Question: Help. Don't round intermediate calculations. d. If the yeld to matunty for each bond remains at 8%, what will be the price of each bond
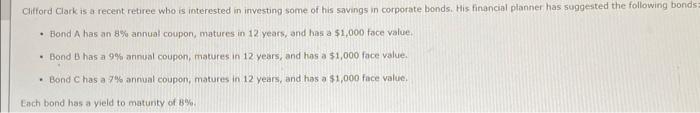
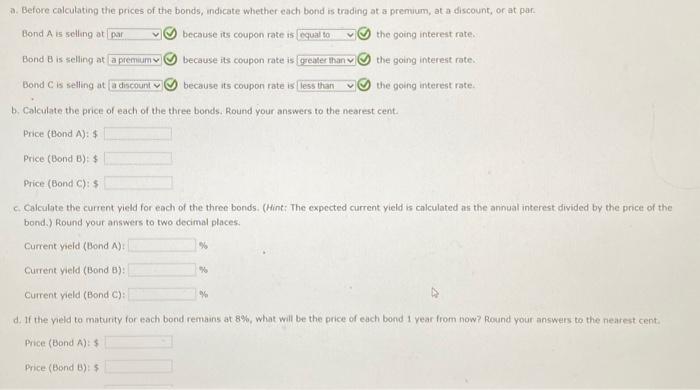
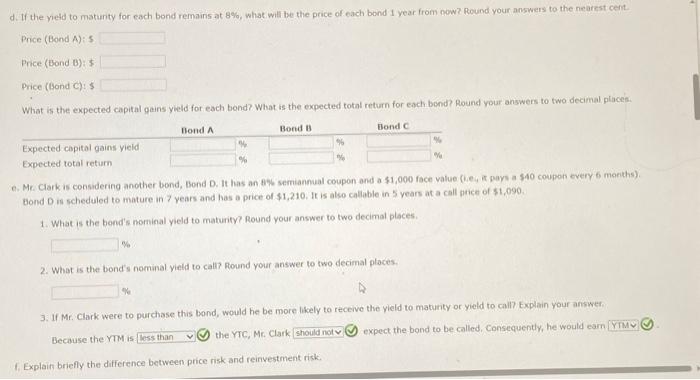
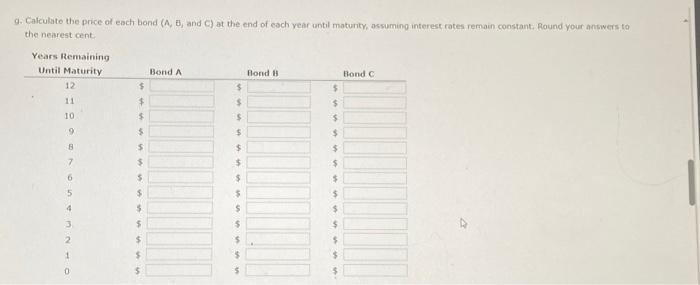
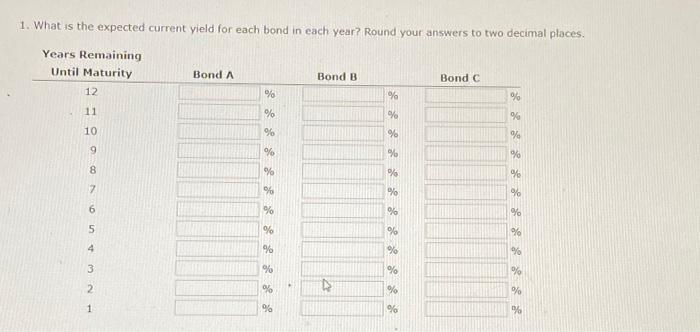
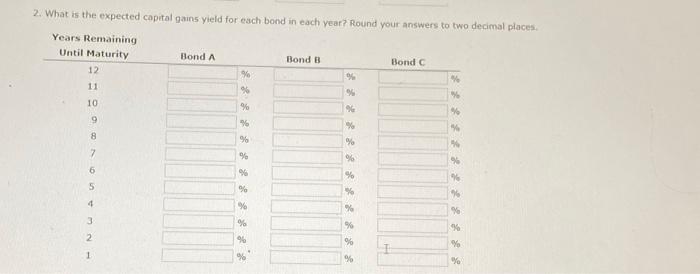
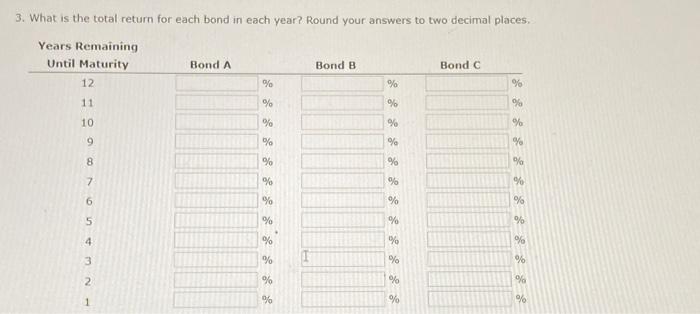
d. If the yeld to matunty for each bond remains at 8%, what will be the price of each bond 1 year from now? Round your answers to the nearest cent. Price (Bond A) is Price (Bond B) : 5 : Price (Bond C): $ What is the expected capital gains yield for each bond? What is the expected total return for each bond? Round your answers to two decimal places. e. Mr. Clark is considering another bond, Bond D. It has an 8% semiannual coupon and a $1,000 face value (j.e, if pays a $40 coupon every 6 morths). bond D in scheduled to mature in 7 years and has a price of $1,210. It is also callable in 5 vears at a call price of $1,090. 1. What is the bond's nominal yield to maturity? Round your answer to two decimal places: 2. What is the bond's nominal yield to call? Round your answer to two decimal ploces. 3. If Mr. Clark were to purchase this bond, would he be more likely to receive the yield to maturity or yield to call? texplain your answer. Becouse the rTM is (5) the YTC, Mr. Clark (5) expect the bond to be called, Consequently, he would earn f. Explain briefly the difference between price risk and reinvestment risk, 3. What is the total return for each bond in each year? Round your answers to two decimal places. a. Before colculating the prices of the bonds, indicate whether each bond is trading at a premium, at a discount, or at par. Bond A is selling ot Bond B is selling at Bond C is selling at b. Calculate the price of each of the three bonds. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Price (Bond A ): $ Price (Bond B) : $ Price (Bond C ) : 5 c. Calculate the current vield for each of the three bonds. (Hint: The expected current yield is calculated as the aninual interest divided by the price of the bond.) Round your answers to two decimal places. Current yeid (Bond A ): Current yeld (Bond B): current vield (Bond C ): d. If the veld to maturity for each bond remains at 8%, what will be the price of each bond 1 year from now? Round your answers to the nearest cent. Price (Bond A): $ Price (Bond B) : $ 9. Cafculate the price of each bond (A,B, and C) at the end of each vear until matunty, assuming interest rates remain coostant; flound your answers to the nearest cent. Cifford Clark is a recent retiree who is interested in investing some of his savings in corporate bonds. His financial planner has suggested the following bonds - Bond A has an 8% annual coupon, matures in 12 years, and has a $1,000 face value. - Bond B has a 9% annual coupon, matures in 12 years, and has a $1,000 face value. - Bond chas a 7% annual coupon, matures in 12 years, and has a $1,000 face value. Each bond has a vield to matunty of B%. 2. What is the expected capital gains yield for each bond in each year? Round your answers to two decimal places. 1. What is the expected current yield for each bond in each year? Round your answers to two decimal places
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


