Question: Hello, I need to check if my program follows the requirements stated below. Especially if it follows the code highlighted on the red square. Thanks.
Hello, I need to check if my program follows the requirements stated below. Especially if it follows the code highlighted on the red square. Thanks.
Requirements:

Code:
Angle.h
#pragma once #include
using namespace std;
class Angle { private: int degrees, minutes; float seconds; char direct; public:
Angle() { degrees = 0; minutes = 0; seconds = 0; direct = 'N'; } //******************************************* //Lat = 0; Lon = 1; //******************************************* Angle(float gpsVal, bool longitude) { degrees = fabs(gpsVal); minutes = ((fabs(gpsVal) - degrees) * 60); seconds = (((fabs(gpsVal) - degrees) * 60) - minutes) * 60;
direct = (!longitude) ? ((fabs(gpsVal) == gpsVal) ? 'N' : 'S') : ((fabs(gpsVal) == gpsVal) ? 'E' : 'W');
}
Angle(int d, int m, float s, char di) { degrees = d; minutes = m; seconds = s; direct = di; }
void setDegrees(int); void setMinutes(int); void setSeconds(float s); void setDirection(char d);
int getDegrees(); int getMinutes(); double getSeconds(); char getDirection();
void print(); string toString();
};
testAngle.cpp
#include "Angle.h" #include
using namespace std;
void Angle::setDegrees(int d) { degrees = d; }
void Angle::setMinutes(int m) { minutes = m; }
void Angle::setSeconds(float s) { seconds = s; }
void Angle::setDirection(char d) { direct = d; }
int Angle::getDegrees() { return degrees; }
int Angle::getMinutes() { return minutes; }
double Angle::getSeconds() { return seconds; }
char Angle::getDirection() { return direct; }
void Angle::print() { cout
string Angle::toString() { stringstream ss; ss
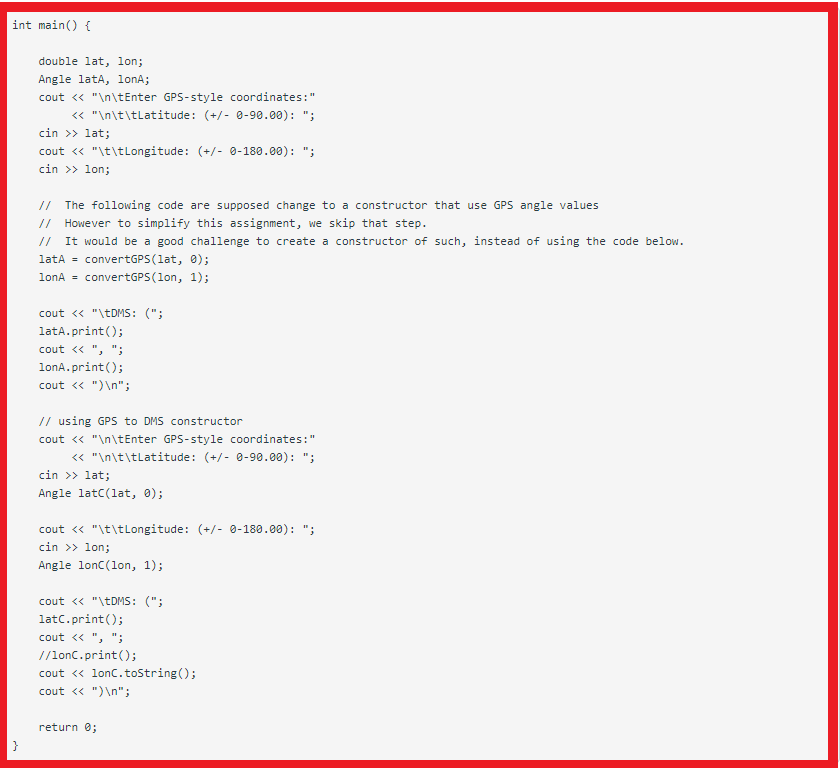
int main() { double lat, lon; Angle latA, lonA; cout > lat; cout > lon;
latA = Angle(lat, 0); lonA = Angle(lon, 1);
cout
// using GPS to DMS constructor cout > lat; Angle latC(lat, 0);
cout > lon; Angle lonC(lon, 1);
cout
return 0; }
Implementation Create a class angle that includes four member variables: an int for degrees, an int for minutes, and a float for seconds, and a char for the direction letter (N or S of equator, E, or W of Greenwich). This class angle can hold DMS coordinate for either a latitude variable or a longitude variable. Write a default constructor to default value as 0 0' O" N (not utilized by main). Write an optional four-argument constructor for the DMS coordinate. Write a constructor to take in digital_degree (GPS). Option 1: a TWO-argument constructor for the (double GPS coordinate, longitude/latitude), where the GPS coordinate is a floating number, and the boolean to represent either longitude or latitude is inputed. This TWO-argument constructor shall convert the digital-degree GPS to DMS and initialize the private data of the angle class. Option 2:just write a ONE-argument constructor for GPS coordinate! A main program is provided below to 1. prompt for the user's favorite location in the GPS format, e.g. DVC, the Eiffel tower, and the Great Pyramid at Giza... etc. 2. convert a GPS location to a DMS location, 3. construct a DMS angle class instances: longitude and latitude with the location value, 4. retrieve the longitude and latitude instances' values and display on the screen. If you like to make it pretty, you can use the hex character constant'\F8', which usually prints a degree () symbol. Each location coordinate shall contains one latitude angle and one longitude angle in either DMS or GPS format. If you have implemented some of the optional constructors, you will need to modify the test driver main() function accordingly. int main() { double lat, lon; Angle lata, lonA; cout > lat; cout > lon; 11 The following code are supposed change to a constructor that use GPS angle values // However to simplify this assignment, we skip that step. // It would be a good challenge to create a constructor of such, instead of using the code below. latA = convertGPS (lat, 0); lonA = convertGPS(lon, 1); cout > lat; Angle latc(lat, 0); cout > lon; Angle lonc(lon, 1); cout > lat; cout > lon; 11 The following code are supposed change to a constructor that use GPS angle values // However to simplify this assignment, we skip that step. // It would be a good challenge to create a constructor of such, instead of using the code below. latA = convertGPS (lat, 0); lonA = convertGPS(lon, 1); cout > lat; Angle latc(lat, 0); cout > lon; Angle lonc(lon, 1); cout
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


