaside issues the new common stock and the new debt, and keeps the same capital structure? j. In general, what are the factors that affect a CCC estimate? Calculations a. What is the market interest rate on Seaside's debt, and what is the component cost of this debt for Corporate Cost of Capital (CCC) purposes? Bond maturity years Compounding period times per year Coupon rate Bond's par value Number of periods (NPER) Coupon payment (PMT) Bond's present value (PV) Bond's future value (FV) Before-tax cost of debt Tax rate After-tax cost of debt b. For now, Seaside doesn't plan to issue new shares of common stock. Using the CAPM approach. what is Seaside's estimated cost of equity? Risk-free rate Market risk premium Beta Estimated cost of equity c. What is the estimated cost of equity using the discounted cash flow (DCF) approach? Stock current price Last dividend payment Expected growth rate Next dividend payment Estimated cost of equity d. What is the cost of equity based on the debt-cost-plus-risk-premium method? Risk Premium Before-tax cost of debt 0.0% =C62 Estimated cost of equity e. What is your final estimate for the cost of equity? CAPM 0.0% =B72 Constant growth 0.0% -B80 Bond cost plus risk premit 0.0% =B86 Final estimate of cost of equity f. What is Seaside's corporate cost of capital (CCC)? wd E(Rd) 0.0% -C64 we = E(Re) 0.0% -D93 CCC g. Seaside estimates that if it issues new common stock, the flotation cost will be 15 percent. Seaside incorporates the flotation costs into the DCF approach. What is the estimated cost of newly issued common stock, taking into account the flotation costs? Price PO Last dividend payment DO Expected growth rate Next dividend payment DI Flotation costs Price after flotation costs Estimated cost of new stock h. Suppose Seaside issues 30-year debt with a par value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 14 percent, paid annually. If flotation costs are 2 percent, what is the after-tax cost of debt for the new bond? Number of periods years Gross par value Coupon rate Coupon payment Flotation costs Net par value Before-tax cost of debt Tax rate After-tax cost of debt i. What will be the CCC if Seaside issues the new common stock and the new debt, and keeps the same capital structure? wd E(Rd) 0.00% =C124 we E(Re) 0.00% =C111 CCC j. In general, what are the factors that affect a CCC estimate? (Narrative)